
This tutorial will help you to test the blower motor on the 1998, 1999, and 2000 3.0L Ford Ranger (Mazda B3000) pickup.
Since the blower motor, on the 3.0L Ford Ranger (Mazda B3000), is a 2 wire electrical component, testing it is a breeze.
In this tutorial, I'll explain how to test it in a step-by-step way. With your test results you'll be able to find out if it's defective or not.
Contents of this tutorial at a glance:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Motor Del Soplador (1998-2000 3.0L Ford Ranger) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Motor Del Soplador (1998-2000 3.0L Ford Ranger) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
NOTE: You can find the blower motor circuit diagram here: Blower Motor Circuit Diagram (1998-2000 3.0L Ford Ranger).
Symptoms Of A Defective Blower Motor
The blower motor on your 1998-2000 3.0L Ford Ranger or Mazda B3000 will fail in one of two ways:
- The blower motor will not run at all.
- The blower motor will run but it will run with a lot of bearing noise.
- The blower motor fuse blows every time it's replaced and the blower motor is turned on.
Blower Motor Basics
As I mentioned before, the blower motor on your 3.0L Ford Ranger or Mazda B3000 pickup is a 2 wire electrical component.
In a nutshell, one wire will supply battery power and the other will supply Ground.
The wire that supplies battery power is the black with light green stripe (BLK/LT GRN) wire. The wire that supplies Ground to the blower motor is the pink with white (PNK/WHT) stripe wire.
To get a good idea of the blower motor circuit, take a look at this simplified wiring diagram: Blower Motor Circuit Diagram (1998-2000 3.0L Ford Ranger).
Where To Buy The Blower Motor
The blower motor on the 1998, 1999, and 2000 3.0L Ford Ranger or Mazda B3000 isn't an expensive component.
You can buy the blower motor in just about any auto parts store. I've included the following links so that you can comparison shop for it and hopefully save a few bucks.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
TEST 1: Testing The Amperage Draw Of The Blower Motor
The fuse that protects the blower motor circuit is a 40 amp fuse (located in the under hood fuse box of your 3.0L Ford Ranger or Mazda B3000).
The fact that this fuse is a 40 amp fuse lets us know that the blower motor needs to run with a current draw of under 40 amps (or the fuse will blow).
When the blower motor is new, it will use a small amount of current. As it ages and wears out it will eventually use 40 or more amps. When this happens this excessive current draw will blow the blower motor fuse, or destroy the blower motor resistor and/or the blower motor switch.
So in this test step, we're gonna' find out if the blower motor is using 40 amps or more. Because if it is, then we can conclude right off the bat that it's defective.
Normally, this test is done with an Ammeter. We will be using a multimeter and Ohm's Law to find out the current draw of the blower motor.
Ohm's law tells us that we can find out the current usage of any electrical component by dividing the voltage it receives by its internal resistance and this is how we're gonna' test the blower motor on your 3.0L Ford Ranger (Mazda B3000) (Ohm's Law: Volts ÷ Resistance = Amps).
NOTE: If you don't have a multimeter and need to buy one, check out my recommendations here: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing.
Let's get started:
- 1
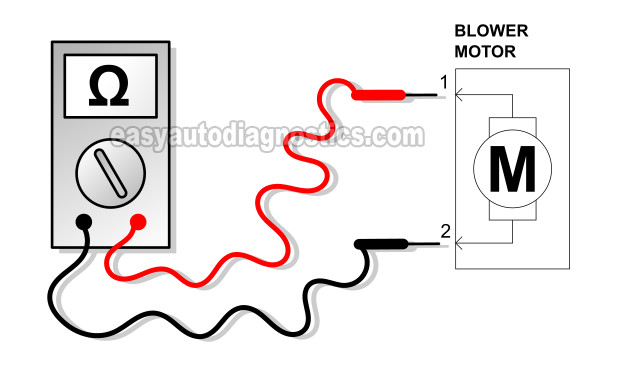
Disconnect the blower motor from its electrical connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Ohms mode.
- 3
Measure the resistance of the blower motor with your multimeter. You'll be testing across the blower motor's connector and not the vehicle's wiring harness connector.
- 4
Divide 12.5 by the resistance value you got in step 3. The result of this calculation is the amount of amperage the blower motor is using.
To be a little more specific: Let's say that the resistance reading was 0.4 Ohms. This is what the math would look like: 12.5 ÷ 0.4 = 31.25 and this would translate to 31.25 Amps.
NOTE: The maximum amperage draw is 40 Amps.
Let's take a look at your test results:
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The blower motor is using less than 40 Amps. This test result lets you know that the blower motor does not have an excessive current draw that could blow the blower motor fuse or burn the blower motor resistor.
The next step is to manually apply battery power and Ground to the blower motor using jumper wires. For this test go to: TEST 2: Applying Power And Ground To The Blower Motor.
CASE 2: The blower motor is using 40 Amps or more. This test result tells you that the blower motor is defective and that it needs to be replaced.
This excessive current draw is usually due to some damaged or worn out component inside the blower motor.



