
If your Nissan Altima CRANKS but does NOT START or runs with a misfire, this is the article that will help you test and diagnose your Altima's 2.4L ignition system (1993-1997).
No expensive tools or diagnostic equipment are needed to test the ignition system, and this tutorial will show you just how to do it step by step.
With the tests in this tutorial, you'll be able to test and diagnose: A bad power transistor (ignition control module), or a bad ignition coil, or a bad distributor cap, or bad spark plug wires on your Nissan Altima's 2.4L four cylinder engine.
NOTE: If you need the 1997-2001 Altima ignition coil and power transistor tests, go here: Index of 2.4L Nissan Articles.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Transistor, Ignition Coil, Spark Plug Wires, Or Dist. Cap.
- Basic Nissan Ignition System Theory.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
- Power Transistor Circuit Descriptions.
- Ignition Coil Circuit Descriptions.
- TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wires.
- TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Distributor Cap.
- TEST 3: Testing The Ignition Coil's High Tension Wire.
- TEST 4: Testing The Ignition Coil For Spark.
- TEST 5: Testing The Ignition Coil's Power (12 V) Circuit.
- TEST 6: Testing The Ignition Coil's Switching Signal.
- TEST 7: The Power Transistor's Ground Circuit.
- TEST 8: Testing The Triggering Signal From PCM.
- Other Causes Of A Misfire.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- Nissan Altima 2.4L: 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997.
Symptoms Of A Bad Transistor, Ignition Coil, Spark Plug Wires, Or Dist. Cap
If your Nissan Altima is suffering a misfire, the check engine light (CEL) will be on to let you know that YES, there really is something wrong (that is if your Altima is a 95-97 OBD II equipped car that's capable of creating and storing misfire codes.). Here are a couple of other symptoms your Nissan Altima may experience with a misfire condition:
- Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC) stored in the computer's (PCM) memory:
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304.
- Misfire that does not light up the check engine light (CEL).
- No power.
- Idles rough.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Black smoke coming out of the tail pipe.
- Rotten egg smell coming out of the tail pipe.
- Smell of unburned gasoline coming out of the tailpipe.
- Won't pass the state emissions test.
If the Altima's power transistor (ignition control module) or the ignition coil is bad, then the most common symptom is that your vehicle will crank but not start and there will be no spark at any of the spark plug wires.
Basic Nissan Ignition System Theory
The Nissan Altima's ignition system is a pretty straight forward distributor type system with an externally mounted ignition coil and a power transistor. This is what happens, in a nutshell, when you turn the key and crank the Altima's engine:
- The crankshaft position sensor (called in Nissan tech speak: crank angle sensor) and camshaft position sensors start to generate and feed their signals to the vehicle's PCM (Powertrain Control Module=Fuel Injection Computer).
- The PCM uses these signals to know where each piston is at in relation to its combustion cycle and with this info, the PCM knows when to start activating the power transistor, the fuel injectors and a host of other things to get your Nissan Altima started and running.
- The power transistor performs the 'ignition control module (ICM)' function in the Nissan vehicles.
- So then, after receiving the crank angle sensor signal, the PCM sends the power transistor a Triggering signal that tells the power transistor exactly when to activate the ignition coil.
- The power transistor activates the ignition coil by opening and closing the Primary Current circuit of the ignition coil and as you may already be aware it's this opening and closing action that makes the ignition coil spark away.
- The spark created by the ignition coil is fed to the distributor cap via a high tension wire that connects the ignition coil do the distributor cap.
- The distributor cap transmits this spark to the rotating distributor rotor and from there to the appropriate distributor cap tower.
- From the distributor tower, the spark is taken directly to the spark plug via a spark plug wire.
Any malfunction in any of these components and the Altima will either not start or will start but run with a misfire. Now, to test either of these conditions is not difficult at all and with the simple and easy tests presented in this test article you'll be able to find the exact cause of your Nissan Altima's ignition system woes.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
Although the tests in this article are easy and simple, you do need some specific tools to perform them with. Here's the list:
- An HEI spark tester
- This inexpensive spark tester is a MUST have tool to be able to correctly diagnose the Coil-On-Plug ignition coils on your Nissan Altima with the info and tests in this article. (don't have an HEI spark tester? Need to buy one? You can buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester).
- Battery jump start cables.
- A digital multimeter that can read Hertz (Hz) frequency.
- Without a multimeter that can read Hertz frequency, you won't be able to accomplish some of these tests. (don't have a digital multimeter that can read Hertz frequency? Click here to see my recommendations: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing).
- A helper.
- You'll need someone to help you crank the engine while you perform the tests in the engine compartment.
- A repair manual.
- For whatever remove and replace info you'll need that is not covered by this article.
Power Transistor Circuit Descriptions
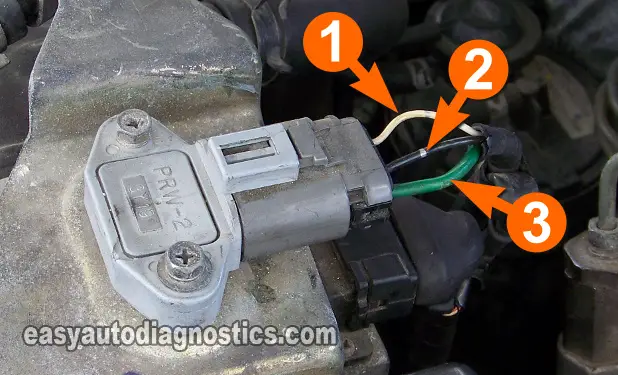
The power transistor (Nissan's name for its ignition control module) has three wires coming out of its connector.
Now, when testing these circuits, the procedure I recommend is to test them by piercing the wire with a wire-piercing probe. Testing the front of the connector can damage the female terminal and then, you're gonna' have a major headache on your hands. Below are the circuit description of each:
- Circuit labeled 1
- Triggering Signal for Power Transistor. This signal comes from the PCM.
- Circuit labeled 2
- Ground Circuit for the Power Transistor.
- Circuit labeled 3
- Camshaft Position Sensor Signal - 120° REF Signal.
Ignition Coil Circuit Descriptions

The ignition coil connector has two wires coming out of it and below are their circuit descriptions.
You may have noticed that the wire labeled with the number 1 has its insulation peeled off, this is a major no no. Not only that, the person responsible for this did not bother to at least insulate the circuit with black electrical tape. This would have caused a short to Ground sooner or later.
- Circuit labeled 1
- Power (12 V) circuit.
- Circuit labeled 2
- Switching signal input. This signal comes from the PCM.

