What Tests Can I Perform To Find The Cause Of The Misfire Condition?
Over the years that I've been working on cars, I've found that there's a specific and logical step by step way of diagnosing a misfire. Basically, this is a strategy of tests that will nail down the exact cause of the misfire.
In this section, I'm gonna' share this strategy of tests with you. I'm certain they'll help you to locate the component causing the problem.
STEP 1: Identify the dead cylinder. This usually means reading the misfire diagnostic trouble codes with a scan tool. Then by matching the misfire code to its engine cylinder using an illustration of the engine cylinders.
If no misfire trouble codes are found, you'll need to do a manual cylinder balance test by unplugging one fuel injector at a time (to see which one has NO effect on the engine's idle).
Once you've found the 'dead' cylinder, the next step is to make sure its COP ignition coil is sparking.
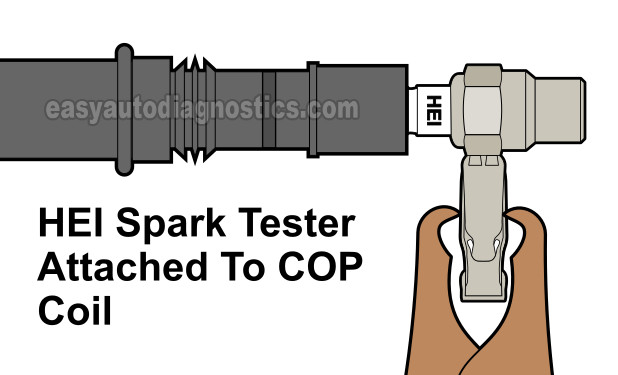
STEP 2: Check the COP ignition coil for spark . Since the majority of misfires are caused by a failed component in the ignition system, it's important to make sure that the misfiring cylinder is getting spark. You should:
- Perform a spark test (using a dedicated spark tester) on the ignition coil of the 'dead' cylinder..
- Testing for spark with a spark tester is the most important first test since you'll know right away if the misfire is due to a lack of spark.
- Check to see if the 'dead' cylinder's COP ignition coil boot and spark plug are swimming in engine oil from a leaking valve cover gasket.
- If the 'dead' cylinder is getting spark (as confirmed by your spark test), the next step is to remove the spark plug and check them for wear and tear, carbon tracks, anti-freeze, etc.
- You can find out about carbon tracks here: Carbon Tracks Are A Common Cause Of Ignition Misfires.
If all your tests indicate that spark is reaching the 'dead' cylinder and all of the ignition system components (spark plug, spark plug wire, distributor cap, etc,) are OK, then the next step is checking that cylinder's fuel injector.
STEP 3: Test the fuel injector. If the ignition system is not the cause of the misfire, then the next step is to check the 'dead' cylinder's fuel injector.
You'll need to:
- Do a resistance test on the fuel injector to make sure it's internal coil does not have a short-circuit or an open-circuit.
- Do a Noid light test on the fuel injector's connector to make sure your Dodge's fuel injection computer is activating it.
- You can find the fuel injector resistance test here:
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (Dodge, Jeep 4.7L V8) (at: troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
If after making sure that the fuel injector's internal resistance matches the other 3 and that the fuel injection computer is activating it, the next step is checking the 'dead' cylinder's compression.
STEP 4: Test the compression of the cylinder. After eliminating the ignition system and the fuel system as the sources of the misfire, we now need to make sure that the 'dead' cylinder is compressing the air that's entering it.
You'll need to:
- Check all cylinders with a compression tester. You can find the test explained here: How To Check Engine Compression (Dodge, Jeep 4.7L V8) (at: troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
- Check for vacuum leaks.
STEP 5: Check the intake manifold gaskets for vacuum leaks. The intake manifold uses rubber gaskets that will harden with time and cause vacuum leaks. These vacuum leaks will cause a rough idle condition (especially when the engine is cold) and eventually a misfire condition.
Troubleshooting a misfire is not a complicated thing. The key is to test the components and eliminate them as good or bad (and thus causing the misfire problem). Depending on your level of 'wrenching' experience, this is something that you can accomplish without taking it to the shop.
What Tools Do I Need To Test A Misfire?
To perform the misfire diagnostic tests mentioned in the previous section, you're gonna' need tools.
Depending on what the root cause of the misfire is, you may need several tools. Most of these you can buy online, none of these will break the bank and I'll make some recommendations on them. Here's a guide to some of the basic tools that can be and are used:
- Ignition System Tests:
- Spark tester.
- Multimeter.
- Test light.
- Fuel System Tests:
- Noid light.
- Fuel pressure gauge.
- Multimeter.
- Engine Mechanical Tests:
- Compression tester.
Keep in mind that using the right tool for the job will save you time, frustration, and /or keep you from damaging the component that you're testing.
More 4.7L Dodge Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 4.7L Dodge tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (2000-2001 4.7L Dakota, Durango).
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (2000-2007 4.7L Dodge).
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (Dodge, Jeep 4.7L V8) (at troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (4.7L Chrysler, Dodge, Jeep) (at troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
- How To Test The COP Ignition Coils (Chrysler, Dodge, Jeep 4.7L) (at troubleshootmyvehicle.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

