
The alternator is one of the easiest components to test on your 1994-1995 4.3L V6 Chevy S10 pickup or GMC Sonoma.
In this tutorial, I'll show you how to test the alternator step by step. With your test results, you'll quickly determine if the alternator is good or bad.
NOTE: This tutorial applies to both the TBI and CPI fuel injected 4.3L V6 engines.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Important Testing Tips.
- Symptoms Of A Bad Alternator.
- Alternator Connector Circuit Descriptions.
- TEST 1: Checking Alternator Voltage Output With A Multimeter.
- TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Output Wire.
- TEST 3: Checking The Alternator's F Circuit (1994 Only).
- TEST 4: Checking The Alternator's L Circuit.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Alternador (1994-1995 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC Sonoma) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Alternador (1994-1995 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC Sonoma) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup: 1994, 1995.
- 4.3L V6 Chevrolet Sonoma: 1994, 1995.
NOTE: You can find the 1988-1993 and 1996-1997 4.3L V6 Chevy S10 pickup, GMC S15 pickup and GMC Sonoma's alternator tests here:
- How To Test The Alternator (1988-1993 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC S15 Pickup, GMC Sonoma).
- How To Test The Alternator (1996-1997 4.3L V6 Chevrolet S10 Pickup, GMC Sonoma).
Important Testing Tips
TIP 1: The battery must be fully charged to get the most accurate result from the alternator test described in this tutorial (since you'll have to crank and start the engine to test the alternator).
TIP 2: You can use a digital multimeter or an analog multimeter.
TIP 3: Take all necessary safety precautions. Be alert and think safety all of the time since you'll be working around a running engine.
TIP 4: This is an on-car alternator test. You don't need to remove it to test it. The photos I'm using may show it off the vehicle, but this is just to better explain the test connections.
Symptoms Of A Bad Alternator
Every time you crank the engine, the battery loses some of its charge (which is normal). Once the engine starts, the alternator recharges the battery.
In addition to charging the battery, the alternator provides all of the power your vehicle's accessories need to operate (e.g. headlights, windshield wiper motor, etc.).
Eventually, the alternator's internal parts will wear out or fail and the alternator will no longer charge the battery.
A bad alternator will cause one or more of the following symptoms:
- The charge light (also known as the battery light) will be shining nice and bright on your vehicle's instrument cluster.
- Whenever you turn on the headlights (night driving), they glow very dim.
- The car won't crank. It will only crank and start if you jump start your vehicle.
- The only way the engine cranks and starts is if you charge the battery.
Alternator Connector Circuit Descriptions
The alternator delivers its output to the battery via the cable that connects to the stud located on the rear of the alternator. This circuit is known as the B+ circuit.
The pigtail connector will have one or two wires coming out of it. Specifically:
- The 1994 Chevy S10 pickup or Sonoma's pigtail connector has two wires (see illustration 1 of 2).
- The 1995 Chevy S10 pickup or Sonoma's pigtail connector has only one wire (see illustration 2 of 2).
Here's a brief description of the wires:
| Wire | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| B+ | Red (RED) | 12 Volts (Battery). Stud On Rear Of Alternator |
| B | Brown (BRN) | 12 Volts. Charge/Battery Lamp Circuit And Voltage Regulator Activation Signal |
| C | Pink With Black Stripe (PNK/BLK) | 12 Volts (Field Coil Circuit). 1994 only |
TEST 1: Checking Alternator Voltage Output With A Multimeter
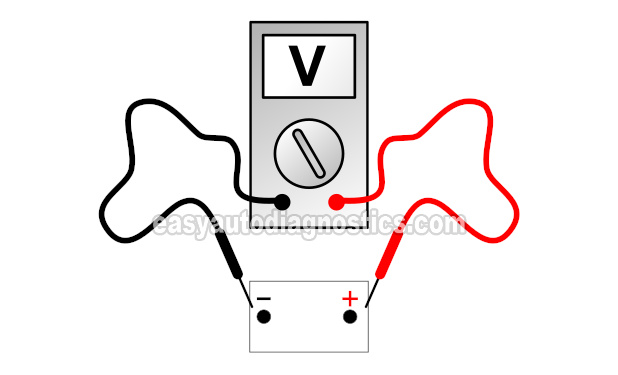
To get this pot of water boiling, I'm going to ask you to check the battery's voltage with the engine running.
If the alternator is OK, you should see a voltage of 13.5 to 14.5 Volts DC. A voltage of 13.5 to 14.5 Volts will confirm the alternator is charging the battery.
If the alternator has failed, the battery voltage will be around 12.5 Volts DC. These 12 Volts will decrease the longer the engine stays running.
NOTE: If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours, take a look at my recommendation here: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing.
Let's get started:
- 1
Start the engine and let it idle.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Check the battery's voltage with your multimeter.
- 4
The multimeter should register 13.5 to 14.5 Volts.
If it doesn't, don't worry about this just yet, continue to the next step. - 5
Turn on every accessory possible while observing the multimeter. Like the headlights, the A/C or heater (high blower speed), the windshield wipers, the radio, the rear window defroster, etc.
As each accessory comes on, they'll place a load on the charging system (alternator). - 6
As each accessory comes on, your multimeter will do one of two things:
1.) The multimeter's voltage reading will decrease slightly and then stabilize around 13.5 to 14.5 Volts DC (when something comes on).
2.) The DC voltage reading will decrease to 10 Volts DC.
Let's analyze your multimeter test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter maintained a 13.5 to 14.5 Volts value thru' out the whole test. This is the correct test result and it tells you the alternator is functioning correctly.
Since the alternator is charging the battery, no further testing is required.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT maintain a 13.5 to 14.5 Volts value. This test result confirms that the alternator is not charging the battery.
The next step is to test the continuity of the wire that connects the alternator to the battery. For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Output Wire.
TEST 2: Testing The Continuity Of The Alternator's Output Wire

The alternator delivers its amperage and voltage output to the battery through the cable that connects to the stud located at the rear of the alternator.
In the image above, I've labeled the stud (the cable connects to) with the orange arrow with the '+' symbol.
An inline fusible link protects this cable, and in this test section, you'll check the integrity of this inline fusible link with a simple multimeter continuity test.
NOTE: The photo above shows the alternator off of the vehicle to better explain the test connections. Do not remove the alternator from the vehicle to perform this test.
OK, let's start:
- 1
Disconnect the battery negative (-) cable from the battery but leave the positive (+) cable connected to the positive (+) post.
IMPORTANT: Do not proceed to the next steps until you do this first. - 2
Set your multimeter to Ohms mode.
- 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the stud shown in the photo above.
The alternator's output wire connects to the stud the arrow points to (in the photo above). - 4
Connect the red multimeter test lead on the battery positive (+) terminal (at the battery).
The battery negative (-) wire must remain disconnected from the battery. - 5
Your multimeter will register one of two values:
1.) Continuity (usually an Ohms value of about 0.5 Ohms).
2.) No continuity (an infinite Ohms reading (OL)).
OK, let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered continuity (usually 0.5 Ohms). This is the correct and expected test result and it tells you that the inline fusible link protecting the alternator's output wire is OK.
If your Chevy S10 pickup (GMC Sonoma) is a 1994 model year, your next step is to go to: TEST 3: Checking The Alternator's F Circuit (1994 Only).
If your Chevy S10 pickup (GMC Sonoma) is a 1995 model year, your next step is to go to: TEST 4: Checking The Alternator's L Circuit.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register continuity, it registered OL. This test result confirms the inline fusible link protecting this wire is blown.
Your next step is to replace the inline fusible link and retest.



