The ignition control module (ICM) on your 3.2L Isuzu Rodeo or Trooper can be tested in 3 easy steps and without taking it off of the vehicle. Testing the crankshaft position sensor is just as easy too.
As you might already know, the ignition control module (ICM) is located under the ignition coil packs on your 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995 3.2L Isuzu Rodeo or Trooper. This tutorial will show you how to test it without a scan tool, all you'll need is a multimeter and a helper to help you crank the engine.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Módulo De Encendido (1992-1995 3.2L Isuzu Rodeo y Trooper) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Módulo De Encendido (1992-1995 3.2L Isuzu Rodeo y Trooper) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.2L V6 Isuzu Rodeo: 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
- 3.2L V6 Isuzu Trooper: 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
- 3.2L V6 Honda Passport: 1994, 1995.
Important Tips And Suggestions
TIP 1: The ICM and crankshaft position sensor tests described in this tutorial are on-car and dynamic tests done with the engine cranking, so you've got to be careful. Take all necessary safety precautions.
TIP 2: This tutorial is designed to help you when your 3.2L Isuzu Rodeo or Trooper cranks but does not start due to a lack of spark from all ignition coil towers.
If your Isuzu has at least one spark plug wire sparking, this test won't help you.
TIP 3: If you need to test a misfire condition (in other words, your 3.2L V6 Isuzu starts and runs, but runs with a misfire) you should take advantage of this tutorial: How To Test The Ignition Coil Packs (GM 3.1L, 3.4L).
The above tutorial also applies to the ignition coils on your 3.2L V6 Isuzu and will help you find the exact cause of the misfire.
How Does The Ignition Control Module Work?

In a nutshell, the ignition control module's job on your 3.2L V6 Isuzu Rodeo or Trooper is to activate the ignition coils that sit on top of it. Also, to relay the crankshaft position sensor signal to the fuel injection computer.
Here's what happens when you turn the key and crank your Rodeo or Trooper:
- The ignition module gets power (12 Volts). With this voltage, it also powers up the 3 ignition coil packs that are connected to it.
- As the engine in your Rodeo or Trooper starts to turn, the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor starts to generate a CKP signal. The sensor then sends this signal to the ignition module.
- When the ignition module gets this CKP signal, it does its little song and dance and starts to activate the 3 coil packs. It does this by interrupting the flow of the voltage that flows thru' them.
- This interruption of the Primary Current (of the coil packs) is an ON/OFF type signal, that's referred to as the switching signal.
- Well, as the ignition module processes the crankshaft position sensor signal (converting it into a digital signal), it now sends it to the fuel injection computer.
- When the fuel injection computer gets this digitized CKP signal, it starts to activate the fuel injectors.
- Your Rodeo (or Trooper) starts since now there's fuel and spark.
Where To Buy The Ignition Module And Save
The following links will help you comparison shop for the AC Delco and Delphi ignition control module (they are factory original parts) and save you a few bucks:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
TEST 1: Making Sure The Ignition Module Is Getting Power
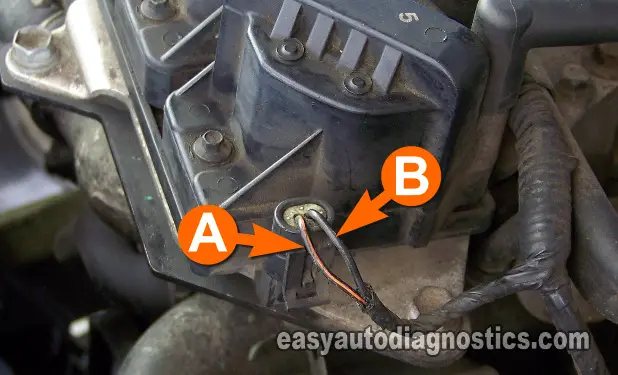
OK, to get this show on the road, you'll test for power first. Power comes in the form of 12 Volts when you turn the key On.
You can use a 12 Volt test light for this test step, or a multimeter (which is the method I prefer, since the result is more accurate).
The following test steps assume you're using a multimeter, this is what you'll do:
- 1
Place your multimeter's dial in Volts DC mode.
- 2
With the red multimeter test lead, probe the wire labeled with the letter A, in the photo above.
- 3
Ground the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Turn the key ON (but don't crank the engine).
- 5
Your multimeter should register 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct test result and let's you know that the ignition control module (ICM) is getting power.
For the next test, let's go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Module Is Getting Ground.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register 12 Volts. Recheck your multimeter connections and retest. If the multimeter still doesn't display the 12 Volts, then this result eliminates the ignition control module (ICM) and crankshaft position sensor as the cause of the no-start no-spark condition on your 3.2L Isuzu Rodeo or Trooper.
Here's why: Without power, the ignition module won't function and this will keep the ignition system from creating and delivering spark to the engine cylinders.




