
There are several components that, when they fail, can prevent the engine from starting.
These can include issues with the ignition coil, ignition control module, fuel pump, a blown head gasket, or even an engine compression issue to name a few.
Thankfully, it's not difficult to figure out why the engine won't start and in this tutorial, I'll help you identify the cause of the engine no-start problem by walking you through the process of testing and troubleshooting these various components.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Difference Between A No-Start And A No-Crank Condition.
- Engine No-Start Diagnostic Basics.
- What Tools Do I Need?
- STEP 1: Testing The Ignition System For Spark.
- STEP 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure.
- STEP 4: Making Sure The Engine Has Good Compression.
- STEP 5: Checking For A Blown Head Gasket.
- No-Start Troubleshooting Summary.
- More 2.8L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup (GMC S15 pickup, GMC Sonoma) Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.8L Chevrolet S10 Pickup: 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993.
- 2.8L GMC S15 Pickup: 1988, 1989, 1990.
- 2.8L GMC Sonoma: 1991, 1992, 1993.
Difference Between A No-Start And A No-Crank Condition
Before we begin, it's crucial to understand the difference between an engine not starting (no-start) and an engine not cranking (no-crank).
Being aware of this difference will accelerate your diagnostic process and aid in identifying the source of the issue without any added difficulties or frustration.
Here's the difference:
- In an engine no-start problem, you turn the key to start the engine, and the engine cranks but does not start.
- In a no-crank problem, you turn the key to start the engine, but nothing happens since the starter motor does not come out to play.
If your 2.8L V6 Chevrolet S10 pickup (GMC S15 pickup, GMC Sonoma) is experiencing an engine no-crank problem, you should start your troubleshooting efforts by testing the battery and/or the starter motor.
Engine No-Start Diagnostic Basics
An engine needs three things to start. They are:
- Air.
- Fuel.
- Spark.
If the engine in your 2.8L V6 Chevrolet S10 pickup (GMC S15 pickup, GMC Sonoma) is not starting, one of the following reasons is behind the issue:
- The engine isn't getting any fuel.
- The engine isn't receiving spark.
- The engine isn't producing any compression (this is the 'air' part).
This also means that we can perform a few basic tests to find out what's causing the engine not to start:
- An ignition system test (spark test).
- A fuel system test (fuel pressure test).
- An engine compression test.
- A blown head gasket test.
In the next sections, I'll walk you through the step-by-step process I use for diagnosing engine no-start issues, which will aid you in identifying the root cause of the no-start problem on your vehicle.
What Tools Do I Need?
You'll need a few basic tools to get to the bottom of what's causing the engine not to start.
These tools are:
- A spark tester.
- A fuel pressure tester.
- An engine compression tester.
- A multimeter.
- A code reader.
To confirm that the ignition system is generating and supplying spark to the spark plugs, I recommend using an HEI spark tester.
The HEI spark tester is one of the most reliable spark testers on the market, easy to use and is reasonably priced. You can find out more about it and where to buy it here: HEI Spark Tester.
Although I didn't include a scan tool in the list, having one is a plus. But you don't need one to follow any of the suggested tests in this tutorial.
STEP 1: Testing The Ignition System For Spark
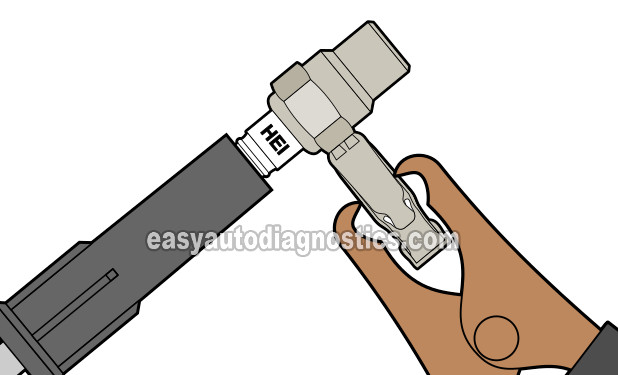
The 2.8L V6 Chevy S10 pickup (GMC S15 pickup, GMC Sonoma) uses a distributor-based ignition system that distributes a high-voltage spark to the individual cylinders of the engine.
The ignition system on the 2.8L V6 Chevy S10 pickup (GMC S15 pickup, GMC Sonoma) consists of the following components:
- Ignition coil.
- Ignition control module (ICM).
- Distributor cap.
- Distributor rotor.
- Distributor.
- Distributor pickup coil (CKP sensor).
- Spark plug wires.
- Spark plugs.
In this system, the ignition coil generates a high-voltage spark, which is then distributed to the spark plugs by the distributor cap and rotor and spark plug wires.
Thankfully, there's a systematic approach to troubleshooting the ignition system to determine if it's causing an engine no-start problem, which begins with checking all six spark plug wires to confirm they're delivering spark to the plugs.
To guide you through the process, the following tutorials will help you test the ignition system step by step.
- How To Test The Ignition Coil -No Start Tests (2.8L V6 GM).
- How To Test The Ignition Control Module (2.8L V6 GM).
- How To Find A Misfiring Cylinder (2.8L V6 GM).
The ignition system is NOT causing the no-start problem if:
- Spark is present at all six spark plug wires when cranking the engine.
If all six spark plug wires delivering spark to their spark plugs, you can conclude that the ignition system is NOT causing the engine no-start problem.
You can also conclude that:
- The distributor pickup coil (CKP sensor) is good.
- The ignition control module (ICM) is good.
- The ignition coil is good.
- The distributor cap and rotor are good.
- The spark plug wires are good.
Since the ignition system is creating and feeding spark to the engine cylinders, the next test steps are to test the fuel pump's pressure. Go to: STEP 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure.
The ignition system IS THE CAUSE of the no-start problem if:
- The six spark plug wires ARE NOT sparking.
The components that can cause this no-spark problem are:
- A bad distributor pickup coil.
- A bad ignition control module (ICM).
- A bad ignition coil pack.
- A bad ignition coil high tension wire.

