The 1994-1998 2.4L Mitsubishi Galant comes equipped with an ignition distributor. This ignition system uses a camshaft position and crankshaft position sensor. This tutorial will help you diagnose the crankshaft position sensor that's located behind the crankshaft timing sprocket (the camshaft position sensor is located in the distributor).
The crankshaft position sensor on your 1995-1998 2.4L Mitsubishi Galant is a pretty easy component to test without a scan tool. In this tutorial, I'm gonna' show you how to test it (very accurately) with a multimeter.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Crank Sensor.
- What Tools Do I Need?
- Circuit Descriptions Of The Crankshaft Position Sensor.
- Basic Operating Theory.
- Where To Buy The Crank Sensor And Save.
- TEST 1: Making Sure The CKP Sensor Is Getting Power.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The CKP Sensor Is Getting Ground.
- TEST 3: Making Sure The CKP Sensor Is Creating A Crankshaft Position Signal.
- More 2.4L Mitsubishi Tutorials.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor De La Posición Del Cigüeñal (1995-1998 2.4L Mitsubishi Galant) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor De La Posición Del Cigüeñal (1995-1998 2.4L Mitsubishi Galant) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Symptoms Of A Bad Crank Sensor
The most obvious symptom of a bad crankshaft position sensor on your 2.4L Mitsubishi Galant is that the engine will crank but not start.
Here are some more specifics:
- The vehicle will not start. The engine will turn over (crank) but won't start.
- Trouble code lighting up the check engine light (CEL) on your instrument cluster.
- P0335: Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- No fuel injector pulses (as checked with a Noid light).
- No spark at any of the spark plug wires (as checked with a spark tester).
Although your Galant's PCM is designed to register a crank sensor trouble code when the crank sensor fail, it rarely does. This is why it's a good idea to test the crank sensor with a multimeter to see if it's behind your 'cranks but does not start' condition.
What Tools Do I Need?
The cool thing about testing the crankshaft position sensor is that it can be very accurately tested with just a simple multimeter. That's right, no scan tool needed for the crank sensor test on your 2.4L Galant.
Here the specifics of what you'll need:
- A multimeter.
- Don't have a digital multimeter that can read Hertz frequency? Click here to see my recommendations: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing.
- A wire piercing probe.
- This tool is a handy tool to have. To see what it looks like, go to: Wire Piercing Probe.
- Hand tools to turn the crankshaft pulley by hand.
To get the most accurate test result, you'll need to turn the engine by hand and not with the starter motor.
Circuit Descriptions Of The Crankshaft Position Sensor

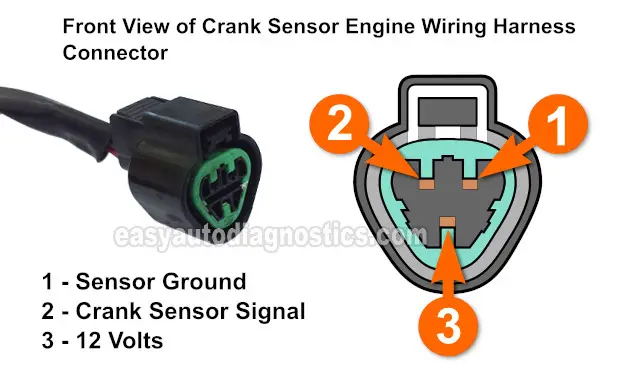
As you're already aware, the crankshaft position sensor on your Galant has 3 wires coming out of it. Each wire has a specific job to do. Here are the crank sensor circuit descriptions:
- Circuit labeled 1:
- Ground Circuit (provided by PCM).
- Circuit labeled 2:
- Crankshaft position signal (output to the PCM).
- Circuit labeled 3:
- Power circuit (12 Volts).
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is located behind the timing belt but you don't have to remove the timing belt covers to test it. This is due to the fact that the crank sensor's connector is located on top of the engine and in plain view.
Basic Operating Theory
The crankshaft position sensor's job boils down to sending your Mitsubishi Galant's PCM voltage pulses. These pulses correspond to specific piston positions.
With this and the cam sensor position info, the PCM controls fuel injection, ignition timing, and of course the ignition coil's ability to create the spark your engine needs to start.
For our testing purposes, this is what happens (in a nutshell of course):
- As you turn the key and crank the engine. The crank sensor gets power and Ground.
- With power and Ground supplied, the engine rotation induces the crankshaft position sensor to start producing a crankshaft position signal.
- This crankshaft position signal is sent to the PCM.
- The PCM, along with other necessary sensor information, starts to do its little song and dance and sends back a Triggering Signal to the ignition power transistor (ignition control module).
- This Triggering Signal contains the instructions for the ignition power transistor (ignition control module) to start firing the ignition coils in the correct firing order.
- With fuel being injected, your Galant's engine starts and stays running.
Where To Buy The Crank Sensor And Save
The following links will help you comparison shop for the crankshaft position sensor.
Not sure if the above crankshaft position sensor fits your particular Galant? Don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure it fits. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Making Sure The CKP Sensor Is Getting Power

We're gonna' start by making sure that the crankshaft position sensor is getting power. This power comes from the MFI Relay and is in the form of 12 Volts DC.
If power is present, then the next step will be to make sure the crank sensor is being fed with Ground (TEST 2).
NOTE: Avoid probing the front of the crank sensor engine wiring harness connector with your multimeter's test lead or you run the risk of damaging the terminal. I recommend that you use a back probe or a wiring piercing probe to check for power.
Here are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode and disconnect the crankshaft position sensor from the engine wiring harness connector.
IMPORTANT: This test is done on the engine wiring harness crank sensor connector and NOT on the sensor's connector. You can further identify the engine wiring harness connector by the fact that it has female terminals. - 2
Connect the red multimeter test lead to RED wire of the crank sensor's engine wiring harness connector using an appropriate tool.
The RED wire connects to the terminal labeled with the #3 in the illustration above. - 3
Ground the black multimeter test lead to a good Ground point on the engine or directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Have your assistant turn the key to the ON position but without cranking the engine.
- 5
Your multimeter should register 12 Volts if the RED wire is feeding the crankshaft position sensor with power.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter showed 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct test result and lets you know that the CKP sensor is getting power.
The next step is to make sure its Ground circuit is OK too, go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The CKP Sensor Is Getting Ground.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT show 10 to 12 Volts. This indicates that the CKP sensor is not getting power. Without 10 to 12 Volts, the CKP will not work and your Mitsubishi vehicle will 'crank but not start'.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial, your next step is to find out why this voltage is missing and restore it to solve your Galant's no-start condition.




