
Testing the starter motor on the 1991-1995 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota is not hard. In this tutorial, I'll explain how to do it so that you can find out if it's bad or not.
All the test steps are explained in a step-by-step manner.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota equipped with an automatic transmission. The 1994-1995 3.9L Dodge Dakota equipped with a standard transmission.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Starter Motor Test Basics.
- Tools Needed To Test The Starter Motor.
- Where To Buy The Starter Motor And Save.
- TEST 1: Bypassing The Starter Motor Relay.
- TEST 2: Confirming The Presence Of 12 Volts At Female Terminal B.
- TEST 3: Applying 12 Volts To The Starter Solenoid's S Terminal.
- TEST 4: Making Sure The Starter Motor Is Getting A Start Signal.
- TEST 5: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery (+) Cable.
- TEST 6: Making Sure The Starter Motor Relay Is Getting An Activation Signal.
- TEST 7: Testing The Park/Neutral Safety Switch Signal.
- Bypassing The Starter Motor Relay Is Not A Repair Solution.
- Jumper Wire Example.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Motor De Arranque (1991-1995 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Motor De Arranque (1991-1995 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
STARTER MOTOR WIRING DIAGRAM: You can find the starter motor circuit wiring diagram here: Starter Motor Circuit Diagram (1991-1995 3.9L Dodge Dakota).
Starter Motor Test Basics
The four main components involved in getting the engine to crank are:
- The ignition switch.
- The park/neutral safety switch (automatic transmission) or the clutch switch (standard transmission).
- The starter motor relay. Located in the Power Distribution Center (under-hood fuse and relay box).
- The starter motor.
In a nutshell this is how the starter motor cranks the engine:
- When you turn the key to start the engine the ignition switch sends a 12 Volt activation signal to starter motor relay terminal A.
- Terminal C now completes the path to Ground for this activation signal and the starter motor 'activates'.
- Once the starter motor relay is 'activated', it lets 12 Volts pass from the ignition switch to the starter motor.
- To be a bit more specific: it lets 12 Volts pass from terminal B to terminal D.
- Terminal B connects to fuse B (30 Amps) of the Power Distribution Center.
- Terminal D connects to the S terminal on the starter motor's solenoid.
- Once the starter motor gets these 12 Volts, it now activates and cranks the engine.
You'll be able to better visualize this by consulting the following starter motor circuit wiring diagram: Starter Motor Circuit Diagram (1991-1995 3.9L Dodge Dakota).
For our starter motor relay test we're gonna':
- Bypass the starter motor relay (TEST 1).
- Make sure that 12 Volts present at all times at female terminal B of the relay socket (TEST 2).
- Make sure that 12 Volts are present at female terminal A of the relay socket when you turn the key to start the engine (TEST 6).
- Make sure that Ground is present at female terminal C of the relay socket (TEST 7).
For our starter motor tests we're gonna':
- Manually apply 12 Volts to the S terminal of the starter motor (TEST 3).
- Make sure that the starter motor is getting a Start Signal on the S terminal wire (TEST 4).
- Voltage drop test the battery cable that connects the battery positive (+) post to the starter motor (TEST 5).
The starting point for all of the above tests is: TEST 1: Bypassing The Starter Motor Relay.
Tools Needed To Test The Starter Motor
Testing the starter motor does require some basic tools. The cool thing is that they aren't expensive. Here's a basic list of what you'll need:
- Remote starter switch.
- If you'd like to see what a remote starter switch looks like, you can follow this link: Innova 3630 Remote Starter Switch (Amazon affiliate link).
- You can either buy this tool online or you can buy it at your local auto parts store (AutoZone or O'Reilly Auto Parts, etc.).
- Multimeter.
- If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours, check out my recommendation here: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter (Amazon affiliate link).
- A jumper wire.
- You can make your own. You can see an example here: Jumper Wire Example.
- A helper.
Where To Buy The Starter Motor And Save
The following starter motor offers will help you comparison shop and hopefully save you a few bucks!
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
Not sure the above starter motor fits your particular 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota? Don't worry, once you get to the site they'll ask you for the specifics of your Dodge Dakota and make sure it does fit. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Bypassing The Starter Motor Relay
The first thing we're gonna' do is remove the starter motor relay and using a jumper wire, we're gonna' jumper female terminal B and female terminal D.
Female terminal B receives battery power from fuse B (30 Amp) of the Power Distribution Center.
Female terminal D connects to the S terminal on the starter motor's solenoid.
If you don't have a jumper wire, you can make your own. You can take a look at an example here: Jumper Wire Example.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the female terminals of the relay socket on the fuse box with the jumper wire. The jumper wire terminals should be of the same thickness as the male spade terminals of the starter motor relay to avoid damaging the female terminals of the socket.
IMPORTANT: Remove the fuel pump relay as a safety precaution before starting this test. The fuel pump relay is located in Power Distribution Center (see photo 2 of 2).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Confirm that the automatic transmission is in Park. If your Dodge Dakota has a standard transmission, make sure it's out of gear and the parking brake is on.
- 2
Remove the fuel pump relay from Power Distribution Center (see photo 2 of 2)
This is a safety precaution. - 3
Remove the starter motor relay from Power Distribution Center.
- 4
Connect one end of the jumper wire to the female terminal labeled with the letter B.
- 5
Connect one end of the jumper wire to the female terminal labeled with the letter D.
- 6
The starter motor should crank the engine.
- 7
Remove the jumper wire when done with the test.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The starter motor cranked the engine. This is the correct and expected test result and lets you know that the starter motor is good.
Now, if the starter motor does not crank the engine with the starter motor relay in place then there's a good chance that:
- The starter motor relay is not getting an activation signal from the ignition switch.
- The park/neutral safety switch is bad.
- The starter motor relay is bad.
Don't worry, I'm gonna' show you how to find out. The next step is check for the presence of the relay's activation signal. For this test to go to: TEST 6: Making Sure The Starter Motor Relay Is Getting An Activation Signal.
NOTE: Bypassing the starter motor relay as a repair solution is a bad idea (safety-wise). Take a look at: Bypassing The Starter Motor Relay Is Not A Repair Solution.
CASE 2: The starter motor DID NOT crank the engine. This test result usually means that the starter motor is bad.
But there's a chance that female terminal B is not getting 12 Volts from fuse B of the Power Distribution Center.
So the next test is to confirm that 10 to 12 Volts are present at female terminal B. For this test go to: TEST 2: Confirming The Presence Of 12 Volts At Female Terminal B.
TEST 2: Confirming The Presence Of 12 Volts At Female Terminal B
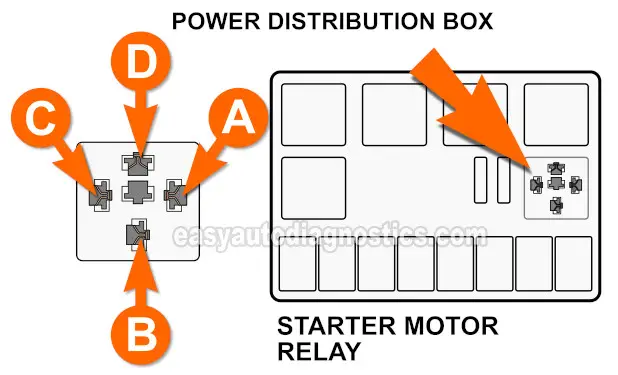
In this section, we're gonna' make sure that 10 to 12 Volts are present at female terminal B of the starter motor relay socket in the Power Distribution Center.
We'll do a simple multimeter voltage test to confirm the presence or lack of these 12 Volts.
CAUTION: Gently probe the female terminal of the starter motor relay socket with the multimeter test leads.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the starter motor relay from the Power Distribution Center.
- 2
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) post.
- 3
Gently probe the female terminal labeled with the letter B with the red multimeter test lead.
- 4
The multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts with the key on or off.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: 10 to 12 Volts are present. This is the correct test result.
If the starter motor did not crank the engine when you jumpered terminal B and terminal D, then your next step is to apply 12 Volts to the starter motor's S terminal. For this test to go to: TEST 3: Applying 12 Volts To The Starter Solenoid's S Terminal.
CASE 2: 10 to 12 Volts ARE NOT present. This test result usually tells you that fuse B is blown.
Your next step is to check the condition of fuse B in the Power Distribution Center. If it's blown, replace it and repeat this test section. If battery power now becomes available at terminal B, install the starter motor relay and try cranking the engine with the key.
If the starter motor still does not crank the engine, your next step is: TEST 3: Applying 12 Volts To The Starter Solenoid's S Terminal.






