TEST 1: Testing For Spark And Fuel Injector Pulses
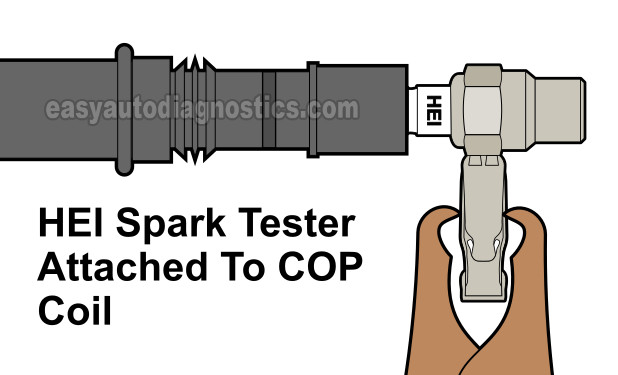
Testing for spark (with a spark tester) and testing the fuel injector pulses (with a Noid light) is the first tests I'm gonna' suggest to you.
If spark and the fuel injector pulses are present, then we can move on with testing the fuel pump pressure.
If spark and the fuel injector pulses ARE NOT present, then the next step is to test the crankshaft position sensor.
NOTE: If you've never done a Noid light test, then you can find out more about it and where to buy a set here: How To Use A Noid Light And Where To Buy It.
Let's get started:
- 1
Remove the #1 cylinder ignition coil and connect the spark tester to it.
NOTE: The ignition coil must remain connected to its electrical connector to test it for spark. - 2
Connect the Noid light to the fuel injector connector for cylinder #1.
- 3
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the spark tester and the Noid light.
- 4
The spark tester should spark and the Noid light should flash On and OFF as your helper cranks the engine.
- 5
Repeat this test on the remaining cylinders.
Let's interpret your spark and Noid light test results:
CASE 1: You got spark and fuel injector pulses at all cylinders. This is the correct and expected test result.
With this test result you can conclude that your Dodge Dakota or Durango's crankshaft position sensor is OK and working correctly.
Your next step is to test the fuel pump's pressure. For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure.
CASE 2: You got NO spark and NO fuel injector pulses at all cylinders. This test result usually tells you that the crankshaft position sensor is defective.
Your next step is to test the crankshaft position sensor.
TEST 2: Testing The Fuel Pump's Pressure
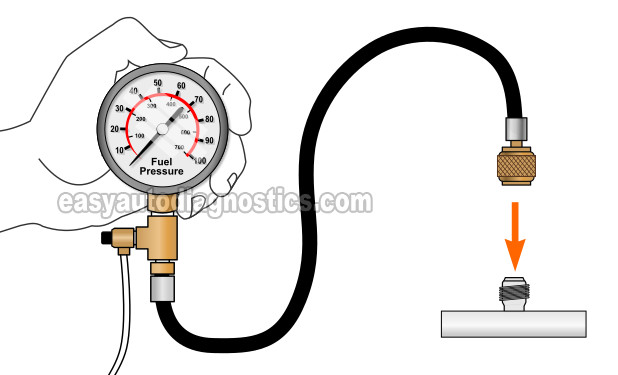
Once you've made sure that your Dodge Dakota or Durango's no-start problem IS NOT being caused by a bad crankshaft position sensor, the next step is to test the fuel pump.
The fuel pump is testing by doing a simple fuel pump pressure test with a fuel pressure test gauge.
This fuel pressure test gauge is connected to a Schrader valve (on the fuel injector rail) to read the fuel pump pressure output.
NOTE: If you need to buy a fuel pressure test gauge kit, take a look at this section: Where To Buy An HEI Spark Tester And A Fuel Pressure Gauge.
NOTE: You can find a more detailed explanation of the fuel pump test here: How To Test The Fuel Pump (4.7L Dodge Dakota, Durango).
Let's get started:
- 1
Place a shop towel around the Schrader valve. The shop towel's job is to absorb any fuel that may leak when doing step 2.
- 2
Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the Schrader valve on your 4.7L Dodge's fuel injector rail.
- 3
When ready, ask your helper to cycle the key ON and OFF but don't crank the engine while you observe the fuel pressure tester's gauge.
Check the connection at the Schrader valve for fuel leaks and if any tighten the fuel pressure a bit more (by hand only) to eliminate them. - 4
Crank and start the engine and check the fuel pressure gauge. Your fuel pressure gauge should register: 44 to 54 PSI with the engine running if the fuel pump is OK.
- 5
If the engine doesn't start, crank the engine enough to get the fuel pressure up. Your fuel pressure gauge should register: 44 to 54 PSI if the fuel pump is OK.
Let's take a look at your fuel pressure test results:
CASE 1: The fuel pressure test gauge registered 0 PSI. This confirms that the no-start problem is caused by a lack of fuel.
CASE 2: The fuel pressure gauge registered 44 to 54 PSI. This fuel pressure gauge result lets you know that the fuel pump is working and delivering enough fuel to the fuel injectors. You can conclude the fuel pump is OK and not behind the no-start problem.
The next test is a compression test. Go to: Making Sure The Engine Has Good Compression.
CASE 3: The fuel pressure is lower than the indicated PSI. This tells you that the fuel pump is defective.
