TEST 3: Voltage Drop Testing The Battery (+) Cable
If you've reached this point, you have confirmed that:
- The battery is fully charged.
- The starter motor is getting a 'start' signal (TEST 2) when you turn the key to crank the engine but the starter motor does not crank your Ford Mustang's engine.
In this test, we're gonna' make sure that the starter motor is receiving the full amount of current it needs from the battery.
In some cases the starter motor, although in perfect working condition, does not crank the engine because it does not receive the full amount of current that the battery provides.
This is usually due to some sort of hidden corrosion on the battery cable that connects the starter motor to the battery.
By doing a simple multimeter voltage drop test, you can find out if this is the case.
Let's get testing:
- 1
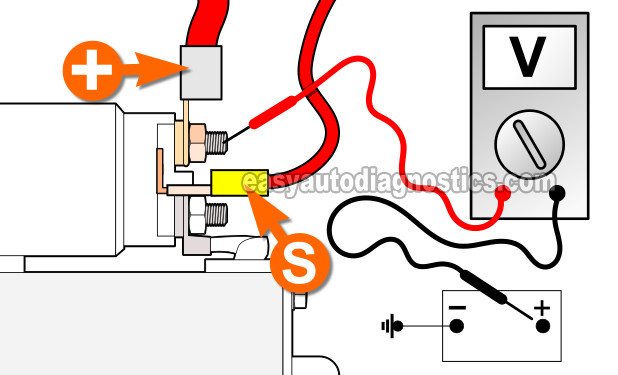
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Attach the black multimeter test lead to the center of the positive (+) battery terminal.
If the positive battery post isn't clean, clean a spot right on the top of it. It's important that the multimeter lead make contact right in the center of the positive battery post. - 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the center of the stud to which the big battery cable attaches to on the starter solenoid.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine even though the starter motor isn't cranking the engine.
This is important, since a voltage drop test has to be done while the component in question is working (or trying to work). - 5
If all is good (no voltage drop), your multimeter will register 0 Volts (.5 Volts is still 0 Volts).
If there's a voltage drop (which is bad), your multimeter will register voltage (usually above 7 Volts DC.)
Let's take a look at what your results mean:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered 0 Volts (no voltage drop). This is the correct test result and tells you that the starter motor is receiving all of the battery voltage and amperage it needs to crank the your Ford Mustang's engine.
You can conclude your Ford Mustang's starter motor is defective if you have:
- Confirmed that the starter motor doesn't work when you apply power to the S terminal wire of the starter motor (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the starter motor is receiving the crank signal (TEST 2).
- In this test step, you have confirmed that no voltage drop exists on the battery positive cable.
Replacing the starter motor should solve your no-crank condition.
I'm going to make two more recommendations to you:
- Before removing the starter motor, manually turn the engine using a 1/2 ratchet and the appropriate socket. This is to make sure that the engine or the A/C compressor have not locked up and causing the no-crank condition.
- Bench test the starter motor after removing it. This is a super easy test to do and this tutorial will help: Bench Testing The Starter Motor.
CASE 2: Your multimeter registered 5 Volts or more. This result tells you that a voltage drop does exist and that the battery's full power is not reaching the starter motor.
The good news is that this can easily be corrected, since a voltage drop is always caused by some sort of corrosion issue on the battery positive cable or terminals or the battery positive post.
The solution is to thoroughly clean the battery positive post and the battery positive (+) terminal (both the end that attaches to the battery positive post and the end the connects to the starter motor's battery (+) cable stud.
After cleaning, try cranking the engine. If it cranks and starts, no further testing is required.
More 3.8L Ford Mustang Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 3.8L Ford Mustang tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (1994-1995 3.8L Ford Mustang).
- Constant Control Relay Module (CCRM) Circuits (1996-1997 3.8L Ford Mustang).
- How To Test The TPS With A Multimeter (1994-1995 3.8L Mustang).
- How To Test The Radiator Fan Motor (1997-1999 3.8L Ford Mustang).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

