Quite a few things can cause your 2000–2009 4.7L Dodge Dakota or Durango to not start.
This tutorial will walk you through the 4 most common causes of a no-start condition: a bad crankshaft position sensor, a defective fuel pump, low or no engine compression, and a blown head gasket.
We'll start by confirming the difference between a no-start and a no-crank condition —because it matters.
Then we'll move into step-by-step tests you can do with basic tools to check for spark, fuel, compression, and signs of internal engine damage.
If you're not sure where to start or just want to avoid guessing, this guide will help you zero in on the root cause —fast.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Difference Between A No Start And A No Crank Condition.
- No Start Condition Basics.
- What Tools Do I Need?
- TEST 1: Testing For Spark And Fuel Injector Pulses.
- TEST 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure.
- TEST 3: Making Sure The Engine Has Good Compression.
- TEST 4: Checking For A Blown Head Gasket.
- No Start Troubleshooting Summary.
- Where To Buy An HEI Spark Tester And A Fuel Pressure Gauge.
- More 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango Tutorials.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Un Arranca Pero No Prende (2000-2003 Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Un Arranca Pero No Prende (2000-2003 Dodge Dakota) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009.
- 4.7L V8 Dodge Durango: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009.
Difference Between A No Start And A No Crank Condition
Before I jump into the tutorial, I want to explain the difference between a 'does not crank' problem and a 'no-start' problem.
When the engine cranks but does not start: Your Dodge Dakota or Durango's starter motor is cranking the engine but the engine is not starting.
When the engine does not crank: Your Dodge Dakota or Durango's engine does not turn over when you turn the key to crank and start the engine. This is usually due to a bad starter motor, bad ignition switch, bad neutral safety switch, or the engine is locked up.
If the engine in your Dodge Dakota or Durango's does not crank, you should test the starter motor. The following tutorial will help you test the starter motor:
No Start Condition Basics
What will usually cause a no-start problem is one of three things: a no-spark condition, or a no fuel condition, or an engine compression problem.
This boils down to doing 3 basic tests to get to the bottom of the no-start problem. We need to:
Test the ignition system: We need to make sure that each cylinder is getting spark. This is accomplished by making sure that the ignition coils are sparking.
A no-spark condition, that's causing the engine not to start, is usually caused by a defective crankshaft position sensor.
Test the fuel system: We need to make sure gasoline is reaching the cylinders. This is accomplished by doing an a fuel pump pressure test.
A no fuel condition, that's causing the engine not to start, is usually caused by a defective fuel pump.
Test the engine compression: We need to make sure that each cylinder has a normal compression value.
An engine compression problem, that's causing the engine not to start, is usually caused by a serious internal engine problem (like a thrown rod or busted timing chain).
Test for a blown head gasket: A blown head gasket is usually the result of severe engine overheating and can cause the engine to crank but not start.
In the following pages, you'll find a basic testing guide so that you can find out what's behind your 4.7L Dodge Dakota or Durango's no-start problem.
What Tools Do I Need?
To find out what's behind your 4.7L Dodge Dakota or Durango's not start problem, you're gonna' need a few specialized tools.
Here's a basic list of what you'll need:
- Spark tester.
- Noid light set.
- Fuel pressure tester.
- Engine compression tester.
I'm gonna' suggest that the spark tester that you use be an HEI spark tester. This tester is the most accurate tester on the market and isn't expensive. You can find out more about it (and where to buy it) here: HEI Spark Tester. Or you can take a look at this section: Where To Buy An HEI Spark Tester And A Fuel Pressure Gauge.
You'll notice that I didn't include a scan tool in the list. But if you have one, I can tell you that it'll come in very handy. Why? Because some of the components that cause a no-start condition can leave a specific trouble code (when they fail).
In this tutorial, I haven't included it (a scan tool) in any of the suggested tests because they can be done without one.
As you can see, none of these tools will break the bank. Most of these you can borrow from your local auto parts store (after leaving a small deposit).
Let's turn the page and get testing.
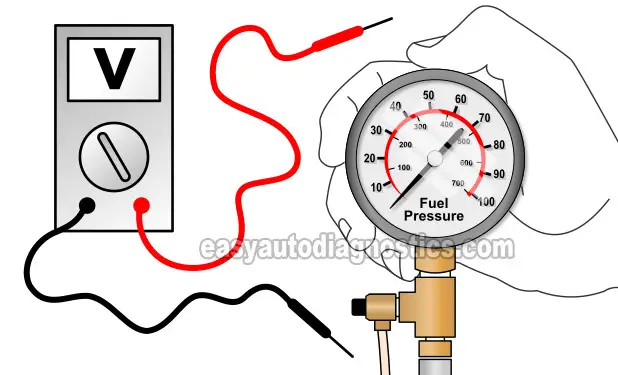
TEST 1: Testing For Spark And Fuel Injector Pulses
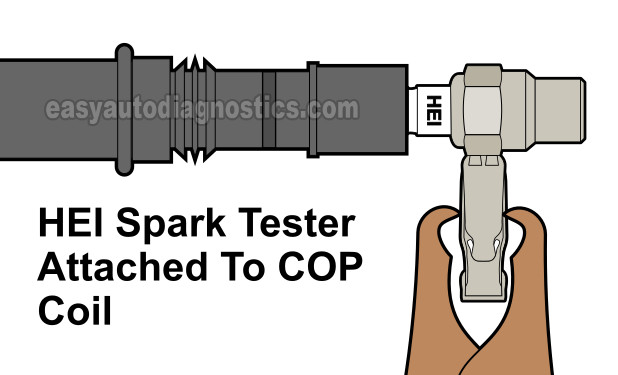
Testing for spark (with a spark tester) and testing the fuel injector pulses (with a Noid light) is the first tests I'm gonna' suggest to you.
If spark and the fuel injector pulses are present, then we can move on with testing the fuel pump pressure.
If spark and the fuel injector pulses ARE NOT present, then the next step is to test the crankshaft position sensor.
NOTE: If you've never done a Noid light test, then you can find out more about it and where to buy a set here: How To Use A Noid Light And Where To Buy It.
Let's get started:
- 1
Remove the #1 cylinder ignition coil and connect the spark tester to it.
NOTE: The ignition coil must remain connected to its electrical connector to test it for spark. - 2
Connect the Noid light to the fuel injector connector for cylinder #1.
- 3
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the spark tester and the Noid light.
- 4
The spark tester should spark and the Noid light should flash On and OFF as your helper cranks the engine.
- 5
Repeat this test on the remaining cylinders.
Let's interpret your spark and Noid light test results:
CASE 1: You got spark and fuel injector pulses at all cylinders. This is the correct and expected test result.
With this test result you can conclude that your Dodge Dakota or Durango's crankshaft position sensor is OK and working correctly.
Your next step is to test the fuel pump's pressure. For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure.
CASE 2: You got NO spark and NO fuel injector pulses at all cylinders. This test result usually tells you that the crankshaft position sensor is defective.
Your next step is to test the crankshaft position sensor.
TEST 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure
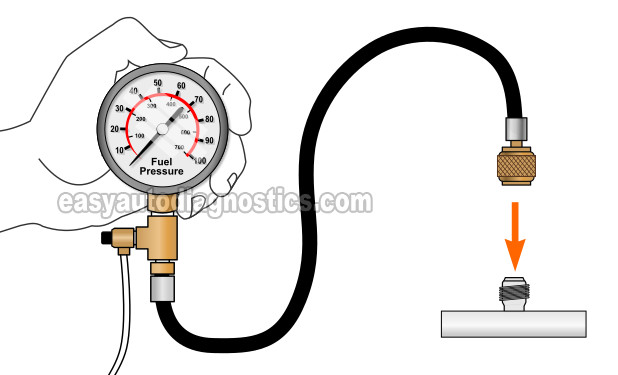
Once you've made sure that your Dodge Dakota or Durango's no-start problem IS NOT being caused by a bad crankshaft position sensor, the next step is to test the fuel pump.
The fuel pump is testing by doing a simple fuel pump pressure test with a fuel pressure test gauge.
This fuel pressure test gauge is connected to a Schrader valve (on the fuel injector rail) to read the fuel pump pressure output.
NOTE: If you need to buy a fuel pressure test gauge kit, take a look at this section: Where To Buy An HEI Spark Tester And A Fuel Pressure Gauge.
NOTE: You can find a more detailed explanation of the fuel pump test here:
Let's get started:
- 1
Place a shop towel around the Schrader valve. The shop towel's job is to absorb any fuel that may leak when doing step 2.
- 2
Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the Schrader valve on your 4.7L Dodge's fuel injector rail.
- 3
When ready, ask your helper to cycle the key ON and OFF but don't crank the engine while you observe the fuel pressure tester's gauge.
Check the connection at the Schrader valve for fuel leaks and if any tighten the fuel pressure a bit more (by hand only) to eliminate them. - 4
Crank and start the engine and check the fuel pressure gauge. Your fuel pressure gauge should register: 44 to 54 PSI with the engine running if the fuel pump is OK.
- 5
If the engine doesn't start, crank the engine enough to get the fuel pressure up. Your fuel pressure gauge should register: 44 to 54 PSI if the fuel pump is OK.
Let's take a look at your fuel pressure test results:
CASE 1: The fuel pressure test gauge registered 0 PSI. This confirms that the no-start problem is caused by a lack of fuel.
CASE 2: The fuel pressure gauge registered 44 to 54 PSI. This fuel pressure gauge result lets you know that the fuel pump is working and delivering enough fuel to the fuel injectors. You can conclude the fuel pump is OK and not behind the no-start problem.
The next test is a compression test. Go to: Making Sure The Engine Has Good Compression.
CASE 3: The fuel pressure is lower than the indicated PSI. This tells you that the fuel pump is defective.
TEST 3: Making Sure The Engine Has Good Compression
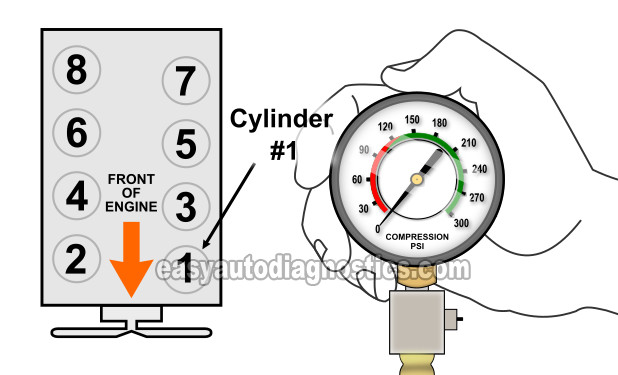
If your tests have confirmed that all 8 cylinders have spark and fuel injector pulses and that the fuel pump is OK, then I suggest testing your Dodge Dakota or Durango's engine compression.
I've written a detailed 'how to test the engine compression' tutorial for the 4.7L Dodge Dakota and Durango, and you can find it here:
Alright, let's get started:
- 1
Remove the ignition coils and the spark plugs from all 8 cylinders.
- 2
Thread the engine compression gauge into the spark plug hole for the number 1 engine cylinder. Hand tighten the compression gauge only! Do not use any type of tool to get it tight.
- 3
Have your helper crank the engine till the needle on the compression gauge stops climbing.
Now, record the value on a piece of paper and repeat steps 3 and 4 on the remaining cylinders.
Let's take a look at what your compression test results mean:
CASE 1: All cylinders have compression above 120 PSI. This is the correct and expected test result.
If all cylinders have at least 120 PSI of compression, then you can conclude that the engine does not have a compression problem (causing it not to start). Now, if your Dakota or Durango's engine is not starting, the next step is to see if you have a blown head gasket on your hands.
CASE 2: All cylinders have 0 PSI compression. This tells you that 0 compression is the cause behind the no-start problem on your 4.7L Dodge Dakota or Durango.
The most likely cause will be a broken timing chain or the engine threw a rod.
CASE 3: Two adjacent cylinders have 0 PSI. This usually indicates a blown head gasket. Specially if your Dodge Dakota or Durango overheated before the no-start problem occurred.
For more testing suggestions, take a look at this tutorial: How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (2000-2009 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango).
TEST 4: Checking For A Blown Head Gasket

A blown head gasket (and the 4.7L V8 engine has two of them) can cause the engine to not start.
In case you're wondering, a blown head gasket is usually caused by severe engine overheating.
Testing for a blown head gasket involves 3 to 4 specific tests. None of them are hard to do and you can find them explained in detail in this tutorial:
No Start Troubleshooting Summary
Testing a 'cranks but does not start' condition all boils down to a process of elimination.
The most important thing you should remember is that the engine is not starting due to a lack of spark, or a lack of fuel, or a lack of compression.
By checking these basic things (spark, fuel, air), you'll save yourself the frustration of replacing components that won't solve the problem.
As you noticed, I started out the troubleshooting tests with a spark test (at all cylinders). This is due to the fact that the culprit behind most no-start problems is the ignition system, specifically a defective crankshaft position sensor.
Once you've confirmed that you've got spark at all cylinders, there isn't any need to spend time testing the crankshaft position sensor. The next step is to make sure the fuel pump is working and so on and so on.
Where To Buy An HEI Spark Tester And A Fuel Pressure Gauge
As I mentioned before, the HEI spark tester (OTC 6589) is an accurate spark tester and it doesn't cost and arm and a leg. The fuel pressure gauge that connects to the Schrader Valve on the fuel rail (of your 4.7L Dodge Dakota or Durango) is a reasonably priced tool too:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
More 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 4.7L Dodge Dakota and Durango tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Do A Manual Cylinder Balance Test (2000-2009 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango).
- How To Resistance Test The Fuel Injectors (2000-2007 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango).
- How To Test The Ignition Coils (2000-2007 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango).
- How Often Should I Replace The Spark Plugs? (2000-2009 4.7L V8 Dodge Dakota And Durango).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!



