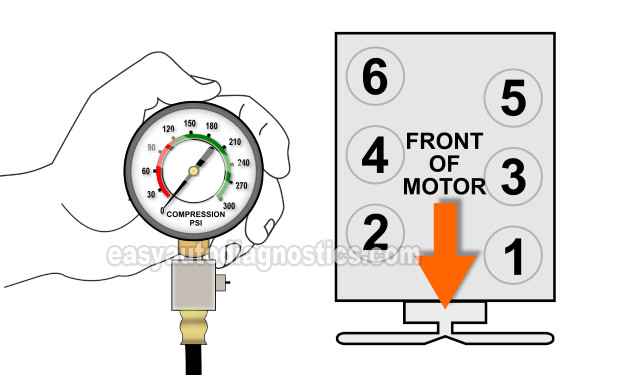
In this tutorial, I'm going to show you how to test the engine compression on the 3.9L V6 engine of the Dodge Dakota and Dodge Durango.
I'm also going to explain how to interpret your test results so that you can find out if your engine has an engine compression problem (or not).
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Compresión Del Motor (1993-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Compresión Del Motor (1993-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota: 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003.
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Durango: 1998, 1999.
Symptoms Of Low Or No Engine Cylinder Compression
Engine compression problems will cause 1 of 2 problems on your 3.9L Dodge Dakota: Either the engine is not going to start or the engine will start and run but it will suffer a misfire or rough idle condition.
On the 1996-2003 3.9L Dodge Durango (that is OBD II equipped) you're gonna see one or more of the following misfire trouble codes:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder #6 Misfire.
Besides a cylinder misfire condition (or a rough idle condition), your 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota (Durango) is gonna' suffer from bad gas mileage. You're also gonna' notice a heavier exhaust smell coming out of its tailpipe. Also, since the engine is not running optimally, it's not gonna' be as peppy as it was once.
Important Tips And Suggestions
TIP 1: If the engine in your 3.9L Dodge Dakota (Durango) has been running for any length of time, let it cool down completely before you remove the spark plugs. Removing the spark plugs from a hot engine can result in damage to the spark plug hole threads.
One method that I have used to cool the engine down in a matter of 15-20 minutes is placing a box fan on top of it to cool it down.
TIP 2: The engine has to be cranked to test the compression, for this reason take all necessary safety precautions while working around the engine when it's being cranked.
TIP 3: Have your helper wait outside of the vehicle till you're done setting up the test. This way you'll avoid having your helper accidentally crank the engine while you're installing the compression tester.
Which Compression Tester Should I Buy?
There are lot of engine compression testers to choose from and many places to buy them. I'm gonna' make some recommendations to you:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
TEST 1: Finding The Dead Cylinders
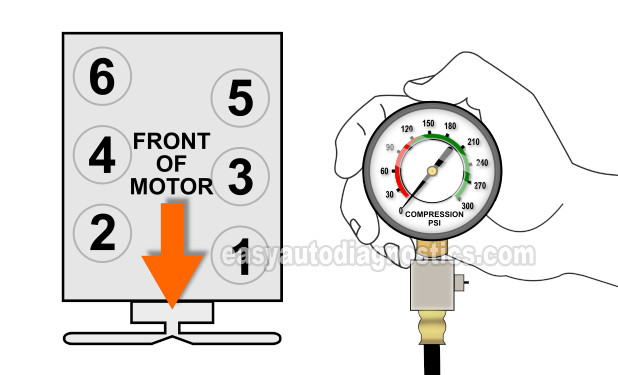
We're gonna' start off by testing the compression of all 6 cylinders.
Once you get your compression test results, I'll help you interpret them in the section: Interpreting The Compression Test Results.
The illustration above will help you to identify the cylinders that you'll be testing on your 3.9L Dodge Dakota.
If you don't have a compression tester you can run down to your local auto parts store and buy or borrow one from them. If you're interested in buying one, then take a look at my recommendations here: Which Compression Tester Should I Buy?
NOTE: Disable the ignition system before doing a compression test. You can easily disable the ignition system by disconnecting the ignition coil from its electrical connector.
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Disable the ignition system by disconnecting the ignition coil from its electrical connector. This will prevent the ignition coil from sparking during the test.
- 2
Remove the spark plugs. Remember, the engine can not be hot!
When removing the spark plugs, be careful not to drop any of them on the floor, or you run the risk of having the spark plug's porcelain insulator crack and then you'll have a misfire on your hands. - 3
Thread the engine compression gauge into the spark plug hole for the number 1 engine cylinder. Hand tighten the compression gauge only! Do not use any type of tool to get it tight.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine till the needle on the compression gauge stops climbing.
- 5
Record on paper the value at which the needle stopped and the number of the engine cylinder on a piece of paper. Release the pressure on the gauge and repeat this step one more time.
- 6
Repeat steps 3 through 5 on the remaining cylinders.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: All six cylinders had 0 PSI. This test result tells you that the engine has an internal mechanical problem.
The most common cause of this condition is a broken timing belt.
Your next steps should be to check the condition of the timing belt. I would also recommend that you check for a blown head gasket.
CASE 2: One or more cylinders had a low compression value compared to the others. This could be normal or it could be causing a problem.
To find out the next step is do some math and see if the low compression value is lower by more than 15% of the highest compression value you got. To find a detailed explanation of this calculation go to: Interpreting The Compression Test Results.
CASE 3: All six compression values were similar and above 120 PSI. This lets you know that a compression problem is not behind the no-start or misfire problem you're trying to troubleshoot.
Interpreting The Compression Test Results
I'm pretty sure that some of the compression values you got in TEST 1 were low compared to the majority of the cylinders.
This is especially common in high-mileage engine or engines that haven't seen a whole lot of maintenance. In some cases these low compression values don't cause a problem.
It's only when these low compression values vary more than 15% of the highest value that you're gonna' have a problem.
The cool thing is that we can find out easily by doing some math. So that I can better explain this 15% thing, I'll use the following compression test results:
- Cylinder #1 175 PSI.
- Cylinder #2 165 PSI.
- Cylinder #3 160 PSI.
- Cylinder #4 120 PSI.
- Cylinder #5 150 PSI.
- Cylinder #6 150 PSI.
The next step is to do the following math:
- Multiply .15 (15%) by the highest value: 175 x 0.15. This gives us 26.25, but we'll round it out to 26.
- Next, we subtract 26 from 175: 175 - 26 = 144.
- So now we know that the lowest possible compression value is: 144 PSI.
This means that cylinder #4, which has a compression value of 120 PSI, is the one causing the misfire because it's below the 144 PSI minimum.
Once we've found the 'dead' cylinder, the next step is to find out what's causing the low compression value. For this step, go to: TEST 2: Wet Engine Compression Test.
TEST 2: Wet Engine Compression Test
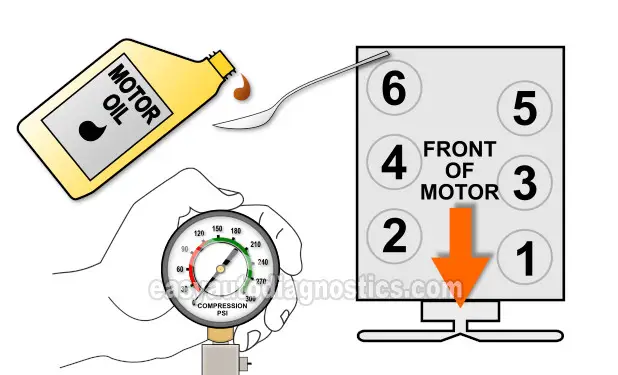
What usually causes a dead cylinder to have a low or 0 PSI compression value is one of two things: Either that cylinder's piston rings are worn out or its cylinder head valves are worn out or damaged.
We can easily find out by doing a 'wet' compression test on the cylinder or cylinders with low compression.
In a nutshell, the wet compression test simply involves adding about two tablespoons of engine oil to the cylinder with low compression and then testing its compression again.
If that dead cylinder's compression value increases, then you can conclude that its piston rings are worn out and causing the problem.
If the dead cylinder's compression value does not increase, then you can conclude that its cylinder head valves have a problem and are behind the low or 0 PSI compression value.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Add 1 or 2 tablespoon of engine oil in the cylinder you need to retest. I suggest using a small and long funnel so that the oil will reach the inside of the cylinder.
- 2
Install the compression gauge on the cylinder you just added oil to.
- 3
Have your helper crank the engine till the needle stops climbing on the compression gauge.
- 4
You'll see one of two results:
1.) The needle will climb higher than the previous compression number you recorded for this specific cylinder.
2.) The needle will not move at all or stay at the same number you recorded earlier.
What ever value your compression tester reads, write it down again. - 5
Repeat steps 1 thru' 4 on any other cylinder you need to check.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The compression value of the cylinder you added oil to increased. This test result tells you that the low or near 0 PSI compression value is due to worn out piston rings of that specific cylinder.
CASE 2: The compression value of the cylinder you added oil to DID NOT increase. This test result confirms that the cylinder head valves of that cylinder are worn-out or damaged.
More 3.9L Dodge Dakota Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 3.9L Chrysler and Dodge tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- Testing The Ignition System (1998-2003 3.9L Dodge Dakota).
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (2000-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota).
- How To Test The TPS Sensor (2000-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1993-1999 3.9L Dodge Dakota).
- Engine Management Sensor Circuit Diagram (1994-1995 3.9L V6 Dodge Dakota).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!





