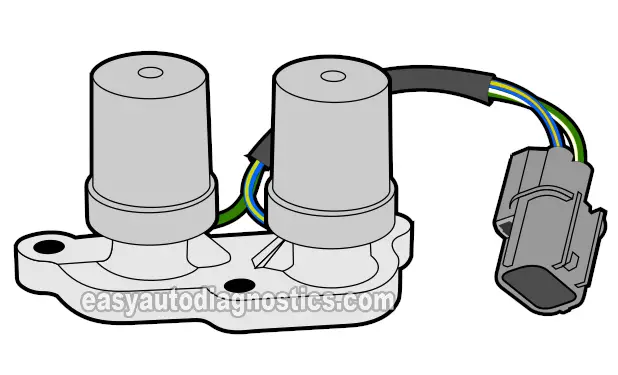
This tutorial will help you to test the automatic transmission shift control solenoids A and B. Both of these shift solenoids are part of the same assembly.
One test involves testing the internal resistance of each solenoid and the other involves applying power (via a jumper wire) to each one.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Conjunto De Solenoides A y B (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Conjunto De Solenoides A y B (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
NOTE: You can find the test procedures for the linear solenoid (clutch pressure control) assembly and the TCC lock-up solenoid assembly here:
- How To Test: A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V).
- How To Test: TCC Solenoids A And B (1997-2001 2.0L Honda CR-V).
Symptoms Of A Defective Shift Solenoid A And B Assembly
Shift solenoid A and B assembly is located on the rear-bottom side of your Honda CR-V's automatic transmission (this is the side that faces toward the passenger side wheel).
Shift solenoid A and B assembly looks very similar in appearance to the torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid A and B assembly. You can tell them apart because the:
- Shift solenoid A and B assembly's connector has:
- A blue with yellow stripe (BLU/YEL) wire.
- A green with white stripe (GRN/WHT) wire.
- TCC solenoid A and B assembly's connector has:
- A yellow (YEL) wire.
- A green with black stripe (GRN/BLK) wire.
Your Honda CR-V's automatic transmission is computer controlled so when one of the shift solenoids fails you're gonna' have one of the following trouble codes stored in the PCM's memory (and lighting the check engine light):
- P0753: Shift Solenoid Valve A
- P0758: Shift Solenoid Valve B
You're also gonna' see:
- Transmission stays in limp-in mode (no upshifting from 1st to higher gears).
- Erratic upshifting from a low gear to a higher gear.
- Transmission fails to downshift from 4th gear (stuck in 4th gear).
Where To Buy The Shift Solenoid A And B Assembly
NOTE: The 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, and 2001 2.0L Honda CR-V (with an automatic transmission), come equipped with two shift solenoid assemblies that look very similar. The one that's covered by this tutorial (shift solenoid A and B assembly) can be identified correctly because the 2 wires of its connector are a blue with yellow stripe (BLU/YEL) wire and a green with white stripe (GRN/WHT) wire.
The following links will help you comparison shop for the shift solenoid A And B assembly:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
TEST 1: Shift Solenoid Resistance Test
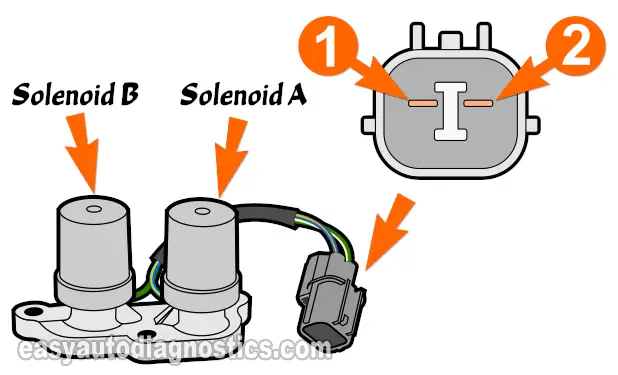
The very first thing we're gonna' do is to check the resistance of each solenoid within the solenoid assembly.
The resistance specification of each solenoid is: 12-25 Ohms and we'll check it with a multimeter in Ohms mode.
NOTE: This test is done on the connector of the shift solenoid assembly itself, which has male spade terminals.
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Ohms mode.
- 2
Disconnect shift solenoid assembly A and B from its electrical connector.
- 3
To check solenoid A, measure the resistance between terminal labeled with the #1 and the solenoid assembly's body (see the illustration above).
NOTE: Shift solenoid A is Grounded by the solenoid assembly's case. If the solenoid assembly is still bolted to the transmission housing, you can Ground your multimeter's lead directly on the battery's negative (-) terminal. - 4
To check solenoid B, measure the resistance between terminal labeled with the #2 and the solenoid assembly's body (see the illustration above).
NOTE: Shift solenoid B is Grounded by the solenoid assembly's case. If the solenoid assembly is still bolted to the transmission housing, you can Ground your multimeter's lead directly on the battery's negative (-) terminal. - 5
Your multimeter should read 12-25 Ohms for the resistance value of shift solenoid A.
Let's analyze your resistance test results:
CASE 1: Resistance was between 12-25 Ohms for both solenoids. This is the correct and expected test result and generally means that shift solenoid A and shift solenoid B are OK.
Although the shift solenoid A and B passed this test, we have one more test to do. This is to manually apply power to the solenoids and see if each one clicks (when it gets power). For this test go to: TEST 2: Applying 12 Volts To Shift Solenoid A And B.
CASE 2: Resistance WAS NOT between 12-25 Ohms. Recheck your multimeter test connections and retest. If you still don't get the correct resistance then shift solenoid A is bad and needs to be replaced.



