TEST 2: Testing The Ignition Coil Control Signal

Now that you have confirmed that the ignition control module (ICM) is receiving 10 to 12 volts, the next critical step is to verify the IC control signal generation.
As previously mentioned, the IC control signal is the signal that activates the ignition coil to initiate spark to the spark plugs.
The IC control signal is transmitted from the ICM to the ignition coil via the white (WHT) wire of the black ignition coil connector.
In the illustration of the ignition coil connectors above, the male terminal marked with the letter C is the one that connects to the WHT wire.
NOTE: Although you may have already verified the presence of the IC control signal, it's important to perform this step again to ensure that no important details have been missed.
IMPORTANT: The ignition coil and the ignition control module must be connected to all of their connectors for this test to work.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Connect the test light's crocodile type connector to the battery positive (+) terminal.
- 2
Connect the metal point of the 12 Volt test light to the white (WHT) wire of the black ignition coil connector.
The WHT wire is labeled with the letter C in the image above.
The WHT wire connects directly to the ignition control module and is the one that delivers the ignition coil activation signal. - 3
Have your helper crank the engine while you observe the 12 Volt test light.
- 4
You'll see one of two things:
1.) The 12 Volt test light flashes ON and OFF.
2.) The 12 Volt test light DOES NOT flash ON and OFF
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The 12 Volt test light flashed ON and OFF. This test result confirms that the ignition control module is creating and delivering an activation signal to the ignition coil.
You can conclude that the ignition coil is bad and needs replacement if you have:
- Confirmed that the ignition coil high tension wire does not spark (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil tower does not spark (TEST 2).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is receiving 10 to 12 Volts (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that the ignition control module is creating and delivering an activation signal to the ignition coil (this test section).
CASE 1: The 12 Volt test light DID NOT flash ON and OFF. This test result tells you that the ignition control module is not activating the ignition coil.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 3: Testing The Pickup Coil Signal.
TEST 3: Testing The Pickup Coil Signal
So far, the result of your previous tests have confirmed the following:
- None of the six spark plug wires are sparking.
- That spark from the ignition coil tower is not present.
- That the ignition coil and ICM are receiving power (TEST 1).
- That the ICM is not generating an IC control signal (TEST 2).
For our final diagnostic test, we'll check the performance of the distributor pickup coil with a multimeter and while the engine is cranking.
This test can be a bit challenging because of the location of the distributor, so to ensure accuracy and safety, I suggest using insulated jumper wires with alligator clips to connect your multimeter test leads to the distributor pickup coil.
NOTE: You'll be probing the female terminals of the pickup coil's connector, so be careful that the test leads you use do not cause any damage to the terminals of the connector or the connector itself.
IMPORTANT: The battery must be fully charged for this test.
CAUTION: You'll need to crank the engine to perform this test. Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Place the multimeter in Volts AC mode.
- 2
Disconnect the pickup coil connector from the ignition control module.
- 3
Connect the black test lead of the multimeter to one of the female terminals of the connector (using an appropriate test lead).
In case you're wondering, it doesn't matter which terminal of the connector you test with the red or black multimeter test leads, since the polarity does not matter. - 4
Connect the red test lead of multimeter to the other female terminal of the pickup coil connector.
- 5
Have an assistant crank the engine while you observe the AC voltage readings on the multimeter.
- 6
As the engine is cranking, the AC voltage readings should fluctuate between 0.3 Volts and 1.8 Volts AC. Oscilloscope users see image below of scope waveform.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered the indicated AC Volts. This is the correct test result and it tells you that the pickup coil is producing its signal.
You can conclude that the ignition control module is bad and needs to be replaced if you have confirmed:
- None of the six spark plug wires are sparking.
- That spark from the ignition coil tower is not present.
- That the ignition coil and ICM are receiving power (TEST 1).
- That the ICM is not generating an IC control signal (TEST 2).
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register the indicated AC Volts (or an analog waveform). Recheck all connections. Try again.
If you still have nothing. The pickup coil is faulty and the cause of the engine's no spark-no-start problem. Replace the pickup coil.
Distributor Pickup Coil Waveform
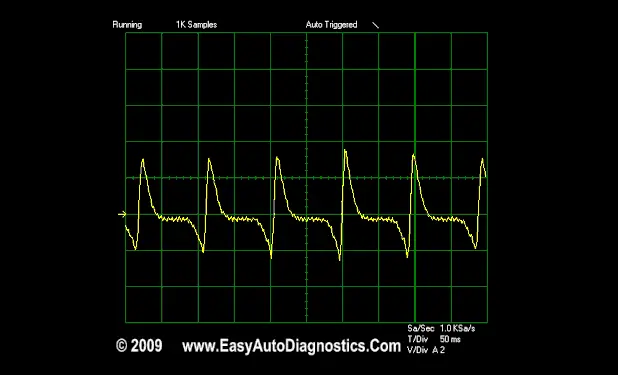
If you have access to an oscilloscope, this is what the pickup coil's waveform should look like.
More 4.3L Chevy S10 Pickup, GMC S15 Pickup, And GMC Sonoma Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 4.3L Chevy S10 pickup, GMC S15 pickup, And GMC Sonoma tutorials here:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1996-2003 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC Sonoma).
- How To Test The EGR Valve (1988-1995 4.3L TBI Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC S15 Pickup, GMC Sonoma).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1988-2003 4.3L Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC S15 Pickup, GMC Sonoma).
- How To Test Engine Compression (1988-2003 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC S15 Pickup, GMC Sonoma).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!




