
The throttle actuator control (TAC) system on your 3.5L V6 equipped Chevrolet Malibu or Pontiac G6 can seem like a very complicated system, but the reality is that this is one of the simplest TAC systems GM has come out with.
In this tutorial, I'll explain the basic operating theory of the TAC system's electronic throttle body.
NOTE: This tutorial applies to the 2007, 2008, 2009 3.5L V6 (N) Chevrolet Malibu and 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010 3.5L V6 (N) Pontiac G6.
Contents of this tutorial at a glance:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Funciona El Cuerpo Del Acelerador Electronico (2007-2009 Chevrolet Malibu Y Pontiac G6) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Funciona El Cuerpo Del Acelerador Electronico (2007-2009 Chevrolet Malibu Y Pontiac G6) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
NOTE: The following tutorials complement this tutorial:
- TAC Circuit Wiring Diagram (2007-2009 3.5L Chevy Malibu And Pontiac G6).
- Electronic Throttle Body Tests (2007-2009 3.5L Chevrolet Malibu And Pontiac G6).
 You can see the electronic throttle body test in action in my YouTube video: How To Test The Electronic Throttle Body. GM Vehicles 2006-2011.
You can see the electronic throttle body test in action in my YouTube video: How To Test The Electronic Throttle Body. GM Vehicles 2006-2011.
How Does The Electronic Throttle Body Work?
The electronic throttle body is made up of 3 basic components:
- Throttle position sensor (TPS) 1.
- Throttle position sensor (TPS) 2.
- Throttle actuator motor.
In a nutshell, when you step on the accelerator pedal, the fuel injection computer commands the throttle actuator motor to open the throttle plate. When you step off of the accelerator pedal, the fuel injection computer commands the throttle actuator motor to close the throttle plate.
On older non-TAC equipped vehicles, when you step on or off the accelerator pedal; a mechanical accelerator cable transmits this motion to the throttle plate. On your TAC equipped vehicle, a mechanical accelerator cable is a thing of the past.
The fuel injection computer controls how much to open the throttle plate by applying a pulse width modulated voltage to the throttle actuator motor. And it also supplies it with Ground.
Both of the throttle position sensors act as feedback sensors to let the computer know how much the throttle plate has opened or closed.
Each of the throttle position sensors get 5 Volts and Ground from the same two wires.
To effectively diagnose the TAC system, on your 3.5L Chevrolet Malibu or 3.5L Pontiac G6, a wiring diagram of the TAC system comes in handy. You can find one here: TAC Circuit Wiring Diagram (2007-2009 3.5L Chevy Malibu And Pontiac G6).
TPS 1 Basic Operating Theory
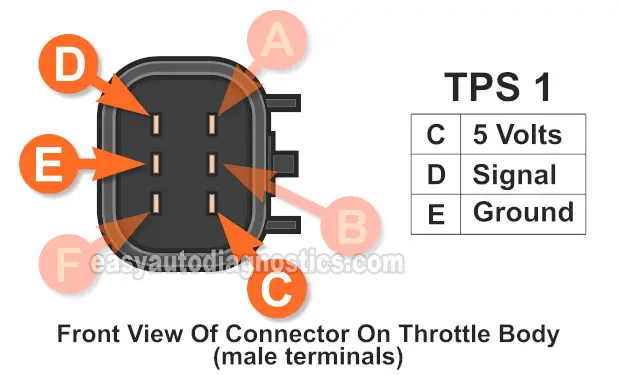
Throttle position sensor (TPS) 1 has three basic circuits and these are:
- 5 Volt circuit.
- Ground circuit.
- TPS 1 Signal circuit.
What this means in plain English is that it receives 5 Volts (power) and Ground from the fuel injection computer to create its throttle position signal.
This throttle position sensor signal is sent directly to your 3.5L Chevy Malibu or Pontiac G6's fuel injection computer.
This throttle position sensor signal is also a feedback input to let the fuel injection computer know that it has opened the throttle plate the corresponding amount of accelerator pedal travel.
One very important thing to note about TPS 1 is that its voltage increases from a low voltage to a high voltage when the throttle plate opens.
Its voltage is around 0.5 to 1.5 Volts DC at idle and increases to about 4.5 Volts at wide open throttle position (WOT).
When throttle position sensor (TPS) 1 fails, the fuel injection computer will light up the check engine light with one of the following trouble codes:
- P0121: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 1 Performance.
- P0122: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 1 Circuit Low Voltage.
- P0123: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 1 Circuit High Voltage.
- P2135: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 1 And Sensor 2 Correlation.
TPS 2 Basic Operating Theory
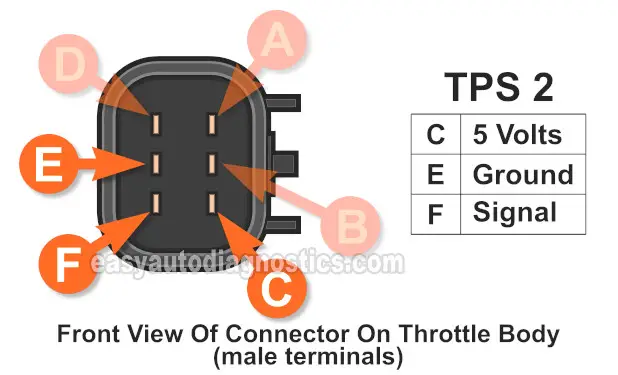
Throttle position sensor (TPS) 2 has three basic circuits and these are:
- 5 Volt circuit.
- Ground circuit.
- TPS 2 Signal circuit.
As mentioned at the beginning of the tutorial, the 5 Volt and Ground circuit are shared by both TPS 1 and TPS 2.
The TPS 2 signal is sent directly to your vehicle's fuel injection computer.
Now, the TPS 2 signal differs from the TPS 1 signal. The TPS 2 signal voltage decreases from a high voltage to a low voltage as the throttle plate is opened.
Its voltage is around 3.5 to 4.5 Volts DC at idle and decreases to about 0.5 Volts at wide open throttle position (WOT).
When throttle position sensor (TPS) 2 fails, the fuel injection computer will light up the check engine light with one of the following trouble codes:
- P0222: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage.
- P0223: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage.
- P2135: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Sensor 1 And Sensor 2 Correlation.

