TEST 2: Making Sure The MAP Sensor Has 5 Volts
If you're reading this, then your test result in TEST 1 indicates that your MAP sensor is stuck producing a single voltage value as you apply/release vacuum to it.
To tie up any loose ends, it's important to make sure that the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is getting 5 Volts from your Dodge Dakota's fuel injection computer.
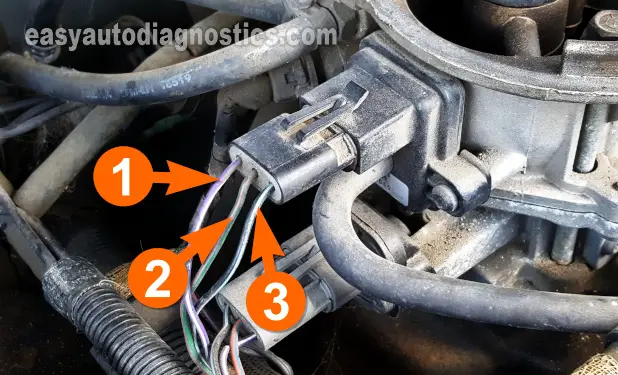
The wire that supplies these 5 Volts to the MAP sensor is the violet with white stripe (VIO/WHT) wire of the 3-wire connector.
This wire is identified with the number 1 in the photo above.
If the MAP sensor is getting 5 Volts, then the next step is to make sure it's getting Ground (in TEST 3).
Let's get testing:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Disconnect the MAP sensor from its electrical connector.
- 3
Turn the key the ON position but don't start the engine.
- 4
Connect the red multimeter test lead (using the appropriate tool) to the VIO/WHT wire.
This is the wire labeled with the number 1 in the photo above. - 5
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the negative (-) battery terminal.
- 6
Your multimeter should read 4.5 to 5 Volts DC.
Let's analyze your test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter confirms that 5 Volts are present in the VIO/WHT wire. This is the correct test result.
Now that you have confirmed that your Dodge Dakota's MAP sensor is getting 5 Volts, the next step is to make sure it's getting Ground. Go to: TEST 3: Making Sure The MAP Sensor Has Ground.
CASE 2: The multimeter confirms that 5 Volts ARE NOT present in the VIO/WHT wire. Without these 5 Volts your Dodge Dakota's MAP sensor will not function.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial to troubleshoot these missing 5 Volts, the most likely cause is an open-circuit problem in the VIO/WHT wire between the MAP sensor's connector and the fuel injection computer's connector.
TEST 3: Making Sure The MAP Sensor Has Ground

By this point your tests have confirmed that:
- The MAP sensor is not creating a decreasing voltage signal as vacuum is applied to it.
- The MAP sensor is getting 5 Volts on the VIO/WHT wire.
For the last test we're gonna' make sure that the black with light blue stripe (BLK/LT BLU) wire is providing Ground to your 5.2L V8 Dodge Dakota's MAP sensor.
In the photo above, the black with light blue stripe (BLK/LT BLU) wire is labeled with the number 3.
NOTE: Ground is provided by the fuel injection computer of your 5.2L V8 Dodge Dakota. So be careful and do not apply battery power (12 Volts DC) to the Ground wire or you'll fry the computer. The voltage test I'm describing below (to test for Ground) is a safe way of verifying the presence of this Ground.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Disconnect the MAP sensor from its electrical connector.
- 3
Turn the key the ON position but don't start the engine.
- 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead (using the appropriate tool) to the BLK/LT BLU wire.
- 5
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the positive (+) battery terminal.
- 6
Your multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's analyze your test results:
CASE 1: Ground is present in the BLK/LT BLU wire. This is the correct test result.
The MAP sensor is defective and needs to be replaced if you have:
- Confirmed that its MAP voltage signal does not decrease/increase as you apply/release vacuum to the MAP sensor (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the VIO/WHT wire is supplying 5 Volts DC (TEST 2).
- Confirmed that the BLK/LT BLU wire is supplying Ground (this test).
Check my MAP sensor recommendations here: Where To Buy The MAP Sensor And Save.
CASE 2: Ground is not present. Without Ground the MAP sensor will not function.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial to troubleshoot this missing Ground, the most likely cause is an open-circuit problem in the BLK/LT BLU wire between the MAP sensor's connector and the fuel injection computer's connector.
Where To Buy The MAP Sensor And Save
The 1990-1991 5.2L V8 Dodge Dakota's MAP sensor isn't an expensive engine management component. The following links will help you to comparison shop and hopefully save you a few bucks on its purchase:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
NOTE: The above manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor fits the following vehicles: 1990 and 1991 5.2L V8 Dodge Dakota.
More 5.2L Dodge Dakota Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 5.2L Dodge Dakota tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- Blown Head Gasket Tests (1997-1999 V8 Dodge Dakota, Durango).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1997-1999 V8 Dodge Dakota, Durango).
- How To Test The Crankshaft Position Sensor (1997-1999 V8 Dakota, Durango).
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (1997-1999 V8 Dakota, Durango).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!



