TEST 1: Spark Test
Whether you know which cylinder is the one that is misfiring or not, I recommend that you test all four cylinders for spark.
As mentioned before, the successful outcome of your troubleshooting/diagnostic lies in the usage of a spark tester.
The following test steps assume that you're gonna' start by testing from the #1 cylinder:
- 1
Remove the spark plug wire (high tension cable) from the spark plug and attach the spark tester to it.
- 2
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal with a battery jump start cable as shown in the photo.
- 3
Have your helper crank the vehicle while you observe the spark tester from a safe distance.
NOTE: The vehicle may or may start, either way be careful. - 4
You're gonna' get one of two results: Spark or no spark.
- 5
Now repeat this test on the other cylinders.
IMPORTANT: Since one Coil-On-Plug ignition coil fires two spark plugs simultaneously, the following result interpretations take into account if the no-spark results that you may have obtained are from the spark tester connected to a spark plug wire or connected directly to the ignition coil. Read all of the options carefully to see which fits your spark result(s):
CASE 1: You got spark from all cylinders. This is the correct test result and indicates that the ignition coils and spark plug wires are OK.
The cause of your misfire condition is not due to a bad ignition coil. If a misfire problem is still present, consult this section: TEST 7: Misfire Due To Carbon Tracks.
CASE 2: You got NO spark from a spark plug wire. Further testing is required to see if this is due to a bad spark plug wire (high tension wire) or if the C.O.P. ignition coil it's attached to is bad.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 5: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil.
CASE 3: You got NO spark from an ignition coil's spark plug boot. This usually indicates that the C.O.P. ignition coil is probably bad.
The good news is that we can make sure it's bad in TEST 6. Go to: TEST 6: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil.
CASE 4: You got NO spark from a spark plug wire and a spark plug boot on the same ignition coil. The next step is to verify that the ignition coil is getting power, Ground and the Triggering signal, go to TEST 2: Testing The Power (12 V) Circuit.
TEST 2: Testing The Power (12 V) Circuit
The Coil-On-Plug (C.O.P.) ignition coil needs 12 Volts to be able to function. The test can be accomplished by testing the C.O.P. coil connected or disconnected to its connector.
The method I recommend to use is with them connected to its connector and with a wire-piercing probe (you can see an example of this tool and where to buy it here: Wire-Piercing Probe.
Now, if you decide to unplug the connector to test the front of the female terminal (of the connector) for 12 Volts, be careful not to damage it.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Re-install the ignition coil back onto its place on the valve cover.
- 2
Disconnect the ignition coil from its 3-wire connector.
- 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 5
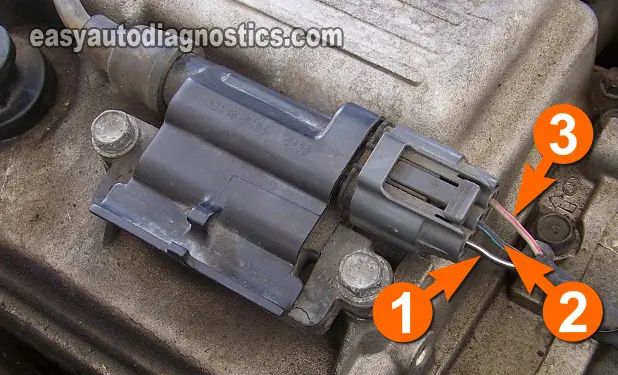
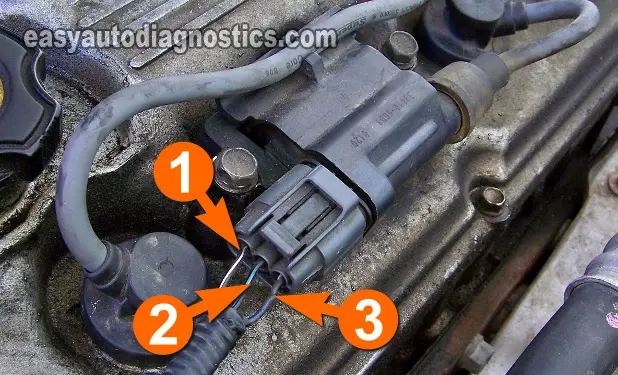
With the red multimeter test lead, gently probe the connector's terminal that connects to the wire labeled with the number 1.
- 6
Have your helper turn the key to the ON position.
- 7
You should see 10 to 12 Volts on your multimeter.
Let's take a look at what your test result means:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts (or the test light lit up). This is the correct test result and it tells you that the ignition coil is receiving power.
The next step is to make sure that the ignition coil is receiving Ground, go to: TEST 3: Testing The Ground Circuit.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts (or the test light DID NOT light up). This tells you that the ignition coil is not receiving power.
This result eliminates the COP ignition coil as the source of the misfire condition. Repairing the cause of this missing voltage will solve the no-spark problem of this ignition coil.
TEST 3: Testing The Ground Circuit
The COP ignition coil needs Ground to be able to function, so in this test section we're gonna' check to see if it's receiving it.
The wire that supplies Ground to the ignition coil is the one labeled with the number 2 in the photo above.
We'll do a simple multimeter voltage test to test for the presence of Ground in the wire.
Let's get testing:
- 1
Put the multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Disconnect the ignition coil from its electrical connector (if it isn't already).
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the battery positive (+) terminal.
- 4
Have your helper turn the key to the ON position.
- 5
With the black multimeter test lead, gently probe the connector's terminal that connects to the wire labeled with the number 2.
- 6
You should see 10 to 12 Volts on your multimeter.
Let's take a look at what your test result means:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct test result and it lets you know that Ground is present in the wire.
The next step is to test for the presence of the ignition coil's Triggering signal, go to: TEST 4: Triggering Signal Test.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts. This confirms that the ignition coil is not receiving Ground. Without it, the ignition coil will not fire spark.
This result eliminates the COP ignition coil as the source of the misfire condition. Repairing the cause of this missing Ground will solve the no-spark problem of this ignition coil.