This tutorial will help you to test the fuel injectors on the 2001-2003 2.7L V6 Dodge Stratus and 2001-2003 2.7L Chrysler Sebring.
The test itself is easy, and is done with a multimeter. Basically what you're going to be doing is testing the internal resistance of the fuel injectors to see if they are defective or not.
I'm also gonna' explain a diagnostic strategy to help you find the bad or clogged fuel injector that may be causing a misfire condition on your Dodge Stratus (Chrysler Sebring). Everything is explained in a step-by-step manner and in plain English.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Inyectores De Combustible (2001-2003 2.7L Dodge Stratus) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Inyectores De Combustible (2001-2003 2.7L Dodge Stratus) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
The following fuel injector wiring diagram may come in handy: Fuel Injector Circuit Wiring Diagram (2001-2002 2.7L Sebring, Stratus).
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Injector
The most common symptom of a defective fuel injector is a misfire condition.
To be a bit more specific, you'll notice that when the engine is idling, it will misfire causing the engine to idle rough.
You'll also notice that when you accelerate the engine, as you drive the car on the road, it will continue to misfire.
In the majority of the cases, a defective fuel injector will cause a misfire trouble code. You'll see one of the following lighting out the check engine light on your Dodge Stratus instrument panel:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder #6 Misfire.
Your Dodge Stratus (Chrysler Sebring) may also set a fuel injector trouble code and if it does, you'll see one of the following:
- P0201: Injector #1 Control Circuit.
- P0202: Injector #2 Control Circuit.
- P0203: Injector #3 Control Circuit.
- P0204: Injector #4 Control Circuit.
- P0205: Injector #5 Control Circuit.
- P0206: Injector #6 Control Circuit.
Just to point out something you'll need to keep in mind, fuel injectors tend to fail in one of several ways:
- The fuel injector's internal coil winding shorts out or becomes 'open'. This causes the fuel injector to stop injecting fuel.
- The fuel injector becomes clogged and doesn't atomize the fuel correctly.
- It comes on and does not turn off (due to electrical issues). In other words: it does not pulse ON and OFF but stays on all of the time spraying a tremendous amount of fuel as soon as you turn the ignition key to the ON position.
Whether the fuel injector is fried internally or clogged, this tutorial will offer you some specific suggestions to help you narrow down the possible solution.
Checking The Injector's Internal Resistance
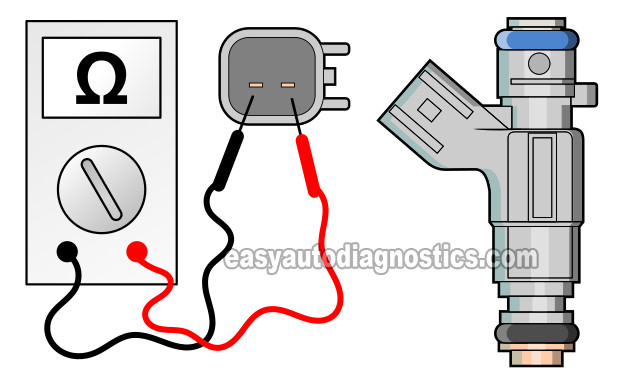
To get our diagnostic started, we're gonna' to test the internal resistance of each fuel injector with the multimeter in its Ohms selection.
The fuel injector resistance specification is 10 to 16 Ohms at room temperature (68° F -20° C). Don't worry if the engine isn't at room temperature, but it should be cold. If the engine has been running, let it cool down completely before you start the test.
You'll need to remove the upper intake manifold plenum to access the fuel injectors. Although I'm not including any step-by-step instructions on how to do it, I do have a few important suggestions for you. You can find them here: Precautions To Take When Removing The Intake Manifold Plenum.
NOTE: Don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours? Check out my recommendation: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing.
Alright, here are the steps:
- 1
Disconnect the fuel injectors from their harness connectors.
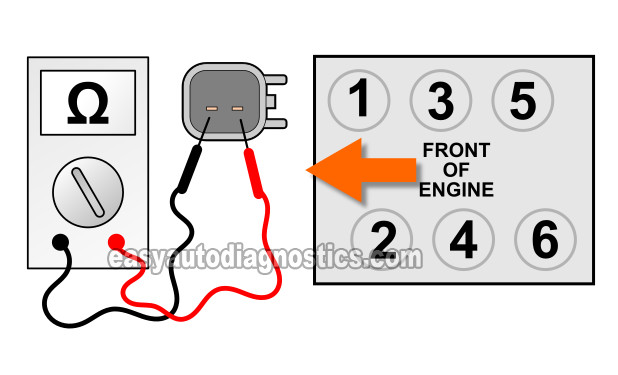
NOTE: The illustration above will help you identify the cylinder # the fuel injector belongs to. - 2
Place your multimeter in Ohms (Ω) mode and:
Measure the resistance of the fuel injector across its two male spade terminals with the multimeter test leads (see the illustration above). - 3
Write down the resistance value that your multimeter records for the specific fuel injector you're testing. The illustration above will help you identify the cylinder # the fuel injector belongs to.
- 4
Repeat steps 1 through 3 on the remaining fuel injectors.
NOTE: The fuel injector resistance specification is approximately: 10 to 16 Ohms.
Let's find out what your specific multimeter test results mean:
CASE 1: Your multimeter reports all fuel injector resistances are within specification. This tells that none are shorted or open internally and this is good news.
Here's why: If any one of the fuel injectors were shorted or open internally, the fuel injector would have registered a radically different resistance value on your multimeter. Since the resistance values for all 6 were uniform, this test result tells you that they are not defective.
CASE 2: Your multimeter reports a fuel injector with a completely different resistance value. This indicates that the fuel injector is bad. Replace the fuel injector.
