This tutorial will help you to diagnose and find out if the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is defective or not on your 2005-2006 2.2L Chevrolet Cobalt.
I think you're going to be surprised at how easy it is to test the MAP sensor with a multimeter.
All of the test steps are explained in a step-by-step manner and in plain English.
Contents of this tutorial at a glance:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor MAP (2005-2006 2.2L Chevrolet Cobalt) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor MAP (2005-2006 2.2L Chevrolet Cobalt) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Symptoms Of A Bad MAP Sensor

The fuel injection computer needs to know the barometric pressure of the surrounding air and it also needs to know what load the engine is under. And it's the MAP sensor's job to provide this info to the fuel injection computer.
In a nutshell it provides the barometric pressure reading when you turn the key on and are about to start the engine.
It provides the engine load information once the engine starts and is running. And as you're probably already aware, it calculates this information from the vacuum pressure that is being fed to it from the intake manifold.
Since it is a critical component of the fuel system and engine management system, when it fails you're going to see the check engine light lit up by a MAP sensor trouble code. You'll see one of the following:
- DTC P0107 MAP sensor Circuit Low Voltage.
- DTC P0108 MAP sensor Circuit High Voltage.
You're also gonna' see one or more of the following symptoms:
- Rough idle.
- 'Rotten egg' smell coming from the exhaust.
- Won't pass the state mandated emissions test.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Lack of power, rough idle, or hesitation.
- Engine cranks a long time before starting.
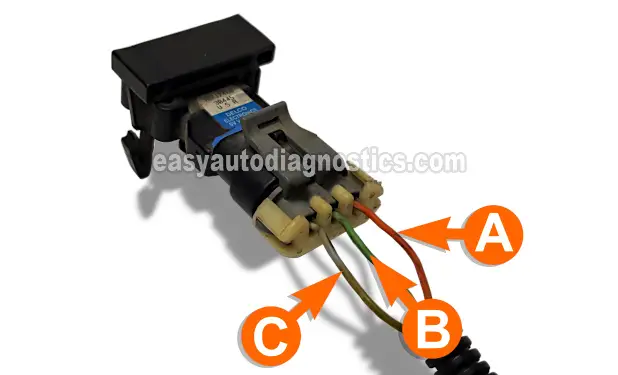
The MAP sensor is a 3 wire type sensor. This means that it has a power wire, a Ground wire and a signal wire. The table below has a brief description of each:
| Terminal | Wire | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | ORG/BLK | Ground |
| B | LT GRN | MAP Signal |
| C | GRY | 5 Volts |
Where To Buy The MAP Sensor And Save
If the MAP sensor is defective and needs to be replaced then take a look at the following links and comparison shop. I think you'll save a few bucks by buying it online (my local auto parts store sells the AC-Delco MAP sensor for $113!! You can buy it online for around $50! -see link below).
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
NOTE: The above MAP sensors fit the 2005-2006 2.2L Chevrolet Cobalt.
TEST 1: Testing The MAP Sensor Voltage Signal

To test the MAP sensor and find out if it's defective (or not) we're going to connect the multimeter to the middle wire of the sensor.
This middle wire is the light green (LT GRN) wire of the connector and is the one that takes the MAP voltage signal to your 2.2L Chevrolet Cobalt's fuel injection computer.
We're then going to apply vacuum to it to see if it's MAP voltage signal decreases as we apply vacuum to it.
Once we release the vacuum that were applying to it, the voltage signal should increase back to the original value you noticed at the beginning of the test.
IMPORTANT: The MAP sensor has to be connected to its electrical connector for this test work. You'll need to use a back probe or a wire piercing probe to access the voltage inside the wires insulation. You can see an example of this tool here: Wire Piercing Probe.
Let's get started:
- 1
Remove the MAP sensor from the intake manifold.
- 2
Connect your vacuum pump to the MAP sensor's vacuum inlet port. Reconnect the MAP sensor to its connector if you disconnected it.
- 3
Set your multimeter's selector to Volts DC mode and with the red test lead, probe the LT GRN wire of the MAP sensor's connector. This wire is identified by the letter B in the photo above.
Remember, the MAP sensor must remain connected to its 3 wire connector. - 4
Ground the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 5
Turn the key ON but don't start the engine. This will power up the MAP sensor and you should see a reading of 4.7 Volts DC on your multimeter.
- 6
Now, apply vacuum to the MAP sensor with the vacuum pump (or your mouth). The voltage signal value should decrease.
If you're using a vacuum pump: At 5 in.Hg → 3.9 Volts. At 10 in.Hg → 3 Volts. At 15 in.Hg → 2.1 Volts. At 20 in.Hg → 1.2 Volts. - 7
Release the vacuum. Once released, your multimeter should show the original voltage value.
Repeat this test step several times making sure that each time the voltage decreases/increases as you apply/release vacuum.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The MAP voltage signal decreased and increased as you applied and released vacuum. This is the correct and expected test result. With this result you can correctly conclude that the MAP sensor, on your 2.2L Chevy Cobalt, is working correctly (not defective).
You can also conclude that the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is receiving 5 Volts DC and Ground from the fuel injection computer. No further testing of the MAP sensor is required.
CASE 2: The MAP voltage signal DID NOT decrease/increase as you applied and released vacuum. You can usually conclude that the MAP sensor defective when it's voltage signal does not decrease/increase as you apply/release vacuum to it.
But in some cases this test result is caused by the MAP sensor not receiving either 5 Volts DC or Ground from the fuel injection computer. So the next step is to make sure that it is getting power and Ground. For this test go to: TEST 2: Verifying MAP Sensor Has 5 Volts And Ground.
CASE 3: The multimeter DID NOT register any voltage. You can usually conclude that the MAP sensor defective when it's voltage signal does not decrease/increase as you apply/release vacuum to it.
But in some cases this test result is caused by the MAP sensor not receiving either 5 Volts DC or Ground from the fuel injection computer. So the next step is to make sure that it is getting power and Ground. For this test go to: TEST 2: Verifying MAP Sensor Has 5 Volts And Ground.




