When a trouble code P0141 lights up the check engine light (CEL) on your 2.5L Dodge Dakota's instrument cluster, it usually means that the rear O2 sensor's heater element is fried.
In most cases replacing the rear O2 sensor will solve the trouble code and life goes on. But sometimes you've got to make sure that the rear O2 sensor is getting power and Ground.
This is where this tutorial is going to help you since I'll explain how to test the rear O2 sensor in a step by step away.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Código P0141 (1996-1997 2.5L Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Código P0141 (1996-1997 2.5L Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Circuit Descriptions Of The Downstream Oxygen Sensor
Testing the rear O2 sensor's heater element involves three basic tests.
First we need to make sure that it's getting power. Second, we need to make sure it's getting Ground. The last test involves testing the internal resistance of the rear O2 sensor's heater element with a multimeter in Ohms mode.
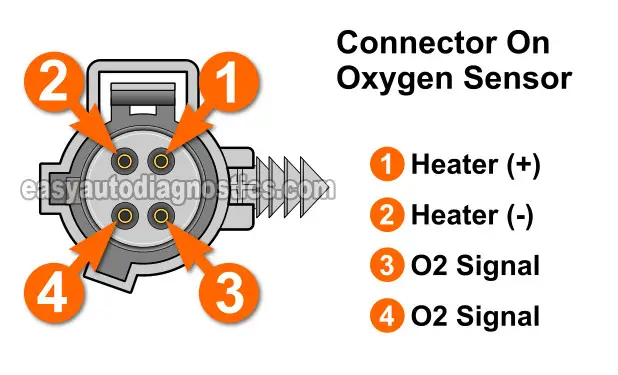
As you have probably already noticed, the rear O2 sensor has 4 wires coming out of the connector. Since we need to know which two wires are the ones that are feeding it with power and Ground, the table below has a brief description of each wire:
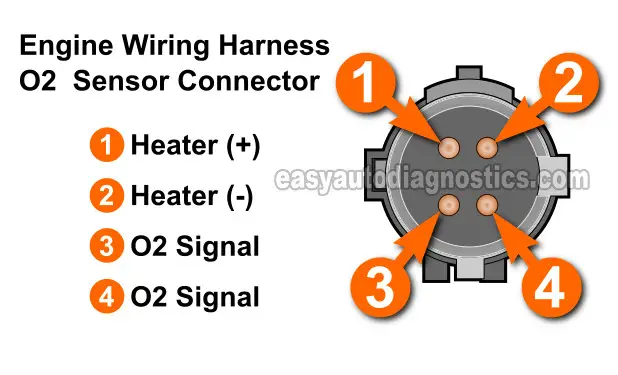
NOTE: You'll notice that I'm using two different illustrations in this tutorial. One is of the connector on the O2 sensor itself. This connector has female terminals. The other illustration is of the engine wiring harness connector (above). This connector has round male terminals.
| Downstream Oxygen Sensor Pinout 1996-1997 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | DK GRN/ORG | Heater (+) |
| 2 | BLK | Heater (-) |
| 3 | BLK/LT BLU | O2 Signal |
| 4 | ORG/BLK | O2 Signal |
TEST 1: Verifying Power And Ground

Making sure the O2 sensor is getting power and Ground involves a simple multimeter voltage test.
The two wires that we are concerned with are the dark green with orange stripe (DK GRN/ORG) and black (BLK) wires of the rear O2 sensors engine wiring harness connector.
The dark green with orange stripe (DK GRN/ORG) wire is one that feeds the sensor's heater element with battery power (12 Volts). The black (BLK) wire is the one that feeds it with Ground.
CAUTION: Perform all O2 sensor tests with a completely cold engine. The O2 sensor gets and stays hot for a long time after engine shut down. So if your Dodge Dakota engine has been running for any amount of time, let it cool down completely before you start. Also, if you raise the vehicle to access the O2 sensor, place it on jack stands.
IMPORTANT: The pinout in the illustration above is of the connector on the oxygen sensor itself. To check for power and Ground, you'll test the two indicated wires of the engine wiring harness sensor connector.
OK, this is what you'll need to do:
- 1
Locate the oxygen sensor and disconnect it from its engine wiring harness connector.
- 2
Set your multimeter to Volts DC mode and turn the key ON but don't crank or start the engine (this will power up the O2 sensor's engine wiring harness connector).
- 3
Make sure that the DK GRN/ORG wire is feeding battery power.
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the DK GRN/ORG wire and connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery Ground (-) terminal.
Your multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts DC. - 4
Make sure that the BLK wire is feeding Ground.
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the BLK wire and connect the red multimeter test lead to the battery positive (+) terminal.
Your multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts DC. This is the correct and expected test result.
Now that we know that the rear O2 sensor's heater element is getting power and Ground, the next step is to check the heater's resistance with a multimeter. For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing The Heater Element's Resistance.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts DC. This is usually the result of a problem in the wiring between the O2 sensor and the ASD relay (since the ASD relay is the one that supplies these 12 Volts to the O2 sensor).
CASE 3: The heater element is not getting Ground. The most likely cause of this missing Ground is an open in the wiring between the O2 sensor's engine wiring harness connector and its Ground point.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial to test for this missing Ground, your next step is to do a continuity test between the O2 sensor Ground wire and Chassis Ground.
