TEST 2: Coolant Shooting Out From Open Radiator

The second most common consequence of a blown head gasket is combustion gases entering the engine's cooling system.
We can easily confirm if this is happening by removing the radiator cap (from the radiator) and cranking the engine.
If the coolant is forcibly shot out of the radiator, you can conclude that the head gasket has failed.
The correct and expected test result is that the coolant (in the radiator) remains undisturbed while you or your helper crank the engine.
IMPORTANT: Do not remove the radiator cap from the radiator when the engine is hot or has been running any length of time. Allow the engine to cool completely before removing the radiator cap.
Let's get started:
- 1
Remove the radiator cap.
- 2
Check the coolant level in the radiator.
Add water or coolant if necessary. - 3
Have your helper crank the engine while you stand at a safe distance from the open radiator.
- 4
You'll see one of two results:
1.) The water or coolant inside the radiator will shoot out of the open radiator.
2.) The coolant remained undisturbed. In other words, cranking the engine will have no effect on the level of the water or coolant in the radiator.
Let's examine your test result:
CASE 1: The coolant shot out from the radiator as you cranked the engine. This confirms the head gasket is blown on your 2.5L Chevy S10 pickup (GMC S15 pickup).
CASE 2: The coolant DID NOT shoot out from the radiator. This is the correct and expected test result.
If your Chevy S10 or GMC S15's 2.5L engine starts but runs with a misfire or doesn't start, your next step is to test engine compression. For this test go to: TEST 3: Engine Compression Test.
If the engine starts but overheats almost immediately, then your next step is to do a 'block' test. For this test go to: TEST 4: Using A Chemical Block Tester (Combustion Leak Tester).
TEST 3: Engine Compression Test
It is not uncommon for a head gasket to fail at a point between two adjacent cylinders. If you look at the photo at the beginning of this tutorial, you'll see such a head gasket failure.
The cylinders on either side of the head gasket failure will produce 0 PSI compression and usually cause the engine not to start.
We can verify that this has happened by performing an engine compression test.
NOTE: You can find a comprehensive explanation of the compression test (and how to interpret its results) here:
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disable the ignition system by disconnecting the ignition coil from its electrical connector(s).
IMPORTANT: This step is important! Do not proceed to the next steps without first disabling the ignition system. - 2
Disconnect the spark plug wires from their spark plugs.
IMPORTANT: Label the spark plug wires with the cylinder number they belong to before disconnecting them. This will help you reconnect them to the correct spark plug. - 3
Remove all four spark plugs.
- 4
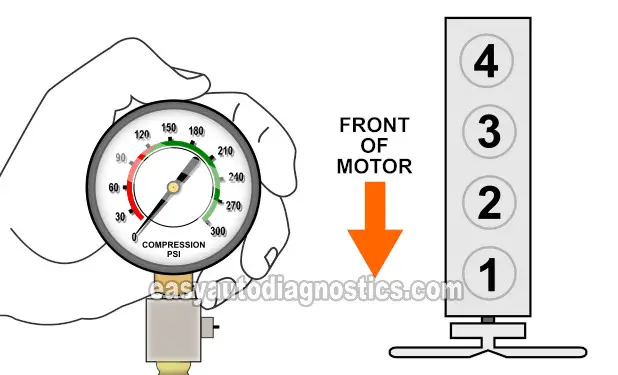
Install the compression tester by hand in the spark plug hole of cylinder #1.
Do not use any tools to tighten the compression tester. Hand tightening the compression tester is more than enough to get the proper results. - 5
Have your helper crank the engine.
The needle on the tester will climb as the engine cranks. Once the cylinder reaches its maximum compression the needle will stop climbing. - 6
Once the gauge's needle stops climbing, have your helper stop cranking the engine.
- 7
Write down the reading and what cylinder it belongs to (you can use the illustration above to help you identify the cylinder).
- 8
Repeat steps 4 through 7 in the remaining cylinders.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: All cylinder compression readings were above 0 PSI. This is the correct and expected test result.
Your next step is to perform a block test with a block tester. For this test go to: TEST 4: Using A Chemical Block Tester (Combustion Leak Tester).
CASE 2: Two side by side cylinders had 0 PSI compression. This engine compression test result confirms that the head gasket is burned at the point between those two cylinders.
Replace the head gasket.

