Testing the Ford ignition coil packs on the 1.9L and 2.0L Ford, Mercury and Mazda equipped cars is pretty easy. This article will walk you thru' the whole diagnostic/troubleshooting process to find out what's causing your car to misfire.
This article covers the two incarnations of the Ford coil pack for four cylinder engines. One is the early type and the other is the late type design. Although they are not interchangeable (since their connectors are different), they are tested in the same way. To see examples of the two styles, go to the section: Circuit Descriptions Of The Ford Coil Pack Connector.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Ford Coil Pack.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
- Circuit Descriptions Of The Ford Coil Pack Connector.
- Basic Operating Theory Of The Ford Coil Pack.
- Precautions, Do's And Don'ts.
- TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wire.
- TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
- TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
- TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit.
- TEST 5: Switching Signal For Cylinders 1 And 4.
- TEST 6: Switching Signal For Cylinders 2 And 3.
- TEST 7: Other Things That Can Cause A Misfire.
- Real Life Case Studies From easyautodiagnostics.com Readers.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Bobina De Encendido DIS (Ford 1.9L, 2.0L) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Bobina De Encendido DIS (Ford 1.9L, 2.0L) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Symptoms Of A Bad Ford Coil Pack
When the ignition coil pack or the spark plug wires are bad, your Ford (or Mercury, or Mazda) vehicle will display one or more of the following symptoms:
- The car idles rough and wants to stall (die).
- When you accelerate the car, it has no power.
- Really bad gas mileage.
- The vehicle will not start.
- The car will not run on all cylinders.
- Misfire codes that are lighting up the check engine light on your instrument cluster.
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304.
- Rotten egg smell coming out of the tail-pipe.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
To successfully use this information to diagnose and troubleshoot your Ford (Mercury or Mazda) four banger, you need a few specific tools. Don't worry, none of this stuff is expensive, here's the list:
- A 12 Volt test light.
- A LED light.
- To see what this tool looks like, click here: Abe's LED Light.
- An HEI spark tester
- This tool is a must have (don't have an HEI spark tester? Need to buy one? You can buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester).
- Battery jump start cables.
- Someone to help you crank the car.
To troubleshoot and diagnose a bad coil pack on your Ford (or Mazda) car, an HEI spark tester is a must have tool. Using the wrong tool or method will have you chasing a wrong diagnostic test conclusion and effectively wasting your time and money.
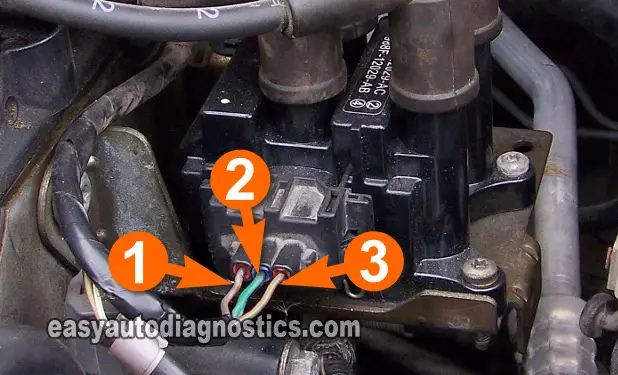
Circuit Descriptions Of The Ford Coil Pack Connector
The Ford coil pack connector has three wires coming out of it. No matter what the style of coil pack or the style of connector that connects to it, the circuit descriptions are the same.
- Circuit labeled 1:
- Switching signal circuit for spark plugs 1 and 4.
- Circuit labeled 2:
- Power (12 Volts) circuit
- Circuit labeled 3:
- Switching signal circuit for spark plugs 2 and 3.
You've probably noticed that there's no mention of the color of the wires of the three wires coming out of the connector, well the color is not important (to take advantage of the info in this article) as long as you're able to correctly identify the circuit by its number in the photos supplied.
Basic Operating Theory Of The Ford Coil Pack
The PCM (Powertrain Control Module=Fuel Injection Computer) is the one that controls the whole show in this type of ignition system since the 'Ignition Control Module' function is handled by the PCM itself. So, in a nutshell, here's what happens when you turn the key to crank and start the car:
- The engine starts to crank, inducing the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to start producing its CKP signal.
- The CKP signal, upon being received by the PCM along with other necessary sensor information, starts to do its little song and dance and sends back two different Switching signals (thru' separate circuits) to the ignition coil pack.
- The coil pack is made up of two separate ignition coils. Each ignition coil within the coil pack has two towers that feed spark to two cylinders at the same time.
- The term Switching signal describes the PCM's action of switching the Primary Current (12 Volts), flowing thru' each ignition coil within the coil pack, ON and OFF by interrupting their Ground path. It's this signal that makes the ignition coils fire spark.
- Each ignition coil (that make up the coil pack) get their own switching signal from the PCM.
- As each individual ignition coil, within the ignition coil pack, get their Switching signal, they then fire spark to two different cylinders at the exact same time (in what's known as the Waste Spark method).
- One ignition coil within the coil pack fires spark to cylinders 1 and 4.
- The other ignition coil that makes up the other part of the coil pack fires cylinders 2 and 3.
You don't need to memorize any of this since this article will take you step by step thru' the whole testing and troubleshooting process so that you can replace the right component, saving time and money in the process.
Precautions, Do's And Don'ts
Most of the testing that you'll be doing is with the engine cranking, so take all necessary safety precautions to keep your fingers, hands and entire self safe. Here are a few other tips and suggestions:
- Do not use a regular spark plug instead of a spark tester to test for spark.
- Do not remove the spark plug wire from the spark plug or the ignition coil while the engine is cranking to test for spark.
- Start your diagnostic from TEST 1, do not skip around from test to test unless instructed to do so by the TEST you are currently on.
- Do not use a test light where an LED light is called for.
- Once again, use the recommended/indicated tools for all of your tests.
TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wire

Whether you know which cylinder is the one that is misfiring or not, I recommend that you test all four cylinders for spark. As mentioned before, the successful outcome of your trouble-shooting/diagnostic lies in the usage of a spark tester.
The following test steps assume that you're gonna' start by testing from the #1 cylinder:
- 1
Remove the spark plug wire (high tension cable) from the spark plug.
- 2
Attach the a spark tester to high tension wire.
Don't have an HEI spark tester? Need to buy one? You can buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester. - 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal with a battery jump start cable as shown in the photo above.
- 4
Have your helper crank the vehicle as you stand at a safe distance from the engine.
The vehicle may or may start, either way be careful. - 5
As the vehicle cranks or starts, observe the spark tester.
- 6
You're gonna' get one of two results: spark or NO spark.
- 7
Now repeat this test on the other cylinders.
IMPORTANT: Read the following options carefully to interpret your NO SPARK result or results. Remember that some cylinders get spark from the same ignition coil within the coil pack (since the coil pack is made up of two individual ignition coils that have two towers each). So if you get a NO SPARK result from two spark plug wires, you need to verify if they're from paired cylinders 1 and 4 or paired cylinders 2 and 3 or from unpaired cylinders (example of unpaired cylinders would be: cylinders 1 and 3, or 2 and 4, or 1 and 2).
CASE 1: You got spark from all four spark plug wires. This indicates that the ignition coils and spark plug wires are OK. The cause of your misfire condition is not due to a bad ignition coil. Go to: TEST 7: Other Things That Can Cause A Misfire to see further tips and suggestions.
CASE 2: You got NO spark from only one spark plug wire. The next step is to check for spark directly on the coil pack tower that feeds that spark plug wire with spark. Go to: TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 3: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires that connect to spark plugs for paired cylinders 1 and 4 or paired cylinders 2 and 3. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 4: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires that DO NOT connect to paired cylinders. The next step is to test each coil pack tower directly for spark one at a time.
For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 5: You got NO spark from none of the spark plug wires. This usually indicates that power is missing from the power circuit or that the crankshaft position sensor is bad.
To find out, go to: TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit.