Interpreting The Compression Test Results
Okay, in this section we're gonna' interpret your Honda CR-V's compression test results and find out if the lowest compression value is within normal parameters.
Let me start off by telling you that it's normal for the compression values to vary between each other somewhat. What isn't normal is if the values vary too much.
The rule of thumb is that the lowest compression value can not vary more than 15% of the highest value (that you wrote down in TEST 1). If any value is lower by more than 15%, then that engine cylinder is going to misfire. This misfire will cause your 2.0L Honda CR-V's engine to idle rough.
How do you figure this out? You can find out by using my online low compression calculator here: Online Low Engine Compression Calculator or by calculating this 15% difference manually.
To understand how to figure out this 15% thing manually, let's say that my 2.0L Honda CR-V produced the following compression test results:
- Cylinder #1 175 PSI.
- Cylinder #2 165 PSI.
- Cylinder #3 160 PSI.
- Cylinder #4 120 PSI.
The next step is to do the following math:
- Multiply .15 (15%) by the highest value: 175 x 0.15. This gives us 26.25, but we'll round it out to 26.
- Next, we subtract 26 from 175: 175 - 26 = 144.
- So now we know that the lowest possible compression value is: 144 PSI.
This means that cylinder #4, which has a compression value of 120 PSI, is the one causing the misfire because it's below the 144 PSI minimum.
Once we've found the 'dead' cylinder, the next step is to find out what's causing the low compression value. For this step, go to: TEST 2: Wet Compression Test.
TEST 2: Wet Compression Test
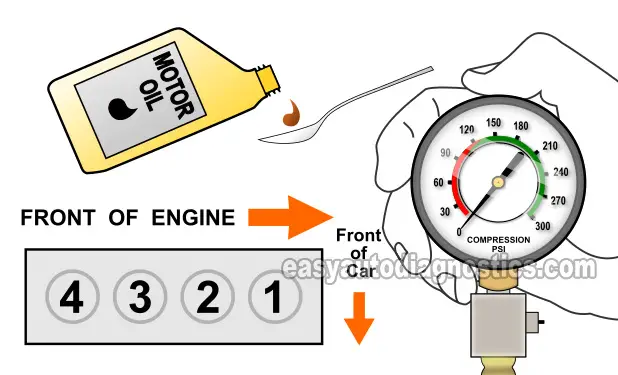
In this test section, we're now gonna' find out what is causing the low compression value that you got from the compression test (in TEST 1).
To give you some more details, what usually ends up causing a low (or zero) compression value in any given engine cylinder are worn/damaged piston rings or cylinder head valves.
Thankfully, you and I can find out which of the two it is by doing a ‘wet’ compression test (instead of tearing into the engine to find out). And that's what we are going to do in this section.
OK, this is what you'll need to do:
- 1
Add a tablespoon (or two) of engine oil in the cylinder you need to retest. I suggest using a small and long funnel so that the oil will reach the inside of the cylinder.
- 2
Once you've added the oil, install the compression gauge, and as before just hand tighten it.
- 3
Now, have your helper crank the engine till the needle stops climbing on the compression gauge.
- 4
As before, your job is to keep an eye on the gauge, and you'll see one of two results:
1.) The needle will climb higher than the previous compression number you recorded for this specific cylinder, or...
2.) The needle will not move at all or stay at the same number you recorded earlier.
What ever value your compression tester reads, write it down again. - 5
If you have another cylinder that needs to be tested, repeat steps 1 thru' 4 on it now.
Let's take a look at what your compression test results mean:
CASE 1: The compression value shot up for the low compression cylinder. This test result lets you know that extremely worn piston rings are the ones causing the low compression value in that specific cylinder.
The reason the compression value shot up is due to the fact that the motor oil you just added helped the piston rings to create a tighter seal. This type of test result only happens when the problem is due to worn piston rings.
CASE 2: Your compression value DID NOT shoot up (stayed the same). This test result lets you know that that cylinder's cylinder head valves are worn/damaged and are the ones causing the low compression value in that specific cylinder.
More 2.0L Honda CR-V Tutorials
You can find a complete list of tutorials here: Honda 2.0L Index Of Articles.
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find there:
- How To Test The Ignition Coil (1999-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V).
- How To Test The Ignition Coil (1997-1998 2.0L Honda CR-V).
- How To Test The Ignition Control Module (1999-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V).
- How To Test The TPS (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V).
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V).
On YouTube, check out my following videos:
- How To Test The Ignition Coil (1999-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V) (at YouTube).
- How To Test The Ignition Control Module (1999, 2000, 2001 2.0L Honda CR-V) (at YouTube).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V) (at: YouTube).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


