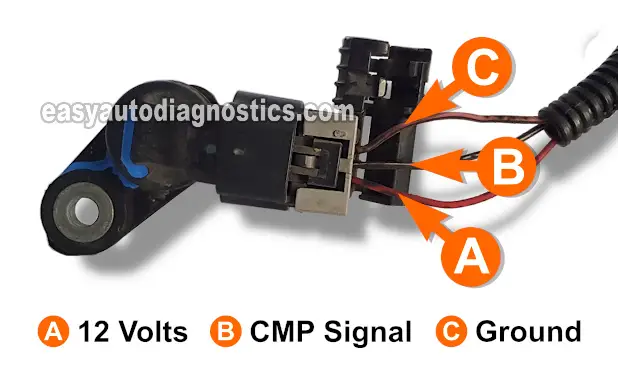
It's not difficult to test the camshaft position (CMP) sensor on your 2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado or GMC Canyon.
The best part is that you don't need any expensive diagnostic test equipment since you can accurately test the CMP sensor with a multimeter.
This tutorial will explain how to test the camshaft position CMP sensor step by step. You'll easily and quickly diagnose the CMP sensor as good or bad with your test results.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Tools Needed To Test The CMP Sensor.
- Symptoms Of A Bad CMP Sensor.
- Where To Buy The Camshaft Position Sensor And Save.
- TEST 1: Testing The CMP Signal With A Multimeter.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The Camshaft Position Sensor Is Getting Power.
- TEST 3: Making Sure The Camshaft Position Sensor Is Getting Ground.
- More 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado (GMC Canyon) Tutorials.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor CMP (2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado, GMC Canyon) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor CMP (2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado, GMC Canyon) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado: 2004, 2005, 2006.
- 2.8L GMC Canyon: 2004, 2005, 2006.
WIRING DIAGRAM: You can find the ignition system wiring diagram here: Ignition System Wiring Diagram (2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado, GMC Canyon).
Tools Needed To Test The CMP Sensor
As mentioned at the beginning of this tutorial, you don't need any expensive tools to test the CMP sensor on your 2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado or GMC Canyon.
Here's what you'll need:
- Multimeter.
- You can use a digital multimeter or an analog multimeter although the digital one is the preferred one.
- If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours, check out my recommendation here: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing.
- 1/2 inch ratchet wrench
- Socket that will fit crankshaft pulley bolt.
- A helper.
Symptoms Of A Bad CMP Sensor
The fuel injection computer on your 2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado or GMC Canyon uses the CMP sensor signal (in conjunction with the CKP sensor signal) to:
- Control the camshaft actuator solenoid.
- Identify the compression stroke of each of the six cylinders.
- To control the sequential injection of fuel of the fuel injectors.
Since the camshaft position sensor is a critical component of the ignition system, when it fails the check engine light will illuminate with a camshaft position sensor trouble code. You'll see one of the following trouble codes:
- P0340 Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Circuit.
- P0341 Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Performance.
You're also gonna' see one or more of the following:
- Bad gas mileage.
- Rough engine idle.
- Hard start (starts after an extended amount of cranking time).
Where To Buy The Camshaft Position Sensor And Save
If the camshaft sensor is defective on your 2004-2006 2.8L Chevrolet Colorado or GMC Canyon, take a look at the following links of known automotive brand CMP sensors (no knock-offs). I think you'll save a few bucks by buying it online:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
TEST 1: Testing The CMP Signal With A Multimeter

When the CMP sensor fails, it stops producing its ON/OFF voltage pulse.
So, to find out if it's good or bad, you'll connect your multimeter to the CMP sensor's signal wire and confirm that the ON/OFF voltage pulse is present (or missing) while manually turning the engine.
Here are some more details about the CMP sensor's ON/OFF voltage pulse:
- ON is when the CMP sensor signal is at 12 Volts DC.
- OFF is when the voltage signal is at 0 Volts DC.
To confirm the ON/OFF voltage pulse, the wire that you're going to connect the multimeter to is the black (BLK) wire of the CMP sensor's three-wire connector (it's labeled with the letter B in the photo above).
If the ON/OFF voltage pulse is missing, the next step is to make sure the CMP sensor is receiving power (in TEST 2).
NOTE: The camshaft position sensor must remain connected to its electrical connector for this test to work. To access the voltage signal within the wire you'll need to use a back probe on the connector or a wire piercing probe. You can see an example of this tool here: Wire Piercing Probe.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disable the ignition system by disconnecting all four ignition coils from their electrical connectors.
This step is important! - 2
Locate the cam sensor's connector and remove some of the plastic wiring loom protector so that you can gain access to the three wires inside.
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the BLK wire identified by the letter B in the photo above.
- 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 5
Turn the key ON but don't crank the engine.
- 6
Manually turn the engine using a 1/2 ratchet and the right socket on the crankshaft pulley.
NOTE: Don't use the starter motor to turn the engine, since your multimeter will not produce the same accurate result as manually turning the engine by hand. - 7
The multimeter should register an ON/OFF 12 Volt DC.
To go into more detail: If the camshaft position sensor is OK, your multimeter will register a reading that changes between 0 Volts and 12 Volts DC as you manually turn the engine.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered the ON/OFF voltage signal as the engine was manually turned. This is the correct and expected test result and lets you know that the camshaft position sensor is working correctly.
This test result also lets you know that the camshaft position sensor is getting both power and Ground from your Colorado or Canyon's fuel injection computer.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register the ON/OFF 12 voltage signal as the engine was manually turned. This means that the camshaft position sensor is not producing a cam signal that the PCM can use.
With this test result alone, you can't condemn the camshaft position sensor just yet. Two more important things have to be checked and they are: 1.) that the camshaft position sensor is getting power and 2.) that it's getting Ground. The next test will help you to verify the power circuit, go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The Camshaft Position Sensor Is Getting Power.



