The throttle position sensor (TPS) can easily be tested with a simple multimeter and in this tutorial, I'm going to show you how to do it.
You'll easily be able to find out if it's bad or not in three simple tests. All of the tests are explained in detail.
And I'm also going to indicate where you can buy the TPS and save a few bucks on its purchase.
Contents of this tutorial at a glance:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Circuit Descriptions.
- Where To Buy The TPS And Save.
- TEST 1: Testing The TPS Voltage Signal.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Receiving 5 Volts.
- TEST 3: Making Sure That The TPS Is Receiving Ground.
- More 3.4L V6 Chevrolet, Pontiac Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.4L V6 Chevrolet Impala: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005.
- 3.4L V6 Chevrolet Monte Carlo: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005.
- 3.4L V6 Chevrolet Lumina Minivan: 1996.
- 3.4L V6 Chevrolet Venture: 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005.
- 3.4L V6 Pontiac Aztek: 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005.
- 3.4L V6 Pontiac Grand Am: 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005.
- 3.4L V6 Pontiac Montana: 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005.
- 3.4L V6 Pontiac Trans Sport: 1996, 1997, 1998.
Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor
As you may already be aware, the throttle position sensor has the job of informing the fuel injection computer the throttle plate's angle.
When the TPS fails, it simply stops measuring and reporting the throttle plate's angle to the fuel injection computer. When this happens you're going to see a trouble code registered in the fuel injection computer.
You'll see one of the following diagnostic trouble codes:
- Code P0121: Throttle Position Sensor Performance Problem.
- Code P0122: Throttle Position Sensor Signal Voltage Low.
- Code P0123: Throttle Position Sensor Signal Voltage High.
- Code P1121: Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent High Voltage.
- Code P1122: Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent Low Voltage.
Besides the check engine light illuminated by a TPS diagnostic trouble code, you'll see one or more of the following symptoms:
- Engine hesitates when you step on the accelerator pedal.
- Lack of power when accelerating the vehicle.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Engine idle either too high or too low.
- Rough engine idle.
- The engine may start and immediately stall.
- The engine cranks but does not start.
You can find out more about the throttle position sensor here: What Does The Throttle Position Sensor Do? (3.4L V6 Chevrolet, Pontiac).
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Circuit Descriptions

The throttle position sensor is a simple 3 wire component that receives 5 Volts and Ground from the fuel injection computer to produce its voltage signal.
To successfully test the TPS, we need to know what each wire does (since we'll be testing them in the following sections of this tutorial).
Here's a brief description of each wire:
| Terminal | Wire | Description |
|---|---|---|
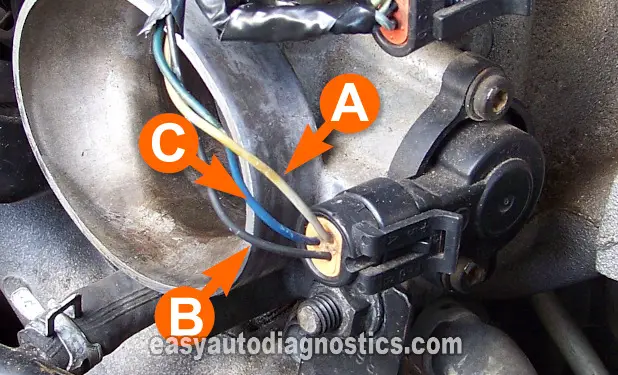
| A | Grey (GRY) | 5 Volts |
| B | Blue (BLU) | TPS Signal |
| C | Black (BLK) | Ground |
Where To Buy The TPS And Save
The GM 3.4L V6 throttle position sensor is not an expensive engine management component. Still, it's important that you replace it with a known automotive brand so that you won't have any complications down the road.
Here are my recommendations:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
NOTE: The TPS above fits all of the 3.4L V6 Chevrolet and Pontiac vehicles covered by this tutorial.
TEST 1: Testing The TPS Voltage Signal

For our first test, we're going to check the voltage signal that the TPS produces with a multimeter.
As I mentioned before, the throttle position sensor's voltage signal increases as the throttle plate is opened and as throttle plate starts to close, the voltage signal decreases.
If the throttle position sensor has failed, it'll usually stay stuck at one voltage value as you open/close the throttle plate.
IMPORTANT: The throttle position sensor must remain connected to its connector to be able to access the signal inside the wire. You'll need to use either a wire piercing probe or a back probe. You can check out what this tool looks like, and where to buy it, here: Wire Piercing Probe.
Let's get started:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the blue (BLU) wire of the TP sensor harness connector.
The BLU wire is identified with the letter C in the photo above.
NOTE: The TPS must remain connected to its connector to test the TPS voltage signal. - 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) post.
- 4
Turn the key on but don't crank or start the engine.
- 5
Manually rotate the throttle plate.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle plate directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 6
The multimeter should show an increasing voltage as you (or your helper) open up the throttle plate.
- 7
The multimeter should show a decreasing voltage as you begin to close the throttle plate.
- 8
Using a screwdriver's handle, gently tap the TP sensor as you open and close the throttle plate and observe the multimeter.
The purpose (of tapping the TP sensor with the screwdriver's handle) is to see if the TP sensor shows gaps in the voltage signal. Why? Because a good TP sensor will show a continuous increasing or decreasing voltage signal even while getting tapped by the screw-driver's handle.
Let's analyze your test results:
CASE 1: The TPS voltage signal increased/decreased as you opened/closed the throttle plate. This is the correct and expected test result and it tells you that the throttle position sensor on your Chevrolet (Pontiac) is functioning correctly.
You can also conclude, with this test result, that the TP sensor is receiving 5 Volts and Ground from the fuel injection computer.
CASE 2: The TPS voltage signal DID NOT increase/decrease as you opened and closed the throttle plate. This test result normally indicates that the TPS has failed.
Before you replace the sensor, it's important that you make sure that it's getting 5 Volts DC and Ground.
The next step is to make sure the TPS is getting power. Go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Receiving 5 Volts.
CASE 3: The multimeter DID NOT register any voltage. This usually means that the TP sensor isn't getting power or Ground.
The next step is to make sure that the TPS is getting 5 Volts. For this test go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Receiving 5 Volts.



