TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting 12 Volts

For our second test, we'll check that the ignition coil that didn't spark is getting power (10 to 12 Volts) on the wire labeled with the number 3 (in the photo below).
That the coil is getting Ground on the wire labeled with the number 2 and then finally test the continuity of the Switching Signal wire labeled with the number 1.
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil that did not spark from it's 3 wire electrical connector.
- 2
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) post.
- 3
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 4
Gently probe the female terminal of the connector that connects to the wire labeled with the number 3 with the red multimeter test lead.
- 5
The multimeter should register 10 to 12 Volts.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct test result and it confirms that the ignition coil is getting power.
The next step is check that the ignition coil is getting Ground. Go to: TEST 3: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Ground.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts. Without this voltage the ignition coil will not function.
Your next step is to restore this missing voltage to the circuit to get the ignition coil to spark again and resolve the misfire condition.
TEST 3: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Ground

So far, you've confirmed that the non-sparking ignition coil is getting power in TEST 2.
In this test section, we'll check that the ignition coil is getting Ground on the wire labeled with the number 2.
OK, let's get started:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil that did not spark from it's 3 wire electrical connector.
- 2
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the battery positive (+) post.
- 3
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 4
Gently probe the female terminal of the connector that connects to the wire labeled with the number 2 with the black multimeter test lead.
- 5
The multimeter should register 10 to 12 Volts.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct test result and it confirms that the ignition coil is getting Ground.
The next step is check that the ignition coil is getting an activation signal. Go to: TEST 4: Swapping The Ignition Coils.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts. Without Ground the ignition coil will not function.
Your next step is to restore this missing Ground to the circuit to get the ignition coil to spark again and resolve the misfire condition.
TEST 4: Swapping The Ignition Coils
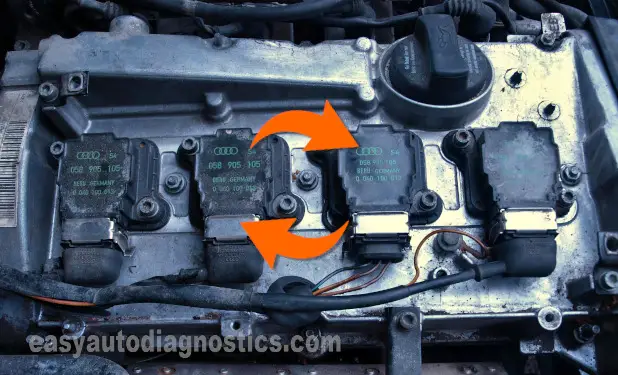
Up to this point, you've confirmed that the non-sparking ignition coil is getting power and Ground. Now we need to see if it's getting an activation signal from the ignition control module.
We can do this one of several ways, but the easiest way to confirm the presence of the ignition coil's activation signal is by simply swapping it with one of its neighbors (that is sparking).
If the sparking ignition coil sparks connected to the non-sparking ignition coil's electrical connector, you can conclude it's getting an activation signal from the ignition control module.
Alright, this is what you'll need to do:
- 1
Remove the non-sparking ignition coil from its place on the engine.
- 2
Unplug and remove one of the other 3 'good' sparking ignition coils.
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the 'good' ignition coil.
- 4
Connect the electrical connector of the 'good' ignition coil to the non-sparking ignition coil.
- 5
Install and bolt down the non-sparking ignition coil in the spark plug hole where the 'good' ignition coil use to be.
Connect it to the electrical connector that the 'good' ignition coil used to be connected to. - 6
When ready, have your helper crank the engine.
- 7
The 'good' ignition coil should spark.
OK, let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The ignition coil sparked. This is the correct and expected test result and it tells you that the ignition control module is providing an activation signal to the ignition coil.
This test result also tells you that the ignition coil that did not spark in TEST 1 is bad if you have:
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is not sparking (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is getting power (TEST 2).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is getting Ground (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is receiving and activation signal from the ignition control module (this test section).
CASE 2: The ignition coil DID NOT spark. This test result confirms that the ignition coil's activation signal is missing.
This usually means that the ignition control module is bad but to make absolutely certain, we need to make sure that the wire that delivers the activation signal is OK. For this test go to: TEST 5: Testing The Continuity Of The Activation Signal Circuit.
