
Testing the ignition coil pack on the 1997-2000 4.2L F150 or F250 really isn't as difficult as it appears. In this tutorial, I'll walk you through the entire testing process step-by-step.
I've included as much information as possible so you'll be able to determine if the coil pack is working properly and firing spark to all six cylinders or if it has failed.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil Pack.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
- Circuit Descriptions Of The Ford Coil Pack Connector.
- Basic Operating Theory Of The Ford Coil Pack.
- Precautions, Do's And Don'ts.
- TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wire.
- TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
- TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack (Paired Cylinders).
- TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit.
- TEST 5: Activation Signal For Cylinders 1 And 5.
- TEST 6: Activation Signal For Cylinders 2 And 6.
- TEST 7: Activation Signal For Cylinders 3 And 4.
- TEST 8: Checking The IC Activation Signals.
- Other Things That Can Cause A Misfire.
- More 4.2L Ford F150 Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 4.2L V6 Ford F150: 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000.
- 4.2L V6 Ford F250 Light Duty: 1998.
WIRING DIAGRAMS: The following diagrams may come in handy:
- Ignition System Circuit Wiring Diagram (1997-1999 4.2L V6 Ford F150, F250).
- Ignition System Circuit Wiring Diagram (2000 4.2L V6 Ford F150).
2001-2008 Coil Pack Tests: The ignition coil pack on the 2001-2008 4.2L V6 F150 is a different/updated style. You can find the tutorial for it here:
E-Series Vans: You can find the ignition coil pack test tutorial here:
- How To Test The Ignition Coils (1997-2000 4.2L V6 Ford E150, E250) (at: troubleshootmyvehicle.com).
Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil Pack
The ignition coil pack is a key component of the ignition system. Its job is to create the spark the engine's six spark plugs need to ignite the air/fuel mixture within their engine cylinder. This spark gets delivered to the spark plugs by the spark plug wires (also known as high tension wires).
When the ignition coil pack fails or the spark plug wires go bad, you'll notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Misfire Codes: You'll see one or more of the following codes:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder 2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder 3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder 4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder 5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder 6 Misfire.
- Engine Performance Issues: You may see one or more of the following:
- The engine idles rough and wants to stall.
- When you accelerate the van, it has no power.
- Bad Gas Mileage: Since the engine isn't running all six cylinders, it has to work harder, thus consuming more fuel.
- Engine No-Start: The engine will crank but not start (if more than 3 ignition coil towers are not firing spark).
- Rotten egg smell: You'll notice a rotten egg smell coming out of the tailpipe from the unburned fuel overloading the catalytic converter.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
To troubleshoot the ignition coil pack and the spark plug wires, you're gonna need a few specific tools. Don't worry, these are inexpensive tools. Here's the list:
- A multimeter.
- A 12 Volt automotive test light.
- An HEI spark tester
- This tool is a must have (don't have an HEI spark tester? Need to buy one? You can buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester).
- Battery jump start cables.
You're also gonna need someone to help you crank the engine while you observer the spark tester.
I want to point out that to diagnose a bad ignition coil pack on your Ford pickup, an HEI spark tester is a must have tool. Using the wrong tool or method will have you chasing a wrong diagnostic test conclusion and effectively wasting your time and money.
Circuit Descriptions Of The Ford Coil Pack Connector
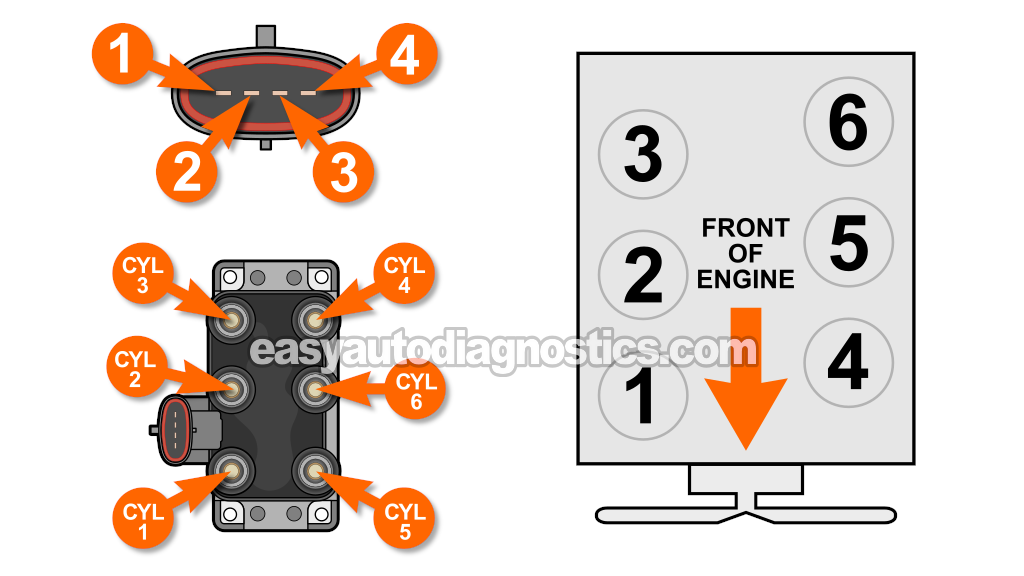
The ignition coil pack has a 4-wire connector that connects to it. Each wire delivers or carries a specific signal. Here's a brief description of each:
| Terminal | Wire | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red with light green stripe (RED/LT GRN) | 12 Volts (in START/RUN) |
| 2 | Dark blue with light green stripe (DK BLU/LT GRN) | IC Activation Signal Cylinders 1 & 5 |
| 3 | Pink with white stripe (PNK/WHT) | IC Activation Signal Cylinders 2 & 6 |
| 4 | Red with light blue stripe (RED/LT BLU) | IC Activation Signal Cylinders 3 & 4 |
Basic Operating Theory Of The Ford Coil Pack
The component that controls when the ignition coil pack fires spark is your Ford pickup's fuel injection computer (Powertrain Control Module -PCM for short). In a nutshell, here's what happens when you turn the key to crank and start the engine:
- The ignition coil pack gets power in the form of 12 Volts.
- These 12 Volts get fed to each of the three individual ignition coils that make up the coil pack. Each ignition coil within the coil pack has two towers that feed spark to two cylinders at the same time.
- These 12 Volts are known as the ignition coil's primary current.
- The engine starts to crank, inducing the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to start producing and sending its CKP signal to the PCM.
- Once the PCM receives the CKP signal (along with other necessary sensor information), it starts to switch each ignition coil's primary current ON and OFF.
- This switching ON and OFF the primary current (by the PCM) is accomplished by interrupting its Ground path. It's this action that makes the ignition coil fire spark and is what I refer to as the ignition coil's activation signal.
- It's important to note that each ignition coil gets its own activation signal from the PCM.
- As each ignition coil, within the ignition coil pack, gets its activation signal, it fires spark to two 'paired cylinders' at the exact same time (in what's known as the Waste Spark method).
- Cylinders 1 and 5 get spark simultaneously from coil 1.
- Cylinders 2 and 6 get spark simultaneously from coil 3.
- Cylinders 3 and 4 get spark simultaneously from coil 2.
You don't need to memorize any of this, but the one thing you do need to keep in mind is that the two cylinders that get spark at exact same time are known as 'paired cylinders'.
These are the paired cylinders:
- Cylinders 1 and 5.
- Cylinders 2 and 6.
- Cylinders 3 and 4.
Precautions, Do's And Don'ts
To test the ignition coil pack (and the spark plug wires), you'll need to crank the engine. Please take all necessary safety precautions to keep your fingers, hands and entire self safe. Here are a few other tips and suggestions:
- Use A Spark Tester To Check For Spark: Using a spark tester will make the task safer and give you the most accurate test result. I suggest keeping in mind the following:
- Do not use a regular spark plug instead of a spark tester to test for spark.
- Do not remove the spark plug wire from the spark plug or the ignition coil while the engine is cranking to test for spark.
- Use Spark Plug Wire Pullers: Use a spark plug wire puller to disconnect the high tension wires from the spark plug. This tip will save you a headache since you'll avoid the hassle of having the wire's metal terminal staying stuck on the spark plug!
- Start Your Diagnostic From TEST 1: Start your diagnostic from TEST 1, don't skip around from test to test unless instructed to do so by the TEST you're currently on.
- Use The Correct Tool: Using the recommended/indicated tools for all of your tests will help you avoid complications.
TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wire
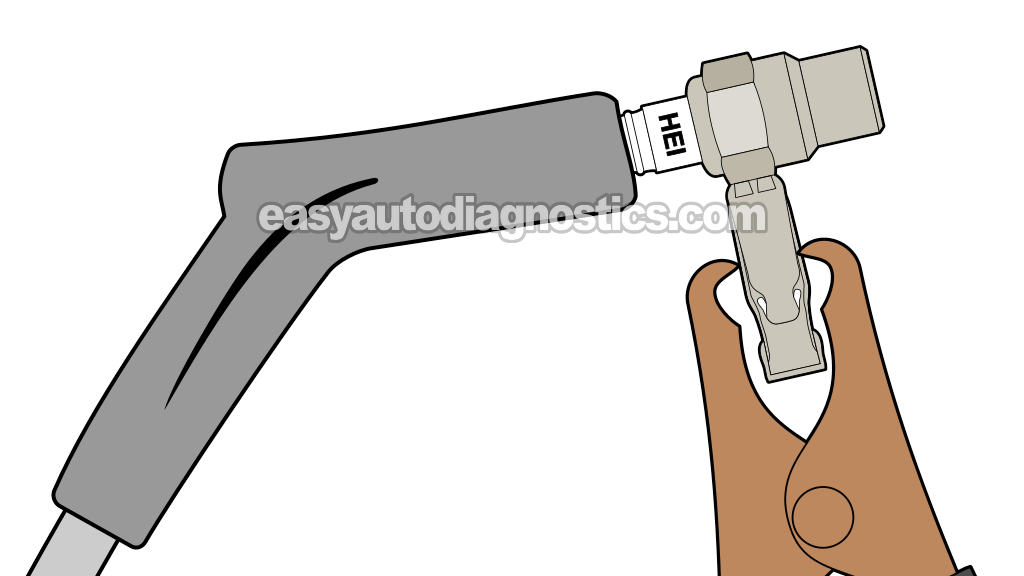
The first order of business is to check all six spark plug wires for spark. For this, you'll need to disconnect the spark plug wire from its spark plug and then connect a spark tester to it. One super important thing to keep in mind is that removing the spark plug wire from the plug without using a spark plug wire puller may damage it.
To be a bit more specific, if you disconnect the spark plug wire from the spark plug without a spark plug wire puller, its metal terminal usually stays stuck to the spark plug. If this happens, you'll either have to reattach the metal terminal back onto the wire, which isn't difficult but is an annoying and time-consuming process, or you might need to replace the entire wire set.
I'm not suggesting you purchase the spark plug wire puller right now, just pointing out that this is a common problem with these spark plug wires. Using a spark plug wire puller tool is the best way to avoid this headache.
Also, it's critical that you use a spark tester -any spark tester will do. The one I own and use is the HEI spark tester because this bad boy is accurate and I don't need to adjust it or interpret the color of the spark. You can see it and buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the spark plug wire (high tension cable) from the spark plug.
- 2
Attach the a spark tester to high tension wire.
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal with a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the vehicle as you stand at a safe distance from the engine.
The engine may or may not start, either way be careful. - 5
As the vehicle cranks or starts, observe the spark tester.
- 6
You're gonna get one of two results: Spark or NO spark.
- 7
Now repeat this test on the other spark plug wires.
IMPORTANT: Read the following options carefully to interpret your NO SPARK result or results. Remember that some cylinders get spark from the same ignition coil within the coil pack (since the coil pack is made up of 3 individual ignition coils that have two towers each). So if you get a NO SPARK result from two spark plug wires, you need to verify if they're from paired cylinders or from unpaired cylinders.
CASE 1: You got spark from all six spark plug wires. This tells you that the ignition coil pack and spark plug wires are OK. The cause of your misfire condition isn't due to a bad ignition coil pack. Go to: Other Things That Can Cause A Misfire to see further tips and suggestions.
CASE 2: You got NO spark from only one spark plug wire. The next step is to check for spark directly on the coil pack tower that feeds that spark plug wire with spark. Go to: TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 3: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires and they connect to spark plugs for paired cylinders 1 & 5. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 4: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires and they connect to spark plugs for paired cylinders 2 & 6. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 5: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires and they connect to spark plugs for paired cylinders 3 & 4. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 6: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires that DO NOT connect to paired cylinders. The next step is to test each coil pack tower directly for spark one at a time.
For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 7: You got NO spark from none of the spark plug wires. This usually indicates that power is missing from the power circuit or that the crankshaft position sensor is bad.
To find out, go to: TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit.
