
Testing the alternator on your 4.0L V6 Ford Ranger (Mazda B4000) isn't hard. The best part is that you don't need any expensive testing equipment.
This tutorial will explain how to test the alternator with a multimeter. You'll find all test steps explained in a step-by-step way. You'll easily find out if the alternator is bad or not.
NOTE: You can find the 1991-2000 4.0L Ford Explorer (Aerostar) alternator test tutorial here:
- How To Test The Alternator (1991-2000 4.0L Ford Explorer And Aerostar) (at: troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 4.0L V6 Ford Ranger: 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
- 4.0L V6 Mazda B4000: 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003.
WIRING DIAGRAMS:
- Alternator Circuit Diagram (1996 4.0L Ford Ranger and Mazda B4000).
- Alternator Circuit Diagram (1997 4.0L Ford Ranger).
- Alternator Circuit Diagram (1998-2001 4.0L Ford Ranger).
Important Testing Tips
The following tips will help you accomplish the tests in this tutorial:
TIP 1: Before starting the alternator tests, you must fully charge the battery.
TIP 2: You can use a digital multimeter or an analog multimeter.
TIP 3: Take all necessary safety precautions. Be alert and think safety all of the time since you'll be working around a running engine.
Symptoms Of A Bad Alternator
As you're aware, the alternator's job is to charge the battery for the next engine start and provide the current that the accessories need (while the engine is running and you're driving around).
So, when the alternator fails, the battery doesn't get charged any more, and you'll see one or more of the following symptoms:
- The battery light will be illuminated in your vehicle's instrument cluster.
- Dim headlight glow dim.
- The engine only start with a jump start. After a few minutes of run time, it dies.
- The engine starts fine if you charge the battery. After your initial trip, the battery needs a jump-start to crank and start the engine.
TEST 1: Checking Alternator Voltage Output With A Multimeter
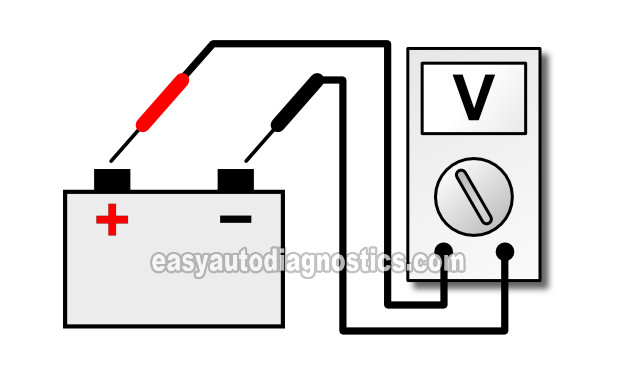
For your first test, you'll check the battery voltage with the engine running.
If the alternator is charging the battery, you'll see a voltage around 13.5 to 14.5 Volts DC (with the engine running).
If the alternator has failed and isn't charging the battery, you'll see a voltage around 12.5 Volts DC. This voltage will decrease the longer the engine stays running.
IMPORTANT: You must perform this test with a fully charged battery.
These are the steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Start the engine and let it idle.
- 3
Probe the battery terminals with your multimeter test leads.
The red multimeter test lead to battery positive (+) post. The black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) post. - 4
You should see 13.5 to 14.5 Volts on your multimeter. If you don't, don't worry about this just yet, continue to the next step.
- 5
Place a load on the battery. You can do this by turning on the headlights, the A/C or heater on high, the windshield wipers, the radio, the rear window defroster, etc.
- 6
You'll see one of two things:
1.) The voltage will decrease slightly and then stabilize around 13.5 to 14.5 Volts DC when something comes on.
2.) The voltage reading will start to decrease till it reaches 10 Volts DC and your vehicle may stall.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The voltage stayed at 13.5 to 14.5 Volts thru' out the whole test. This result confirms that the alternator is charging the battery and providing enough electrical power for any electrical load that is applied to it.
CASE 2: The voltage decreased below 13.5 Volts as you turned on all accessories. This usually means that the alternator is bad.
Your 4.0L Ford Ranger (Mazda B4000) is running off the battery only since the alternator is not charging the battery or providing power for all the stuff you turned on.
This condition will cause your multimeter to show a decreasing voltage reading as the battery's juice starts to deplete.
Around 90% of the time, you would hit the nail right on the head and solve the no-charging condition by replacing the alternator. But to be sure the alternator is bad, I suggest doing two more very simple tests. For this first one, go to: TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Battery Circuit.

