The throttle position sensor on the 1993-1995 2.5L SOHC Dodge Dakota can be easily tested with just a multimeter. As a matter of fact, you don't even have to remove it from its spot on the engine to do it.
In this tutorial, I'm going to explain where you need to make all of your multimeter test connections. With the test results of the TP sensor test, you'll be able to to find out if the TP sensor is bad or not and diagnose the following trouble codes:
- P0122: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Low Input.
- P0123: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High Input.
- P1121: Throttle Position Sensor Signal Lower Than Expected.
- P1122: Throttle Position Sensor Signal Higher Than Expected.
Contents of this tutorial:
NOTE: If you need to test the 1996-1999 2.5L OHV Dakota TPS, you can find the tutorial here: How To Test The TPS (1996-1999 2.5L OHV Dodge Dakota).
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor TPS (1993-1995 2.5L Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor TPS (1993-1995 2.5L Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Basics Of The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)

The throttle position sensor on your 2.5L SOHC Dodge Dakota has the job of measuring the throttle plate angle.
As you're probably already aware, the throttle plate opens and closes as you step on or off the accelerator pedal. As the throttle plate opens, the throttle position sensor generates a higher voltage signal.
When the throttle plate is closed (like when you have your foot off the accelerator pedal), the throttle position sensor produces a small voltage signal. When the throttle plate opens (like when you step on the accelerator pedal), the TP sensor produces a higher voltage.
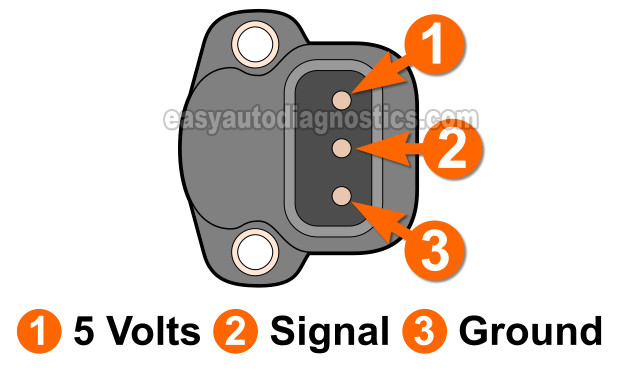
Since the throttle position sensor is a 3 wire type sensor, in the table below, you will find a description of each wire:
| 2.5L Dodge Dakota TP Sensor Circuits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | VIO/WHT | 5 Volt Reference |
| 2 | ORG/DK BLU | Throttle Plate Position Signal |
| 3 | BLK/LT BLU | Ground |
TEST 1: Checking The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Signal

What's really going to help you to understand the TPS test, is to know that the throttle position sensor reacts to the throttle plate angle.
And as mentioned before, the throttle plate angle reacts to the accelerator pedal's movement.
So the very first thing that we're gonna' do is to test the TPS voltage signal. Specifically, we want to see if it increases/decreases as we open/close the throttle plate.
If, during your TP sensor test, the voltage signal stays stuck at a specific voltage value (no matter how much you open or close the throttle plate) then we'll know that the TPS is defective.
IMPORTANT: This is on a car test of the sensor and the throttle position sensor (TPS) must remain connected to its harness connector.
Here are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode and connect the red test lead to the ORG/DK BLU wire of the TP sensor harness connector.
NOTE: The TP sensor connector needs to be connected to the TPS, so you'll need to either back-probe the connector or use a wire piercing probe to get to the signal inside the wire (to see what a wire piercing probe looks like: Wire Piercing Probe Tool). - 2
Ground the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) post.
- 3
Manually rotate the throttle plate.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 4
The multimeter should show an increasing voltage as you (or your helper) open up the throttle.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 5
The multimeter should show a decreasing voltage as you begin to close the throttle.
- 6
Using a screwdriver's handle, gently tap the throttle position sensor (TPS) as you open and close the throttle and observer the multimeter.
The purpose (of tapping the throttle position sensor (TPS) with the screwdriver's handle) is to see if the throttle position sensor (TPS) shows gap's in the voltage signal. Why? Because a good throttle position sensor (TPS) will show a continuous increasing or decreasing voltage signal even while getting tapped by the screw-driver's handle.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The TP sensor signal's voltage increased and decreased smoothly and without gaps. This is the correct and expected TPS test result and lets you know that the throttle position sensor on your 2.5L SOHC Dodge Dakota is working correctly.
This test result also let you know that the TP sensor is being fed with power and Ground.
CASE 2: The TP sensor signal's voltage did not increase or decrease. In most cases this test result confirms that the throttle position sensor is defective and needs to be replaced.
But before you do that, it's a good idea to make sure that the TP sensor is getting power and Ground. These two tests are very easy and simple test to do. Go to: TEST 2: Checking Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Power and Ground.
CASE 3: The TP sensor signal's voltage showed gaps in its voltage output as you tapped the sensor with the screwdriver. If tapping the TP sensor with the screwdriver's handle caused the voltage reading to react on your multimeter, then you can conclude that the TP sensor is defective internally and needs to be replaced.
