TEST INFO: Circuit Descriptions Of The Ignition Module
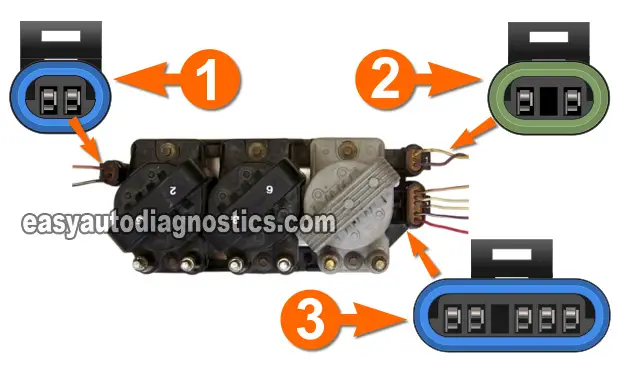
Below you'll notice that the photo of the ignition control module has its three connectors labeled with numbers (in white) and letters (in black). To diagnose a bad ignition module (in a no-start situation) we only have to worry about testing the circuits in the connectors labeled 1 and 2. I have included some circuit descriptions for Connector 3 in case you need this info.
IMPORTANT: If the vehicle you're working on is NOT equipped with a tachometer, the ignition module connector labeled with a 3 WILL NOT HAVE all five wires coming out of it. This is no cause for concern, since the missing wire (circuit) is the feed for the tachometer on the instrument cluster.
If you take a look at each connector of the ignition module on your vehicle, you'll see that each wire is labeled with a letter. This letter is embossed on the connector itself. To make it easier for you to identify what circuit does what, I'll be using those same letters for the descriptions below:
Connector 1
- A- PINK (or PINK with BLACK stripe) wire. 12 Volts with Ignition ON.
- B- BLACK with WHITE stripe wire. Engine Ground.
Connector 2
- A- YELLOW wire. CKP Sensor Signal Circuit.
- B- Empty. No circuit exists.
- C- PURPLE wire. CKP Sensor Signal Circuit.
Connector 3
- A- TAN with BLACK stripe wire. 5 Volt Reference from ECM (above 400 RPM).
- B- WHITE wire. ECM control signal for Ignition Module (above 400 RPM).
- C- WHITE wire. Tach signal (IF EQUIPPED WITH TACHOMETER).
- D- Empty. No circuit exists.
- E- PURPLE with WHITE stripe wire. Fuel control circuit.
- F- RED with BLACK stripe (or TAN with BLACK stripe) wire. Ground circuit for ECM.
Now, don't worry, it's not necessary to check every single wires' signal to test the ignition control module. All right, let's get started!

How This Test Works
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, you'll be able to pinpoint the problem to the ignition control module or the crankshaft position sensor in a no-start condition.
But before you start testing the ignition control module or the crankshaft position sensor, you need to first check and verify that:
- There's NO SPARK present at any of the coil towers.
This is important since if you have spark coming out of all of the ignition coils, the ignition module and the crankshaft position sensor is is good.
If your vehicle is suffering a misfire (where it starts and runs but the engine misses), the article you need is the one about testing the ignition coils, go to: How To Test The Ignition Coil Packs (GM 3.1L, 3.4L).
The test I'm gonna' show you here starts involves the following 3 steps:
- Check that the ignition control module is getting power (12 Volts).
- Power can be checked with a multimeter.
- Check that the ignition control module is getting Ground.
- Ground can be checked with a multimeter.
- Check that the crankshaft position sensor is producing a CKP signal.
- The CKP signal can be checked with a multimeter.
From the results you get from these three simple tests, you'll be able to pinpoint the problem to the ignition control module or the crankshaft position (7X CKP) sensor or completely eliminate these as the cause of the no-start condition.
IMPORTANT: All of the tests are on-car tests, do not remove the coil/module assembly from the vehicle (all of the figures show the coil/module assembly off of the car but this is just for illustration purposes only).
