TEST 2: Verifying The MAP Sensor Is Getting Power
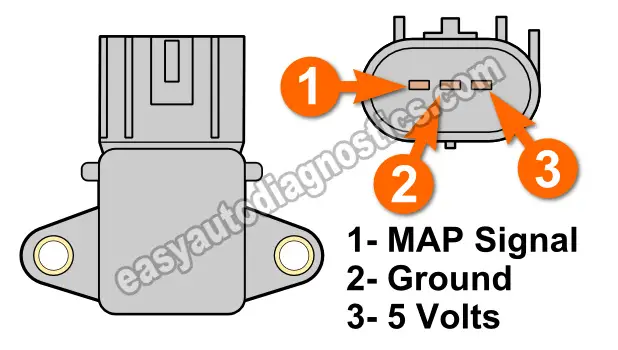
On the 2002-2003 4.7L Durango and 2003-2004 4.7L Dakota, the VIO/WHT wire, of the MAP sensor connector, is the one that feeds 5 Volts DC to the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor.
On the 2004-2009 4.7L Durango and 2005-2009 Dakota, the YEL/PNK wire, of the MAP sensor connector, is the one that feeds 5 Volts DC to the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor.
The power, that the VIO/WHT (or YEL/PINK) wire supplies is in the form of 5 Volts DC and comes from the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) on your 4.7L Dodge Durango (Dakota).
We can easily check to see if these 5 Volts are present by doing a simple multimeter voltage test.
These are the steps:
- 1
With your multimeter still in Volts DC mode from the previous test and the key on (but engine off).
- 2
Probe the VIO/WHT (or YEL/PNK) wire of the MAP sensor connector. This is the wire that connects to MAP sensor pin #3.
NOTE: the color of the wire depends on the specific year of your vehicle.
You can test for these 5 Volts with the MAP sensor's electrical connector connected to the MAP sensor or not, just avoid probing the front of the connector. - 3
Now Ground the black multimeter test lead on the battery's negative post.
- 4
If the VIO/WHT (or YEL/PINK) wire has power, your multimeter will register 4.5 to 5 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at what your results mean:
CASE 1: The VIO/WHT (or YEL/PNK), of the MAP sensor connector, has 5 Volts DC. This is the correct result and it's starting to look like the MAP sensor is bad but you still need to check that the MAP sensor is getting Ground.
For the Ground test, go to: TEST 3: Verifying The MAP Is Getting Ground.
CASE 2: The VIO/WHT (or YEL/PNK), of the MAP sensor connector, DOES NOT have 5 Volts DC. This results lets you know that the MAP sensor is not bad, since without these 5 Volts DC, the MAP sensor can not function.
Although it's beyond the scope of this article to troubleshoot the cause of these missing 5 Volts, you have now eliminated the MAP sensor as bad. Resolving the issue that is keeping these 5 Volts from being supplied will solve the MAP sensor issue on your 4.7L Dodge Durango (Dakota).
TEST 3: Verifying The MAP Sensor Is Getting Ground

On the 2002-2003 4.7L Durango and 2003-2004 4.7L Dakota, the BLK/LT BLU wire, of the MAP sensor connector is the one that feeds Ground to the MAP sensor.
On the 2004-2009 4.7L Durango and 2005-2009 4.7L Dakota, the DK BLU/DK GRN wire, of the MAP sensor connector is the one that feeds Ground to the MAP sensor.
The BLK/LT BLU (or DK BLU/DK GRN) wire connects to MAP sensor pin #2 in the illustration above.
IMPORTANT: Be careful that you don't intentionally or accidentally short the BLK/LT BLU wire to battery power or you'll fry your Durango's PCM. Checking for Ground by doing a voltage test with a multimeter, as described in the test steps below, is a safe way to test this circuit.
These are the steps:
- 1
With your multimeter still in Volts DC mode from the previous test and the key ON (but engine OFF).
- 2
Probe the BLK/LT BLU (or DK BLU/DK GRN) wire with the black multimeter test lead.
NOTE: the color of the wire depends on the specific year of your vehicle.
NOTE: It doesn't matter if you probe this circuit (wire) with the connector connected to the MAP sensor or not, but do not probe the front of the connector (if you decide to unplug the connector to test for this path to Ground). - 3
Now connect the red multimeter test lead on the battery's positive (+) Post.
- 4
If the BLK/LT BLU (or DK BLU/DK GRN) wire has Ground, then your multimeter will register 10 to 12 Volts DC.
OK, let's take a look at what your results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter confirms that the BLK/LT BLU (or DK BLU/DK GRN) wire is feeding Ground to the MAP sensor. This is the normal result and it means that the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor on your 4.7L Dodge Durango (Dakota) is fried and needs to be replaced.
Here's why: In MAP sensor TEST 1 and 2, you verified that the MAP sensor is not producing the correct values (when you applied vacuum) and that it does have power. Since in this test step you have confirmed that the MAP sensor does have a solid path to Ground, these results, interpreted together, indicate that the MAP sensor is bad.
CASE 2: The multimeter confirms that the BLK/LT BLU (or DK BLU/DK GRN) wire IS NOT feeding Ground to the MAP sensor. Double check your multimeter connections and repeat the test.
If your multimeter results still do not indicate 12 Volts, then the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is not fried and not the cause of the MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code (DTC) issue.
Here's why: Without a good path to Ground, that the PCM provides internally, the MAP sensor will not work. With this test result, you have eliminated the MAP sensor as bad.
MAP Sensor Code Won't Go Away
Over the years I've learned that quite a few conditions can cause the PCM to think the MAP sensor is bad when it isn't.
Below, I've highlighted the two most common problems I've run across that have caused a MAP sensor code (when the MAP sensor was good):
- Low engine compression condition:
- You can check this by doing an engine compression test.
- Low fuel pump pressure condition:
- Check fuel pump pressure with a fuel pressure gauge. A failing fuel pump will cause a lean air fuel mixture that can set a MAP sensor trouble code.
- The fuel injection computer is bad (internal short). Although this problem is not very common, it does happen.
- Check the MAP sensor's connector for damage. The most common problem with the connector is the locking tab has broken. This causes the connector to work itself loose, causing an intermittent false connection.
Before you jump the gun and start replacing the above, test the components first. This will help you save time, money, and the frustration of replacing parts your 4.7L Durango (4.7L Dakota) does not need.
More 4.7L Dodge Diagnostic Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 4.7L Dodge tutorials in these two indexes:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (2000-2007 4.7L Dodge).
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (Dodge, Jeep 4.7L V8) (at troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (4.7L Chrysler, Dodge, Jeep) (at troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
- How To Test The COP Ignition Coils (Chrysler, Dodge, Jeep 4.7L) (at troubleshootmyvehicle.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


