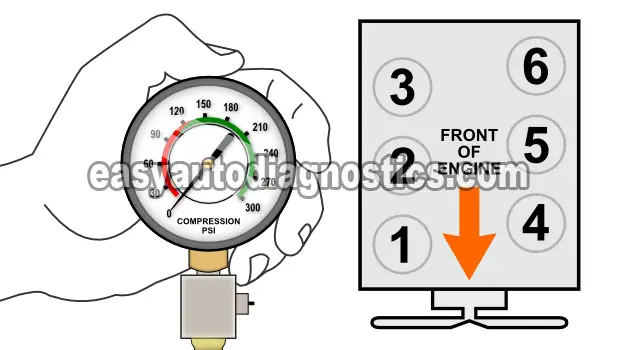
Testing engine compression is probably one of the most over-looked tests when diagnosing a hard to find misfire or no-start condition.
In this tutorial, I'll show you how to do and interpret an engine compression test on 4.2L equipped Fords.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Verificar La Compresión Del Motor (4.2L Ford V6) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Verificar La Compresión Del Motor (4.2L Ford V6) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Important Tips And Suggestions
TIP 1: If possible, it's a good idea to warm up the engine for about 10 minutes (from a completely cold condition). The key words here are 'slightly warmed up engine' since the engine should not be hot.
A slightly warmed up engine will improve the accuracy of your compression test results.
TIP 2: Take all necessary safety precautions as you work around a cranking engine. Your safety is your responsibility, so use common sense and think safety all of the time.
TIP 3: Your 4.2L V6 Ford engine's cylinder heads are made of aluminum, so do not remove the spark plugs with a hot engine. Removing the spark plugs from a hot engine can/will damage the spark plug hole threads in the aluminum cylinder head.
Symptoms Of Low Or No Cylinder Compression
As mentioned at the beginning of this tutorial, engine compression issues usually cause one of two problems: a misfire condition or a no-start condition.
Low engine compression in one or more cylinders will cause a rough idle (misfire) issue that can seem very hard to diagnose.
No compression in all cylinders results in a 'cranks but does not start' condition.
Here are some other specific symptoms you may see with low cylinder compression:
- Engine cranks but does not start (0 compression in all cylinders).
- Blue smoke coming out of the tailpipe.
- Rough idle (engine misfires).
- Bad gas mileage.
- Engine 'misses' at idle but 'miss' disappears as you accelerate.
- Check engine light is illuminated with a MAP sensor trouble code (even tho' the MAP sensor is good).
- Misfire trouble codes: P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306.
With this info under our belts, let's head down to the next subheading and get testing.
Which Compression Tester Should I Buy?
There are lot of engine compression testers to choose from and many places to buy them. I'm gonna' make two recommendations to you:
1) Which one to buy: The engine compression tester that I have always used is the Actron CP7827 Compression Tester Kit. My only complaint about this engine compression tester is that it does not come with a case to store it in.
2) Where to buy: You can buy an engine compression tester in any auto parts store in any neighborhood, in any city, but you'll be paying at least twice as much. Go to the above compression tester links, browse and compare, you'll see a big price difference!
TEST 1: Dry Compression Test
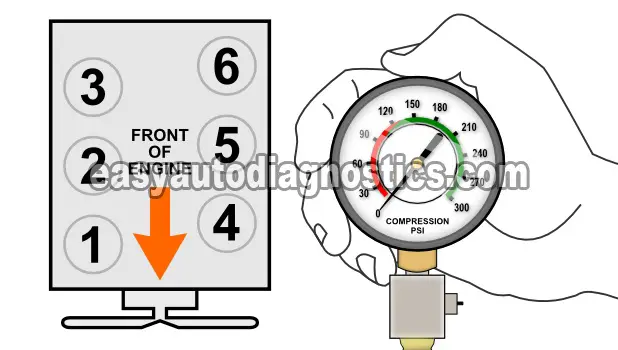
As you're already aware, doing a compression test involves disconnecting the spark plug wires from the spark plugs and then removing the spark plugs. To avoid damaging the spark plug wire and/or losing the firing order of the spark plug wires, I recommend two very important things:
- Label the spark plug wires with the cylinder number they belong to.
- Use a spark plug wire puller tool to unplug the spark plug wire from the spark plug.
Why use a spark plug wire puller? Cause pulling on the wire boot by hand can cause the wire's metal terminal to pull off and stay stuck on the spark plug. The following tutorial offers you more info: How To Use A Spark Plug Wire Puller And Where To Buy One.
OK, to get started this is what you'll need to do:
- 1
Disable the ignition system by disconnecting the ignition coil from its electrical connectors. This will prevent the ignition coil from sparking during the test.
- 2
Disable the fuel system by disconnecting the fuel injectors. Disabling the fuel system will prevent fuel from being injected into each cylinder when the test is performed.
- 3
Remove the spark plugs from a slightly warmed up engine (if it starts and runs). Remember, the engine can not be hot!
When removing the spark plugs, be careful not to drop any of them on the floor, or you run the risk of having the spark plugs porcelain insulator crack and then you'll have a misfire on your hands.
If the engine does not start, don't worry about it being warmed up. - 4
Thread the engine compression gauge into the spark plug hole for the number 1 engine cylinder. Hand tighten the compression gauge only! Do not use any type of tool to get it tight.
- 5
Have your helper crank the engine till the needle on the compression gauge stops climbing.
Now, record on paper the value at which the needle stopped and the number of the engine cylinder on a piece of paper. Release the pressure on the gauge and repeat this step one more time.
Repeat this test step on the remaining 5 cylinders.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The engine does not start and the results of the engine compression test are 0 PSI on all 6 cylinders. This test result tells you that the engine has one of the following conditions:
- Timing chain problem.
- Blown head gasket.
- Blown engine.
Any compression value below 100 PSI (even if it does not 0 PSI) means internal mechanical engine trouble.
CASE 2: The engine does start and the compression values you wrote down for each cylinder are slightly different from one another. Up to a certain point this could be normal.
What is NOT normal is if the values vary too much. The cool thing is that we can find out if the variations in the values, you wrote down, indicate a problem (with that cylinder) or not.
The rule of thumb is that they can not vary more than 15% from each other and if they do, you're gonna' have a genuine misfire condition on your hands or possibly a no-start condition (if more than one cylinder is affected).
How do you figure this out? You can find out by using my online low compression calculator here: Online Low Engine Compression Calculator or manually this way:
- Grab a calculator and multiply the highest compression reading that you recorded by 0.15. So, let's say that cylinder #4 gave you the highest reading of 170 PSI. Well 170 X 0.15 gives you 26 (25.5 rounded off).
- Now, the next step is to subtract 26 from 170 -which gives us 144 PSI.
- So then, 144 PSI is the lowest possible compression reading that any one of the rest of the engine cylinders can have. Any compression reading below this and that engine cylinder will misfire.
To make better sense of the above calculation, let's say that my 4.2L Ford Pick Up produced the following compression test results:
- Cylinder #1 170 PSI.
- Cylinder #2 165 PSI.
- Cylinder #3 160 PSI.
- Cylinder #4 120 PSI.
- Cylinder #5 165 PSI.
- Cylinder #6 160 PSI.
The next step is to do the math: 175 x 0.15= 26, 175-26= 149. So, now I know that cylinder #4 is the one causing the misfire!!
The final thing we need to do is to figure out what's causing the low or zero compression value. Go to: TEST 2: Wet Compression Test.




