TEST 2: Testing The Power Circuit (12 Volts)
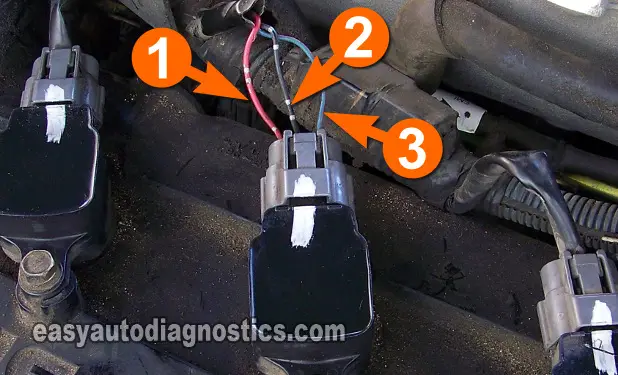
Testing the power (12 Volts) circuit of the ignition coil on your Nissan Altima or Sentra can be accomplished using a multimeter or a 12 Volt test light.
Power (in the form of 10 to 12 Volts DC) is fed to the ignition coil by the wire labeled with the number 1 in the photo above.
NOTE: It's important that you do not probe the front of the connector (or you run the risk of damaging the female terminal). Use an appropriate tool to back probe or pierce the wire to get to the voltage within the wire. You can see an example of a wire piercing probe here: Wire-Piercing Probe.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove enough of the plastic tube, that protects the connector's wires, to expose the 4 wires within it for testing.
- 2
Disconnect the ignition coil form its electrical connector and set the multimeter to Volts DC mode.
- 3
Probe the circuit labeled with the number 1 (see photo above) with the red multimeter test lead (using an appropriate tool to pierce the wire or back probe the connector).
- 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 5
Have your helper turn the key to the ON position but don't crank or start the engine.
- 6
You should see 11-12 Volts on your multimeter if power is present.
Let's see what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 11-12 Volts (or the test light lit up). This test result confirms that the power circuit is OK and is delivering voltage to the ignition coil.
The next step is to test the Ground circuit. For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing The Ground Circuit.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 11-12 Volts (or the test light DID NOT light up). Then the power circuit has a problem. This result eliminates the COP ignition coil as the source of the misfire condition.
The same power circuit is shared by all of the COP ignition coils so this usually means that all 4 ignition coils are not sparking. Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial, your next step is to restore this missing voltage to get the ignition coils to spark again.
TEST 3: Testing The Ground Circuit

In this test, you're gonna' verify that the ignition coil is getting Ground. This is a Chassis Ground.
Ground is fed to the ignition coil by the wire labeled with the number 2 in the photo above.
We'll do a simple multimeter voltage test to check for the presence of this Ground.
Let's get testing:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its connector.
- 2
Put the multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Probe the circuit labeled with the number 2 (see photo above) with the black multimeter test lead (using an appropriate tool to pierce the wire or to back probe the connector).
- 4
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the battery positive (+) terminal.
- 5
Have your helper turn the key to the ON position but don't crank or start the engine.
- 6
You should see 11-12 Volts on your multimeter if the ignition coil is being fed power.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 11-12 Volts (or the test light lit up). This is the correct test result and confirms that the chassis Ground circuit is OK.
The next step is to check that the fuel injection Computer (PCM=Powertrain Control Module) is feeding a Triggering signal to the ignition coil, go to: TEST 4: Ignition Coil Triggering Signal Test.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 11-12 Volts (or the test light DID NOT light up). Then the chassis Ground circuit has a problem. Recheck all of your multimeter connections and retest. If still the multimeter does NOT register the specified voltage, then this result eliminates the COP ignition coil as the source of the misfire condition.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial, your next step is to find out the cause of this missing Ground and restore it.
TEST 4: Ignition Coil Triggering Signal Test

Testing the Triggering Signal that the PCM provides each ignition coil on your Nissan Altima or Sentra can be done in two ways.
The first one presented in this test step is done without using any testing equipment and simply involves swapping the non-sparking coil with one of its neighbors (that does spark).
If the sparking coil spark connected to the non-sparking coil's electrical connector, then we can confidently conclude that the triggering signal is present.
The second way presented in TEST 5 is done with an oscilloscope. Beyond these two techniques, there's no other way to see this Triggering signal.
OK, let's start:
- 1
Disconnect the Coil-On-Plug (COP) ignition coil that didn't fire off spark from its connector and set aside somewhere.
- 2
Remove one of the adjacent COP ignition coils (that you know for a fact that is firing off spark).
- 3
Connect the good COP ignition coil (that sparks) to your HEI spark tester. Now connect it to the connector of the ignition coil that did not spark.
- 4
Have your trusty assistant crank the engine and notice if the HEI spark tester sparks. Be careful, the engine may start.
- 5
If the Triggering signal is present, then the good COP ignition coil will fire spark. If the Triggering signal is missing for any reason, it won't spark.
Let's interpret your ignition coil swap test results:
CASE 1: You got spark. Then the Triggering signal is present. This result indicates, beyond a shadow of a doubt, that the Coil-On-Plug ignition coil on your Nissan Altima or Sentra is bad and needs to be replaced. Replacing the ignition coil will solve the misfire code (P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304) that's lighting up the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on your instrument cluster.
CASE 2: You got NO spark. Re-check all of your connections and repeat the test again. If still no spark, then this results eliminates the ignition coil as the source of the no-spark condition/misfire, since without the Triggering signal the COP ignition coil will not work.
The most likely cause of this missing signal is an open-circuit problem in the signal wire between the coil's connector and the fuel injection computer.

