Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor failures, on the 1997, 1998, and 1998 2.5L Dodge Dakota, are common (after all, it ain't gonna' last forever). The good news is that testing it is a pretty simple affair and you only need a multimeter (for the test itself).
In a nutshell testing the crankshaft position sensor involves three simple tests. These are making sure that the CKP sensor is creating a crankshaft position signal and then make sure it's getting both power and Ground. These three tests are explained in a step-by-step manner in this tutorial.
Contents of this tutorial at a glance:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Crankshaft Position Sensor.
- OBD II Trouble Code P0320: No Crank Reference Signal At PCM.
- Circuit Descriptions Of The Crankshaft Position Sensor.
- Where To Buy The Crankshaft Position Sensor.
- TEST 1: Testing The Crankshaft Position Signal.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The Crank Sensor Has Power And Ground.
- Intermittent Failure Of The Crankshaft Position Sensor.
- More 2.5L Dodge Dakota Tutorials.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor De La Posición Del Cigüeñal (1997-1999 2.5L OHV Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor De La Posición Del Cigüeñal (1997-1999 2.5L OHV Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
NOTE: The test for the 1996 Dodge Dakota crankshaft position sensor can be found here: How To Test The Crankshaft Position Sensor (1996 2.5L Dodge Dakota).
Symptoms Of A Bad Crankshaft Position Sensor
There are two basic types of crankshaft position sensor failures: either it fails completely or fails intermittently.
9 times out of 10, the CKP sensor fails completely and the engine no longer starts. These are the easiest to troubleshoot and resolve.
In some cases, it fails intermittently. In these situations, the engine starts and runs but stalls every now and then.
Here's a list of symptoms you're gonna' see when the crankshaft position sensor fails on your 2.5L Dodge Dakota:
- Engine cranks but doesn't start.
- No spark at all spark plug wires.
- No fuel injector activation pulses.
- Trouble Code P0320: No Crank Reference Signal At PCM.
OBD II Trouble Code P0320: No Crank Reference Signal At PCM
Usually (but not always) when the crankshaft position sensor fails, your Dodge Dakota fuel injection computer is gonna' set a P0320: No Crank Reference Signal At PCM trouble code.
This P0320 trouble code simply tells you that the fuel injection computer, on your Dodge Dakota, is not receiving CKP signals from the crankshaft position sensor.
For the most part, a trouble code P0320 is caused by a defective sensor that it needs to be replaced with a new one. Still, it's always a good idea to make sure that it's getting power and Ground before replacement.
In some cases, the fuel injection computer doesn't always register a P0320 code when the CKP sensor fails. In these cases, the only way to verify that the crankshaft position sensor is defective is by testing it with a multimeter or an oscilloscope.
Circuit Descriptions Of The Crankshaft Position Sensor
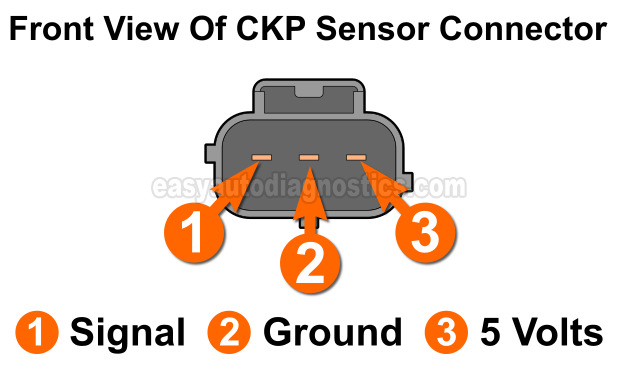
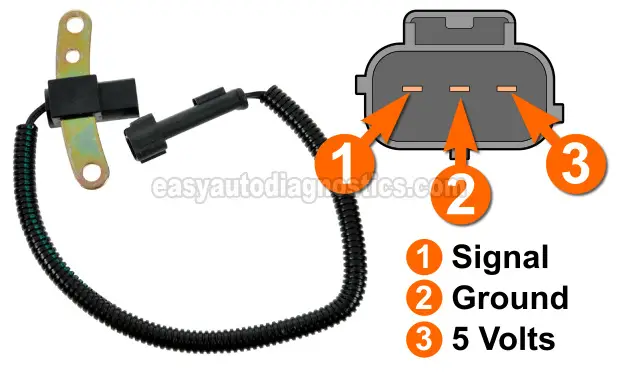
The crankshaft position sensor is a 3-wire sensor. One wire is a power wire, one is a Ground wire, and one is a signal wire.
Below is a brief description of the power, Ground, and signal wires of the CKP sensor's connector:
| Crankshaft Position Sensor Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Gray with black stripe (GRY/BLK) | CKP Signal |
| 2 | Black with light blue stripe (BLK/LT BLU) | Sensor Ground |
| 3 | Purple with white stripe (PPL/WHT) | Power (5 Volts DC) |
NOTE: The connector on the crankshaft position sensor itself are male terminals. The connector on the engine wiring harness crank sensor connector has female terminals.
Where To Buy The Crankshaft Position Sensor
Checkout the following links and comparison shop the crankshaft position sensor:
TEST 1: Testing The Crankshaft Position Signal

The most important thing to know (when testing the crankshaft position sensor) is that it produces an ON/OFF voltage signal when the engine is cranking.
In plain English, this means that the CKP signal voltage switches between 5 Volts and 0 Volts DC as the engine is turning.
What you and I are gonna' do, to test this ON/OFF signal, is to connect the multimeter to the CKP signal wire and then manually rotate the engine.
As we rotate the engine, your multimeter should read an ON/OFF voltage signal that switches between 5 Volts and 0 Volts DC.
I can tell you from personal experience, that when the crankshaft position sensor fails, it'll usually stay stuck producing 5 Volts DC.
By the way, we don't have to remove the crankshaft position sensor from the transmission bell-housing to be able to test it.
NOTE: Be careful and don't short-circuit the Ground wire to battery voltage or you will fry your Dodge Dakota's computer. The multimeter voltage test described below is a safe and effective way to test the Ground circuit.
IMPORTANT: The crankshaft position sensor must remain connected to its engine wiring harness connector for this test to work. This means that you'll need to use a back probe or a wire piercing probe to get to the signal within the CKP signal wire. You can check out what a wire piercing probe looks like here: Wire Piercing Probe Review (Power Probe PWPPPPP01).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
With the red multimeter test lead, probe the GRY/BLK wire of the crank sensor connector (on the engine wiring harness).
The gray with black stripe (GRY/BLK) wire connects to the male terminal labeled with the number 3 in the illustration above. - 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Turn the ignition key to the ON position and turn the engine by hand using the 1/2" ratchet wrench and appropriate socket on the crankshaft pulley. For the accuracy of the test, do not use the starter motor.
- 5
Your multimeter will read an ON/OFF voltage of 5 Volts and 0 Volts (if the crankshaft position sensor is functioning correctly).
ON is when the multimeter reads 5 Volts DC and OFF is when it reads 0 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at what your crank sensor test result means:
CASE 1: The voltage signal switches between 5 Volts and 0 Volts DC. This is the correct and expected test result.
If your Dodge Dakota is experiencing an intermittent engine stall or you have a P0320 trouble code stored in the PCM's memory, take a look at the suggestion found here: Intermittent Failure Of The Crankshaft Position Sensor.
CASE 2: The voltage signal DOES NOT switch between 5 Volts and 0 Volts DC. This test result usually means that the CKP sensor is defective and needs to be replaced.
Before you replace it, make sure that it's getting power and Ground. You can find these tests here: TEST 2: Making Sure The Crank Sensor Has Power And Ground.



