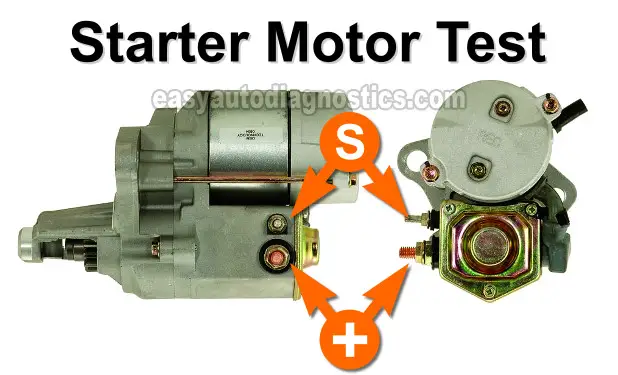
This tutorial will help you to test the starter motor on your 1997, 1998, or 1999 V8 Dodge Dakota or Durango.
The starter motor tests are explained in a step-by-step way. You'll be able to find out if it's defective or not.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Motor De Arranque (1997-1999 V8 Dakota, Durango) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Motor De Arranque (1997-1999 V8 Dakota, Durango) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 5.2L, 5.9L V8 Dodge Dakota: 1997, 1998, 1999.
- 5.2L, 5.9L V8 Dodge Durango: 1997, 1998, 1999.
Important Safety Tips And Precautions
TIP 1: The starter motor test in this tutorial is an on-car test. You don't have to remove the starter motor to test it.
If you have removed it, you can bench-test it and the following tutorial will help you: Bench Testing The Starter Motor.
TIP 2: The battery, in your Dodge Dakota (Durango) must be fully charged to get a correct test result. Also, the battery cable terminals and battery posts must be clean and corrosion free.
Testing your V8 Dakota (Durango)'s starter motor with a low battery or corrosion on the battery cables/terminals will lead to false test results that'll have you replacing good parts that don't need replacement.
TIP 3: If your vehicle has a standard transmission, make sure that it's out of gear and in neutral, and that the parking brake is activated/on.
TIP 4: You may need to raise your vehicle, with a jack, to access the starter motor. Don't trust the jack to keep your pick up or SUV up in the air, use jack stands!
Symptoms Of A Bad Starter Motor
When the starter motor goes bad on your V8 Dakota (Durango), you'll see one of the following symptoms:
- When you turn the key to start your the engine, nothing happens.
- Jump starting the engine doesn't make it crank over.
- The battery has been charged and/or replaced and still your Dakota (Durango) does not crank.
- When you turn the key to crank the engine, all you hear is a small knock and nothing else.
As you can see, the theme that runs thru' most of the symptoms of a bad starter motor is that the engine will not crank over when you try to start it.
Tools Needed To Test The Starter Motor
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
You don't need expensive test equipment to test the starter motor on your V8 equipped Dakota (Durango). Here are my recommendations:
- Remote starter switch.
- If you'd like to see what a remote starter switch looks like, you can follow this link: Innova 3630 Remote Starter Switch (Amazon affiliate link).
- You can either buy this tool online or you can buy it at your local auto parts store (AutoZone, O'Reilly Auto Parts, etc.).
- Multimeter or a 12 Volt automotive test light.
- If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours, check out my recommendation here: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter (Amazon affiliate link).
- A wire piercing probe.
- This tool is not an 'absolute must-have tool' but I can tell you from experience that it makes it a whole lot easier to probe the S terminal wire for the start signal.
- If you'd like to see what this tool looks like, you find out more about it here: Wire Piercing Probe Tool Review (Power Probe PWPPPPP01).
- A helper.
As you can see you don't need anything expensive. OK, let's turn the page and get starter with the first starter motor test.
TEST 1: Applying 12 Volts To The Starter Motor S Terminal
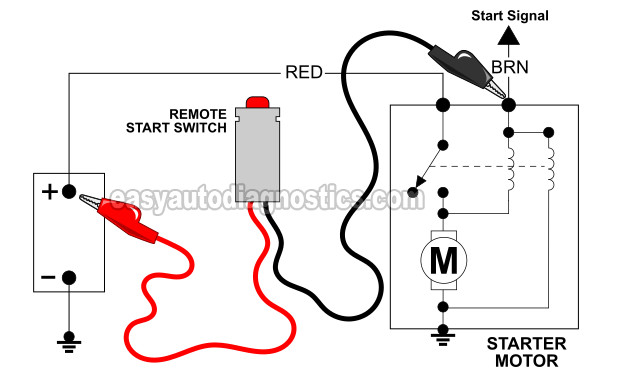
In this test section, we're gonna' manually apply 12 Volts to the starter motor's S terminal.
Once the S terminal gets battery power, the starter motor should engage and crank the engine. If the starter motor is defective, it will not crank the engine.
The best and safest way to perform this test is with a remote start switch.
IMPORTANT: Before you perform this test remove the key from the ignition switch to prevent the engine from accidentally starting.
IMPORTANT: Place your Dakota or Durango on jack stands if you raise it to access the starter motor!
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal.
You'll reconnect it back in one of the following steps, for now, it's a safety precaution as you set up the test. - 2
Attach one of the alligator-type terminals of the remote starter switch to the S terminal of the starter motor.
- 3
Reconnect the battery negative (-) cable to the battery negative (-) post.
NOTE: Make sure that the battery cables and posts are clean. - 4
Connect the remaining alligator-type terminal of the remote starter switch to the battery positive (+) post.
IMPORTANT: If your Dakota (Durango) has a standard transmission, make sure it's out of gear before you make this last connection. - 5
Activate the starter motor with your remote starter switch. As you apply these 12 Volts (to the S terminal of the starter motor), you'll get one of two results:
1) The starter will activate and will turn over the engine -OR- 2) The starter motor won't do a thing.
Let's examine your test result:
CASE 1: The starter motor cranked the engine. This test result lets you know that your Dakota (Durango)'s starter motor is OK and functioning.
If the starter motor is NOT cranking the engine when you turn the key to start it, then it's probably not receiving the activation signal from the ignition switch.
To further test this, go to the next test: TEST 2: Verifying The Start Signal.
CASE 2: The starter motor DID NOT crank the engine. This usually means that your Dakota (Durango)'s starter motor is bad and needs to be rebuilt or replaced.
I suggest 2 more tests and these are make sure that the starter motor is getting its 12 Volt signal signal and to test the battery cable (that attaches to the starter motor solenoid) for corrosion. This can be accomplished very easily with a voltage drop test.
- Go to: TEST 2: Verifying The Start Signal.
- Go to: TEST 3: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery (+) Cable.
If the above two tests confirm that the start signal IS present and there's no voltage drop on the battery cable (feeding battery power to the starter motor), then you can confidently conclude your Dakota or Durango's starter motor is bad and needs to be replaced.
TEST 2: Verifying The Start Signal
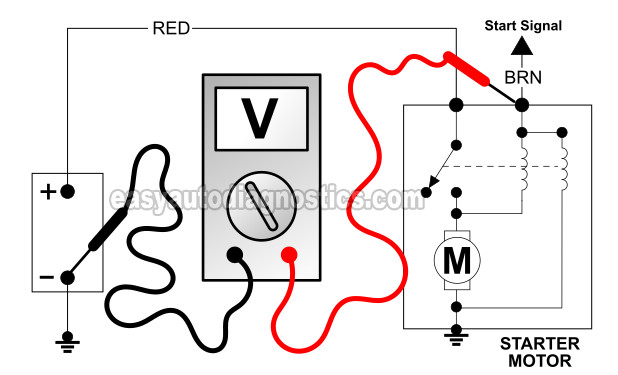
If in TEST 1 the starter motor did crank up the engine (when you manually applied power to it), then the next step is to see if the Start signal is present when you turn the key to start the engine.
You can use a 12 Volt test light for this test or multimeter (the test instructions below call for a multimeter).
OK, let's get started:
- 1
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the S terminal of the starter motor.
- 2
Attach the black multimeter test lead to a clean and rust-free spot on the engine or on the vehicle frame.
I recommend that you use a battery jump start cable to Ground the black multimeter test lead directly to the battery negative (-) terminal. - 3
Have your helper crank the engine from inside your Dodge Dakota (Durango).
The engine won't turn over, but the idea is to verify that the starter motor's internal solenoid is getting the 12 Volt start signal from the ignition switch (or not). - 4
Your multimeter is going to register one of two results: Either 9 - 12 Volts DC or no voltage at all.
Let's examine your test result:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This test result lets you know the starter's internal solenoid is receiving the start signal.
This means that we can forget about the safety neutral switch and the ignition switch being bad. OK, now the next test is to do a very easy and simple voltage drop test. Go to: TEST 3: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery (+) Cable.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts. This result exonerates the starter motor. Your starter motor is not bad.
Here's the reason why: Without this 10 to 12 Volt crank signal, your Dakota (Durango)'s starter motor will not crank the engine. Now, although it's beyond the scope of this article to test the neutral safety switch or the ignition switch, you have eliminated the starter motor and this means saving money by not buying a part your vehicle does not need.
TEST 3: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery (+) Cable
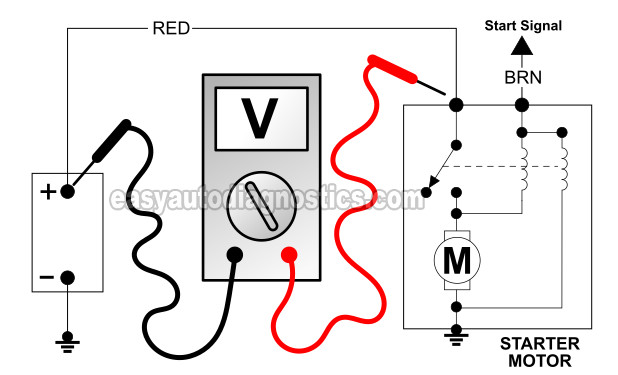
In this test section, we're gonna' use the multimeter to make sure that the starter motor is getting the battery's full power.
This involves doing a simple voltage drop test with the multimeter in Volts mode.
Don't worry, this is a very easy test and I'll explain it all in a step-by-step way.
Why a voltage drop test? Because it'll let us know if hidden corrosion is keeping your Dakota or Durango's starter motor from cranking the engine.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Attach the black multimeter test lead to the center of the positive battery terminal.
If the positive battery post isn't clean, clean a spot right on the top of it. It's important that the multimeter lead make contact right in the center of the positive battery post. - 3
With the red multimeter test lead, touch the center of the stud to which the big battery cable attaches to. The red multimeter test lead must remain touching the center of the stud throughout the next step.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine even though the starter motor isn't cranking the engine.
This is important, since a voltage drop test has to be done while the component in question is working (or trying to work). - 5
If all is good (no voltage drop), your multimeter will register 0 Volts (.5 Volts is still 0 Volts).
If there's a voltage drop (which is bad), your multimeter will register voltage (usually above 7 Volts DC.)
Let's take a look at what your results mean:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered 0 Volts (no voltage drop). This result indicates that the starter motor is receiving all of the battery voltage and amperage it needs to crank the vehicle.
You can conclude your Dakota or Durango's starter motor is defective if you have:
- Confirmed that the starter motor doesn't work when you apply power to the S terminal wire of the starter motor (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the starter motor is receiving the crank signal (TEST 2).
- In this test step, you have confirmed that no voltage drop exists on the battery positive cable.
Replacing the starter motor should solve your no-crank condition.
I'm going to make two more recommendations to you:
- Before removing the starter motor, manually turn the engine using a 1/2 ratchet and the appropriate socket. This is to make sure that the engine or the A/C compressor have not locked up and causing the no-crank condition.
- Bench test the starter motor after removing it. This is a super easy test to do and this tutorial will help: Bench Testing The Starter Motor.
CASE 2: Your multimeter registered 5 Volts or more. This result tells you that a voltage drop does exist and that the battery's full power is not reaching the starter motor.
The good news is that this can easily be corrected, since a voltage drop is always caused by some sort of corrosion issue on the battery positive cable or terminals or the battery positive (+) post.
The solution is to thoroughly clean the battery positive (+) post and the battery positive (+) terminal (both the end that attaches to the battery positive (+) post and the end the connects to the starter motor's battery (+) cable stud.
After cleaning, try cranking the engine. If it cranks and starts, no further testing is required.

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


