The fuel pump test is probably one of the easiest tests you can perform on your 1998-2001 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger (Mazda B3000) and it also doesn't require expensive tools.
In this tutorial, I'll show you how to check the fuel pump pressure with a fuel pressure gauge. You'll quickly determine if a fuel pump failure is causing an engine no-start problem or an engine performance problem.
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger: 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
- 3.0L Mazda B3000: 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
NOTE: The following tutorials will help you test the fuel pump on the 1991-1997 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger:
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1991-1994 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1995-1997 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger).
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Pump
A bad fuel pump usually causes one of two problems:
- An engine no-start problem.
- An engine performance problem.
Yes, a fuel pump can fail and the engine can still start and run. Of course, the engine won't run optimally as the failed fuel pump will cause engine performance problems.
In these cases, the fuel pump will deliver just enough fuel for the engine, but once the engine is under load, one or more of the following problems will occur:
- Engine takes longer than usual to start (extended cranking).
- Engine idle is very rough.
- Engine backfires thru' the intake manifold under load.
- Engine starts, then dies.
- Lack of power when accelerating the engine under load.
- The check engine light illuminated by lean air/fuel mixture diagnostic trouble codes.
Whether the fuel pump is causing an engine starting problem or an engine performance problem, a fuel pump pressure test will help you determine the source of the problem.
Where To Buy A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge
The following fuel pressure tester kits include the Ford Schrader valve adapter you need to test the fuel pressure on your 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger and Mazda B3000.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you. Thanks for your support —it really means a lot!
Fuel Pump Pressure Specification
| Ford | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year/Engine/Model | KOEO | KOER |
| 1998 3.0L Ranger (Gasoline) | 56-72 PSI | |
| 1998 3.0L Ranger (Flex Fuel) | 47-63 PSI | |
| 1999 3.0L Ranger | 55-75 PSI | 47-63 PSI |
| 2000 3.0L Ranger (Gasoline) | 56-72 PSI | 56-72 PSI |
| 2000 3.0L Ranger (Flex Fuel) | 47-63 PSI | 47-63 PSI |
| 2001 3.0L Ranger | 60-65 PSI | 60-65 PSI |
| Mazda | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year/Engine/Model | KOEO | KOER |
| 1998 3.0L B3000 (Gasoline) | 56-72 PSI | |
| 1998 3.0L B3000 (Flex Fuel) | 47-63 PSI | |
| 1999 3.0L B3000 | 55-75 PSI | 47-63 PSI |
| 2000 3.0L B3000 (Gasoline) | 56-72 PSI | 56-72 PSI |
| 2000 3.0L B3000 (Flex Fuel) | 47-63 PSI | 47-63 PSI |
| 2001 3.0L B3000 | 60-65 PSI | 60-65 PSI |
KOEO = Key On Engine Off.
KOER = Key On Engine Running.
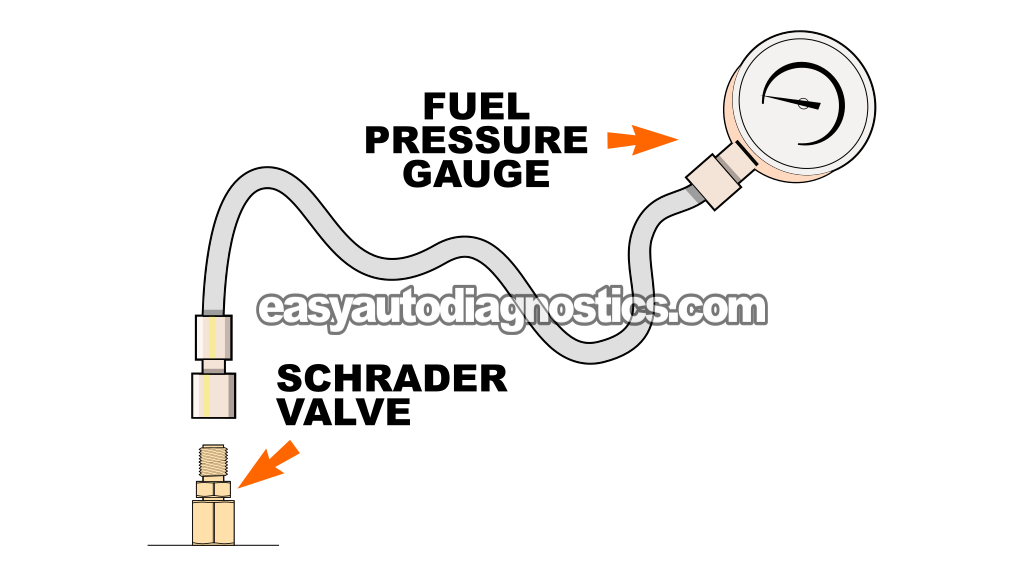
Using A Fuel Pump Pressure Tester To Test The Fuel Pump
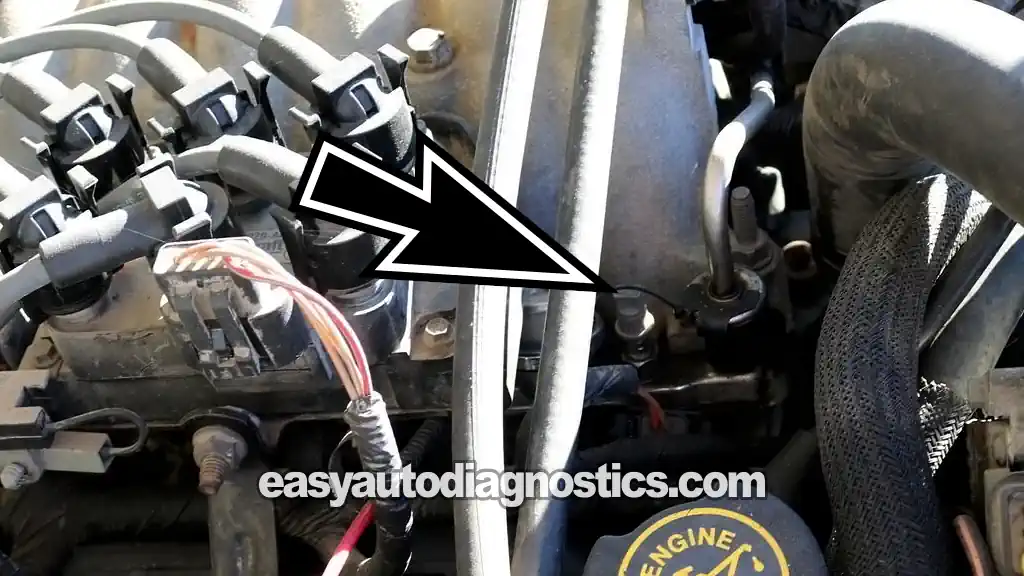
Testing the fuel pump pressure simply involves connecting a fuel pressure test gauge to the Schrader valve located on the fuel injector rail.
If the fuel pump is producing the correct pressure, your fuel pressure gauge will show the posted fuel pressure specification when you crank or start the engine.
If the fuel pump has failed, your tester will report a fuel pressure below the posted fuel pressure specification or 0 PSI.
IMPORTANT: If the engine does not start, check the fuel pump inertia switch and reset it if necessary. A fuel pump inertia switch activated by a vehicle impact (or even just hitting the curb) will cut power to the fuel pump and cause an engine no-start problem. You can find out more about it and its location here: Fuel Pump Inertia Switch Commonly Asked Questions (1991-2008 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the plastic dust cap from the Schrader valve.
- 2
Place a shop towel around the Schrader valve.
The shop towel's job is to absorb any fuel that may leak when doing step 2. - 3
Connect the fuel pressure test gauge to the Schrader valve.
NOTE: The Schrader valve is located on the fuel injector rail next to the fuel pressure regulator and on the passenger side of the engine (see photo 2 of 2 in the image viewer above). - 4
When ready, ask your helper to cycle the key ON and OFF but don't crank the engine while you observe the fuel pressure tester's gauge.
Check your connections for fuel leaks. Resolve any fuel leaks before continuing to the next step. - 5
Crank the engine and check the fuel pressure gauge.
- 6
Your fuel pressure gauge should register the specified fuel pressure.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The fuel pressure gauge shows 0 PSI. This confirms that the engine starting problem is caused by lack of fuel.
This usually means that the fuel pump is defective and needs to be replaced.
CASE 2: The fuel pressure gauge registered the specified fuel pressure specification. This test result lets you know that the fuel pump is working properly.
You can conclude that the fuel pump is fine and is not responsible for the engine starting problem.
CASE 3: The fuel pressure gauge has registered a fuel pressure well below specification. This test result indicates that the fuel pump is defective.
Using Starting Fluid

The starting fluid test is usually the first test I run when beginning an engine no-start diagnostic.
This test simply involves spraying starting fluid into the engine's throttle body and then starting the engine.
If a lack of fuel is causing the engine to not start, the starting fluid will cause the engine to start and run for a few seconds.
While this is not the most accurate way to diagnose an engine no-start problem caused by a bad fuel pump, it will definitely steer your troubleshooting efforts in the right direction.
IMPORTANT: The accuracy of the starting fluid test depends on all six spark plugs delivering spark to their cylinders. If you haven't checked the spark plug wires for spark (using a spark tester), do so before beginning the test. Otherwise, you may get a false positive result with this test.
Alright, let's get the ball rolling:
- 1
Remove the intake air duct from the throttle body.
You don't have to completely remove it, since you'll have to reconnect it in one of the next steps. - 2
Open the throttle manually, and spray starting fluid down the bore.
When you have sprayed a good squirt of starting fluid, quickly reconnect the air duct to the throttle body (you don't have to tighten the hose clamp).
Reconnecting the intake air duct is a very important safety precaution in case you get a back-fire thru' the intake manifold. - 3
Crank the engine once the intake air duct is back on the throttle body.
- 4
You'll get one of two results:
1.) The engine will start momentarily and after a few seconds will die.
2.) The engine will only crank but not start at all.
OK, let's analyze your test result:
CASE 1: The engine started and ran for a few seconds. This result confirms that the engine no-start problem is caused by a lack of fuel.
Next, I suggest that you test the fuel pump fuel pressure with a tester. For this test go to: Using A Fuel Pump Pressure Tester To Test The Fuel Pump.
CASE 2: The engine DID NOT start, even briefly. This result generally tells you that a lack of fuel is NOT the reason the engine won't start.
Remember what I said about this test not being very accurate? Well, I suggest you do one more test and test the fuel pressure with a fuel pressure tester. For this test go to: Using A Fuel Pump Pressure Tester To Test The Fuel Pump.
More 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger And Mazda B3000 tutorials here:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find there:
- How To Test The Engine Compression (1991-2008 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger).
- How To Test The Blower Motor (1998-2000 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1991-1994 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger) .
- How To Test The MAF Sensor (1998-2001 3.0L V6 Ford Ranger).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!