
Sooner or later, the alternator on your 2.8L equipped S10 pickup (S10 Blazer, GMC S15 pickup, or GMC S15 Jimmy) is going to fail.
Thankfully, testing it is a pretty easy and straightforward process. In this tutorial, I'll show you just how easy it is.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Alternator.
- Alternator Connector Circuit Descriptions.
- Important Alternator Testing Tips.
- Where To Buy The Alternator And Save.
- TEST 1: Battery Voltage Test with Engine Running.
- TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Output Wire.
- TEST 3: Checking The Alternator's F Circuit.
- TEST 4: Checking The Alternator's L Circuit.
- More 2.8L Chevy S10 Pickup, GMC S15 Pickup, And GMC Sonoma Tutorials.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Alternador Con Multímetro (2.8L V6 GM) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Alternador Con Multímetro (2.8L V6 GM) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.8L Chevrolet S10 Pickup: 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993.
- 2.8L GMC S15 Pickup: 1988, 1989, 1990.
- 2.8L GMC Sonoma: 1991, 1992, 1993.
This tutorial also applies to the 2.8L Chevy S10 Blazer, 2.8L GMC S15 Jimmy. See the 'Applies To' box on the left column (desktop) or at the bottom of the page (mobile device) for more info.
Symptoms Of A Bad Alternator
The alternator is one of the most important components your S10 needs to start and keep and stay running. What? Why? Well, it's job pretty much boils down to two important things:
- Charge the battery after it has cranked the engine.
- Provide all of the current the vehicle needs (think: headlights, fuel pump, ignition coil, radio, wipers, etc.).
So, when the alternator fails in your 2.8L equipped S10 pickup (Blazer), you'll notice one or several of the following symptoms:
- The charge light (also known as the battery light) will be shining nice and bright on your S10/S15's instrument cluster.
- Whenever you turn on the headlights (night driving), they glow very dim.
- The engine won't crank. It will only crank and start if you jump start it with another vehicle.
- The only way the car cranks and starts is if you charge the battery.
- The idle may get high when you come to a stop.
Thankfully, testing the alternator is not hard to do at all and in this tutorial, I'll show you how.
Alternator Connector Circuit Descriptions
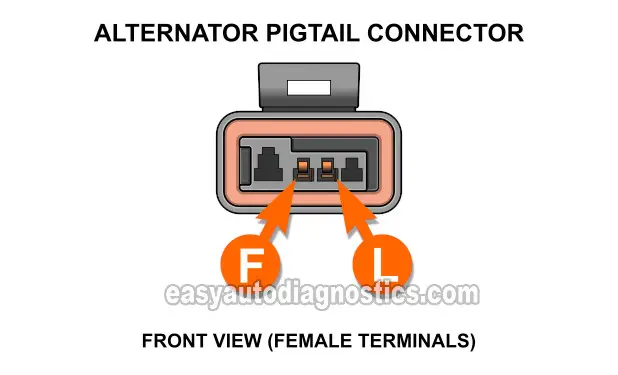
The alternator has three wires connected to it. One wire (cable) is attached to a stud on the back of the alternator with a nut.
The other two wires go to the alternator pigtail connector. Here is a brief description of each:
| Wire | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| B+ | Red (RED) | 12 Volts (Battery). Stud On Rear Of Alternator |
| F | Pink with black stripe (PNK/BLK) | 12 Volts (Field Coil) |
| L | Brown (BRN) | 12 Volts (Charge Lamp Circuit) |
Important Alternator Testing Tips
TIP 1: Make sure the battery is fully charged before beginning any of the tests in this tutorial.
TIP 2: Check the battery posts and battery cable terminals for corrosion. Clean and remove any corrosion you find.
TIP 3: Check for bad or loose connections between the battery cables and the battery.
TIP 4: Take all necessary safety precautions. Be alert and think safety all of the time since you'll be working around a running engine.
Where To Buy The Alternator And Save
The alternator, for the 2.8L S10/S15 doesn't come cheap. The links below will help you shop/compare and see where you can find the best deal on the original AC/Delco (Remy) alternator:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
Not sure if the above alternator and alternator belt fit you particular 2.8L equipped S10 pickup (Blazer)? Don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure the parts fit and if they don't they'll ask you about your S10/S15's specifics to find you the right parts.
TEST 1: Checking Battery Voltage With The Engine Running
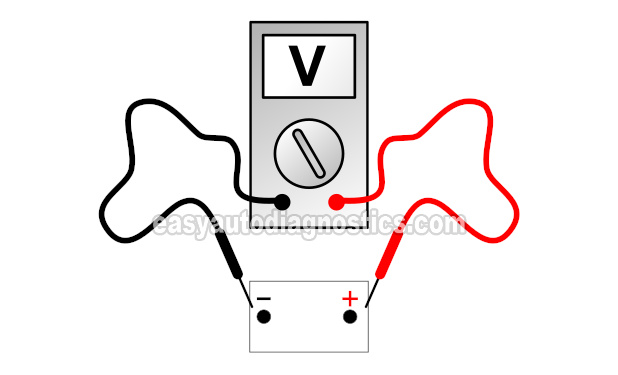
The very first thing we need to do is test the battery voltage with the engine running.
The purpose of checking battery voltage test with the engine running is to see if the voltage reading is around 13.5 Volts to 14.5 Volts.
If the battery voltage reading is hovering around these values, you can conclude that the alternator is fine.
If the battery voltage is 12.5 Volts (or less) with the engine running, then this test result would be a clear indication that the alternator is not charging the battery.
IMPORTANT: The battery must be sufficiently charged to run the engine for at least 10 to 20 minutes, otherwise you won't be able to complete TEST 1 or TEST 2 of this tutorial. If the engine won't start due to a discharged/dead battery, please charge the battery before you begin.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Crank and start the engine.
- 2
Select Volts DC mode on your multimeter.
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the battery positive (+) terminal.
- 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 5
Your multimeter will register a steady voltage of 13.5 to 14.5 Volts DC.
If it doesn't, don't worry about this just yet, continue to the next step. - 6
Put an electrical load on the alternator.
You can do this by turning on every accessory possible (inside the vehicle): turn on the A/C or heater on high, turn on the windshield wipers, turn on the headlights, turn on everything and anything that uses electricity inside and outside of the vehicle. - 5
As each accessory comes on, your multimeter will do one of two things:
1.) The multimeter will register a steady DC voltage of 13.5 to 14.5 Volts no matter what is switched on.
2.) It will register 12.5 Volts DC and that voltage will decrease more and more as you turn things on.
OK, let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered 13.5 to 14.5 Volts. This means that the alternator is charging the battery and therefore not defective.
No further testing is required as this multimeter test result eliminates the alternator as bad.
NOTE: If the battery is dead every morning, it usually means you either have a bad battery or a parasitic discharge (drain). A parasitic drain refers to the current used by a component that stays on (usually inside the vehicle, for example: a courtesy light) and drains the battery while the engine is off.
CASE 2: Your multimeter registered a voltage that steadily dropped down to 10 Volts. This is a clear indication that the alternator is NOT charging the battery.
Replacing the alternator at this point usually solves around 90% of the cases, but I suggest that you go on to TEST 2 just to make sure: TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Output Wire.
TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Output Wire
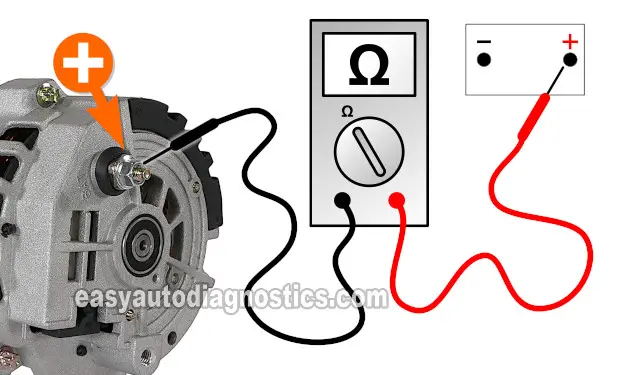
For our second test, we'll make sure that the battery cable connecting the positive (+) battery terminal to the back of the alternator does not have an open-circuit problem.
To be a little more specific, we're doing a continuity test on the cable to see if the inline fuse protecting it is good or blown.
If the result of this continuity test confirms that the cable has no continuity, we can conclude that the inline fuse has blown.
If the battery cable has continuity, we'll proceed to TEST 3.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the battery negative (-) cable from the battery negative post. We'll leave the negative (-) cable disconnected from the battery for the entire test.
The positive (+) cable remains connected to the battery.
IMPORTANT: Don't continue to the next step without first disconnecting the negative cable from the negative battery post. - 2
Place your multimeter in Continuity test mode.
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the stud shown in the photo above.
The alternator's output wire connects to the stud the arrow points to (in the photo above). - 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead on the battery positive (+) terminal (at the battery).
- 5
Your multimeter should register continuity (usually with a beeping sound).
Let's take a look at what your results mean:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered continuity. This is good, since it indicates that the entire circuit is OK and that if the alternator were charging the battery, this charge would actually reach the battery.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 3: Checking The Alternator's F Circuit.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register continuity. This result tells you that the alternator output cable has an open-circuit problem and that the alternator current output is not reaching the battery.
The most likely cause of this open-circuit problem is the inline fusible link that protects this cable is blown. Check the inline fusible link and if blown, replace it with a new one of the same gauge (thickness).




