
This tutorial will help you to diagnose a bad ignition control module (ICM) causing a misfire condition on your VW 1.8L Passat (New Beetle, Jetta, Golf) . It will also help you to troubleshoot a bad Coil-On-Plug (COP) ignition coil.
One of the most common failures with this type of ignition control module (ICM) is a misfire condition in which the ignition module doesn't activate one of the ignition coils.
This condition is usually misdiagnosed as a bad ignition coil and the end result is money spent on parts that don't solve the misfire issue.
In this tutorial, I'll show you my way of testing the ignition control module that doesn't involve using any expensive diagnostic equipment (not even a scan tool!). I've used this testing method time and time again over the years with very accurate results.
Contents of this tutorial:
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Control Module And The COP Coils.
- Ignition Module Circuit Descriptions.
- COP Ignition Coil Circuit Descriptions.
- Identify The Misfiring Cylinder.
- TEST 1: Testing The Ignition Coils For Spark.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting 12 Volts.
- TEST 3: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Ground.
- TEST 4: Swapping The Ignition Coils.
- TEST 5: Testing The Continuity Of The Activation Signal Circuit.
- Article Conclusion.
For your cross reference information, the ignition control module that this article covers are:
- AutoZone part #:
- Duralast RB155
- O'Reilly part #:
- MasterPro 2-7122
- Import Direct 14-0284
- Import Direct 14-0279
- AC Delco F1909A
- Others:
- STANDARD MOTOR PRODUCTS Part # LX920
- Airtex Part # 6H1022
- WELLS Part # RB155
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Control Module And The COP Coils
As I mentioned at the beginning of this tutorial, you don't need a scan tool. Here are the tools you'll need:
- Multimeter
- A digital or analog multimeter will work.
- If you need to buy one or are looking to upgrade, check out my recommendations here: Buying A Digital Multimeter for Automotive Diagnostic Testing.
- A spark tester
- A dedicated spark tester is a must-have tool to correctly diagnose an ignition system misfire or no-spark condition. I'm gonna' recommend to you the HEI spark tester because of its accuracy and ease of use. To find out more about this spark tester, you can read more here: HEI Spark Tester.
- Wire Piercing Probe
- Although not an absolute must, this tool is a time saver of the first order. To see what this tool looks like, go here: Wire Piercing Probe.
You'll also need basic hand tools to remove the ignition module (if it tests bad that is), like a ratchet wrench, sockets, etc.
Ignition Module Circuit Descriptions
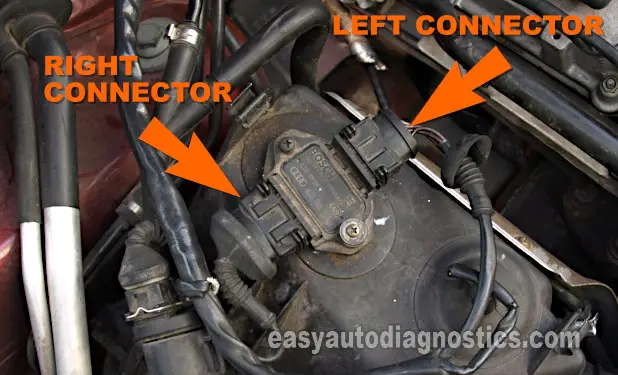
The ignition control module has two connectors. Looking down at the ignition module (with the ignition module still bolted in place), you'll notice that the ignition control module has a left connector and a right connector.
In the pin out charts below is a brief job description of what each wire does.
NOTE: Although I've included the color of the wires, in the charts below, I can tell you that they are not gonna' match the colors that are on your vehicle (it's been my experience that the colors described on the wiring diagrams usually never matches what's on the VW).
So then, how can you locate the wire you'll need to test? Very easily, because the connector labeled as the 'Left Connector' (in the photo above) has only 4 wires connected to it and the connector labeled as the 'Right Connector' has 5 wires connecting to it.
Also, you'll find the number of the wire embossed on the ignition control module (Igniter) and this will also help you further identify the wire to be tested.
| Right ICM Connector Pin outs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Gray * | Cyl. #1 Ignition Coil Signal |
| 2 | Gray w/ Brown stripe * | Cyl. #2 Ignition Coil Signal |
| 3 | Gray w/ Black stripe * | Cyl. #3 Ignition Coil Signal |
| 4 | Brown w/ Black stripe * | Cyl. #4 Ignition Coil Signal |
* Your specific VW vehicle may have different colors.
| Left ICM Connector Pin out | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Grey w/ Yellow stripe * | To Fuel Injection Computer |
| 2 | Yellow w/ Grey stripe * | To Fuel Injection Computer |
| 3 | Brown * | Chassis Ground |
| 4 | Red w/ Gray stripe * | To Fuel Injection Computer |
| 5 | Green w/ White stripe * | To Fuel Injection Computer |
* Your specific VW vehicle may have different colors.
COP Ignition Coil Circuit Descriptions

OK, before we jump into the testing part, you need to know a few more things and this is what each of the three wires that connect to the ignition coil connector do.
This is important because in the tests (in this tutorial), I'm gonna' ask you to verify Power (12 Volts), Ground and continuity between the ICM and coil at the ignition coil's 3-wire electrical connector.
OK, these are the circuits (wires):
| COP Ignition Coil Connector Pin outs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Color will vary with coil * | ICM Switching Signal |
| 2 | Brown w/ Yellow stripe * | Chassis Ground |
| 3 | Black w/ Blue stripe * | Power -12 Volts |
* Your specific VW vehicle may have different colors.
Once again, I want to tell you that you don't have to worry about the specific colors of the wires on your vehicle since you'll be able to locate the correct wire to test with the photo I'm providing.
OK, let's turn the page and get testing!
Identify The Misfiring Cylinder
The very first thing you need to do is identify the misfiring cylinder (if you haven't already). This can be very easily done with a simple cylinder balance test.
For those of you who may not know what a cylinder balance test, this test involves unplugging each ignition coil (from its 3-wire electrical connector) while the engine is running. Why? To see if unplugging that ignition coil's 3-wire electrical connector has an effect on the engine's idle. If unplugging the electrical connector does not worsen the engine's idle, then that cylinder is 'dead'.
I'm going to emphasize the above point one more time: If the cylinder is 'dead', then when you unplug the ignition coil, the engine's idle will not get rougher. If the cylinder is working like it should, then unplugging the ignition coil from its connector will cause the engine's idle to get worse (rougher) and you'll see/notice a drop in the engine's RPMs too.
NOTE: When performing the cylinder balance test, it's important that you don't keep the ignition coil unplugged for too long a time, since this will add unburned gasoline to an already overburdened catalytic converter (remember, you already have a misfire that's adding unburned fuel to the exhaust system).
TEST 1: Testing The Ignition Coils For Spark
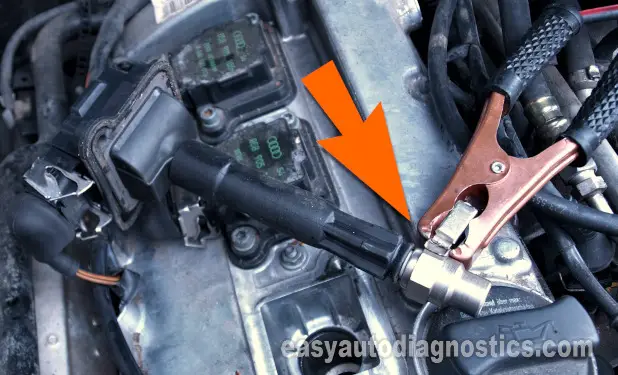
To get our diagnostic started, we're gonna test all four ignition coils for spark with a spark tester.
You don't have to test all four ignition coils, since you can test just the ignition coil of the 'dead cylinder' you've already identified.
My recommendation, even if you know which cylinder is 'dead', is to test all of them for spark.
This is what you'll need to do:
- 1
Disconnect the COP ignition coil from its electrical connector and remove it from the engine.
- 2
Attach a dedicated spark tester to the COP coil (see photo above).
- 3
Ground the spark tester directly to battery negative (-) terminal using a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Reconnect the COP ignition coil to its electrical connector.
- 5
Have a helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester from a safe distance.
- 6
The spark tester should spark the whole time the engine is cranking.
- 7
Repeat steps 1 thru 6 on the remaining ignition coils.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked. This is the correct test result and it tells you that this particular ignition coil is good.
Since the ignition coil sparked, you can conclude that the ignition control module is activating it.
If you've identified that the cylinder this ignition coil belongs to is misfiring ('dead'), it may have one of the following issues:
- Bad spark plug.
- Bad or clogged fuel injector.
- Bad compression.
CASE 2: The spark tester DID NOT spark. The next step is check if the non-sparking ignition coil is getting power. Go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting 12 Volts.
