TEST 2: Making Sure The Fuel Pump Relay Has Power
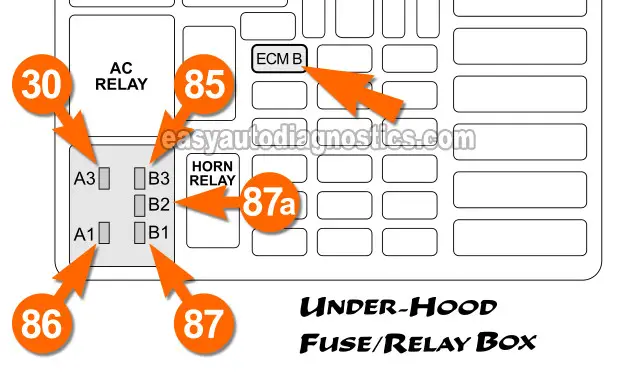
If swapping out the fuel pump relay did not get the fuel pump working, then the next step is to make sure that the fuel pump relay is getting battery power.
The fuel pump relay slot that we're gonna' check for battery power is the one labeled B1 (87) in the illustration above.
Slot B1 gets power from the ECM B 20 Amp mini-fuse located in the same under-hood fuse/relay box. The orange arrow points to it in the illustration above.
We'll do a simple multimeter test to test for this voltage.
IMPORTANT: Don't insert the multimeter test leads into the fuel pump relay female terminal slot, or you'll damage it. Use an appropriate sized tool to probe the slot.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Locate and remove the fuel pump relay from its location in the under-hood fuse and relay box.
- 2
Place your trusty multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Probe the female terminal slot labeled with the B1 (in the illustration above) with the red multimeter test lead.
NOTE: Use an appropriate tool to connect the multimeter test lead to the female terminal slot to avoid damaging the terminal. - 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) post.
- 5
Battery power (10-12 Volts DC) should be present with the key off or on.
Let's analyze your voltage test result:
CASE 1: 10 to 12 Volts are present in the indicated relay terminal slot. This is the correct test result and let's you know the fuel pump relay has power.
The next step is to bypass the fuel pump relay with a jumper wire to see if the fuel pump activates. Go to: TEST 3: Bypassing The Fuel Pump Relay.
CASE 2: 10 to 12 Volts ARE NOT present in the indicated relay terminal slot. The most likely cause of this missing voltage is a blown fuse.
Check that fuse ECM B is not blown. If it's blown, replace it and retest.
TEST 3: Bypassing The Fuel Pump Relay
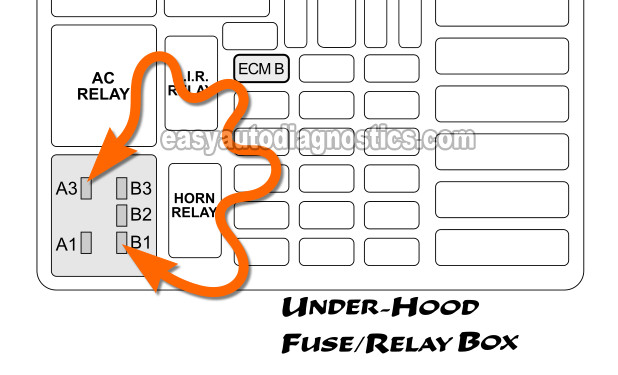
We're gonna' bypass the fuel pump relay and see if the fuel pump activates with a jumper wire.
To get the most accurate test result from this test you should connect a fuel pressure test gauge to the fuel injector rail's Schrader Valve.
NOTE: It's important that you make sure that power is available in slot labeled B1 before doing this test.
IMPORTANT: Make sure your jumper wire terminals are the same thickness as the relay male spade terminals to avoid damaging the female terminal slot. Using anything thicker than the thickness of the relay male spade terminals will permanently damage the fuse/relay box.
Let's get this show on the road:
- 1
Connect the fuel pressure test gauge to the Schrader valve on the fuel injector rail.
- 2
Remove the fuel pump relay from the under-hood fuse and relay box.
- 3
With a jumper wire, jumper slots labeled B1 and A3 of the under-hood fuse box (see illustration above).
IMPORTANT: Use a jumper wire that will not damage the female terminal inside the slot. - 4
The fuel pump should activate when you turn the key ON (but don't crank or start the engine).
The fuel pressure tester should indicate a fuel pressure of 56-62 PSI.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The fuel pump activated and the fuel pressure tester registered the indicated fuel pressure PSI. This is the correct test result and tells you several things:
- The wiring between the underhood fuse box and the fuel pump is OK.
- The fuel pump fuse is OK (not blown).
If the fuel pump doesn't activate with the relay in place, then this test result confirms that it's defective and needs to be replaced.
You can also bench test the fuel pump relay itself: TEST 4: Bench Testing The Fuel Pump Relay.
CASE 2: The fuel pump DID NOT activate and the fuel pressure tester DID NOT register the indicated fuel pressure PSI. This test result could be caused by one of several things:
- The wiring between the underhood fuse box and the fuel pump has a problem.
- The fuel pump fuse is blown.
