TEST 1: Applying 12 Volts To The Starter Motor S Terminal
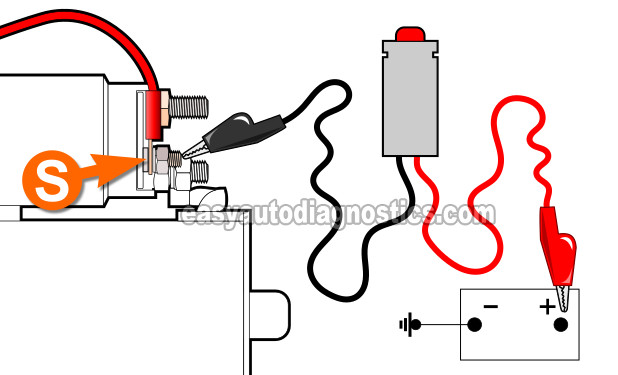
We're gonna' apply battery power to the starter motor's S terminal. This terminal is on the starter motor's solenoid.
What we're doing is basically bypassing the ignition switch and the neutral-safety switch by applying battery power directly to the starter motor's S terminal.
The fastest, safest, and easiest way to do this is using a remote start switch. You can see an example of this tool (and where to buy it), here: Sunpro Actron CP7853 Remote Starter Switch.
If the starter motor cranks the engine, when we apply this voltage, then we can conclude that it's OK (not defective) and that something else is causing it not to engage the engine when we turn the key to crank and start it.
IMPORTANT: Before you perform this test remove the key from the ignition switch to prevent the engine from accidentally starting. If your 2.3L Ford Ranger is equipped with a standard transmission, place it in neutral.
IMPORTANT: Place your Ford Ranger on jack stands if you raise it to access the starter motor!
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal.
You'll reconnect it back in one of the following steps, for now, it's a safety precaution as you set up the test. - 2
Attach one of the alligator-type terminals of the remote starter switch to the S terminal of the starter motor.
- 3
Reconnect the battery negative (-) cable to the battery negative post.
NOTE: Make sure that the battery cables and posts are clean. - 4
Connect the remaining alligator-type terminal of the remote starter switch to the battery positive post.
IMPORTANT: If your Ford Ranger has a standard transmission, make sure it's out of gear before you make this last connection. - 5
Activate the starter motor with your remote starter switch. As you apply these 12 Volts (to the S terminal of the starter motor), you'll get one of two results:
1) The starter will activate and will turn over the engine -OR- 2) The starter motor won't do a thing.
Let's examine your test result:
CASE 1: The starter motor cranked the engine. This is the correct test result and confirms that the starter motor itself is functioning correctly.
You can also conclude that the starter motor IS NOT cranking the engine probably because it's not getting an activation signal from the ignition switch.
So our next test is to see if the start signal is present when turning the key to turn over the engine. For this test go to: TEST 2: Verifying The Start Signal.
CASE 2: The starter motor DID NOT crank the engine. This test result usually means one of two things: either the starter motor is defective or it's not getting enough current.
I'm gonna' suggest that you do a voltage drop test on the battery cable that attaches to the starter motor. You can find this test here: TEST 3: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery Cable.
I'm also going to suggest that you make sure that the starter is getting an activation signal: TEST 2: Verifying The Start Signal.
If the above two tests confirm that the start signal IS present and there's no voltage drop on the battery cable (feeding battery power to the starter motor), then you can confidently conclude your Ford Ranger's starter motor is bad and needs to be replaced.
TEST 2: Verifying The Start Signal
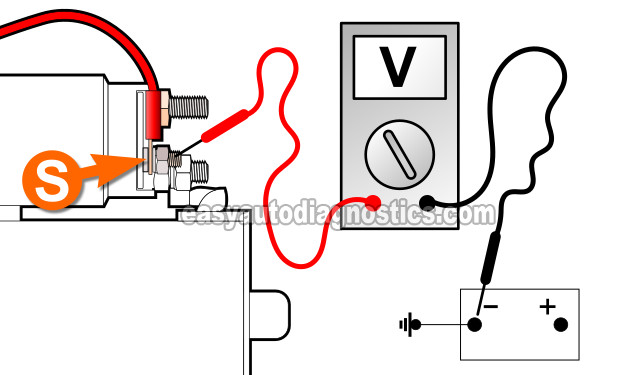
If in TEST 1 you're able to get the starter motor to crank the engine with the remote start switch but won't engage when you turn the key, then there's a good chance that it's not getting its activation signal.
The wire that connects to the S terminal on the starter motor's solenoid is the one that carries and feeds the start signal to the starter motor.
In this test, we're gonna' check to see if it's present or not.
OK, let's get started:
- 1
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the S terminal of the starter motor.
- 2
Attach the black multimeter test lead to a clean and rust-free spot on the engine or on the vehicle frame.
I recommend that you use a battery jump start cable to Ground the black multimeter test lead directly to the battery negative (-) terminal. - 3
Have your helper crank the engine from inside your Ford Ranger (Mazda B2300).
The engine won't turn over, but the idea is to verify that the starter motor's internal solenoid is getting the 12 Volt start signal from the ignition switch (or not). - 4
Your multimeter is going to register one of two results: Either 9 - 12 Volts DC or no voltage at all.
Let's analyze your test result:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct test result and tells you that the starter motor is receiving its activation signal.
This test result eliminates the safety neutral switch and the ignition switch as being faulty. The next step is to do a voltage drop test on the starter's battery cable. For this test go to: TEST 3: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery (+) Cable.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts. This result tells you that the starter motor is not getting its activation signal. Without it, the starter motor will not crank the engine when you turn the key to crank and start the engine.
Usually, when the starter's activation signal is not present on the wire that connects to the starter solenoid's S terminal, it's usually because:
- The ignition switch is faulty.
- The starter relay is defective.
- The neutral safety switch is faulty or misaligned.
Although it's beyond the scope of this article to test the neutral safety switch, the starter relay, or the ignition switch, you have eliminated the starter motor as defective.
