TEST 7: Checking For Spark Directly On The 1/4 Ignition Coil Towers (Intake Side)
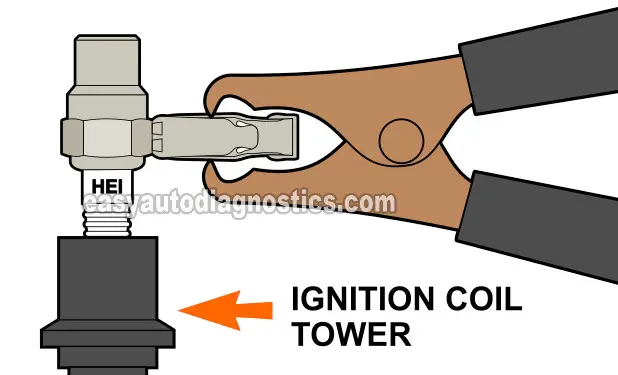
In this test section, we'll check for spark directly at the ignition coil towers for cylinders 1 and 4 (intake side spark plugs).
In order to get the correct result from this test, it is important that you perform this test with a spark tester.
If you don't have one, I recommend the HEI Spark Tester and you can buy one here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
NOTE: To perform this test, you'll need to crank the engine. Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions!
OK, to start this test, this is what you need to do:
- 1
Disconnect the spark plug wire from the cylinder 1 ignition coil tower.
NOTE: This test is performed on the intake side ignition coil pack. - 2
Place your spark tester in the ignition coil tower (see the illustration above).
- 3
Ground the spark tester directly on the battery negative (-) post using a jump-start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you observer the spark tester.
- 5
The spark tester should spark.
- 6
Repeat steps 1 through 5 on the cylinder 4 ignition coil tower.
OK, let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked. This test result tells you the spark plug wires are bad.
Replace all of the spark plug wires if you have:
- Confirmed that the intake side spark plug wires for cylinders 1 and 4 ARE NOT sparking (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the intake side ignition coil pack towers for cylinders 1 and 4 are sparking (this test section).
Replacing all of the spark plug wires should solve the issue.
CASE 2: The spark tester DID NOT spark. This test result eliminates the spark plug wires as bad, since the ignition coil towers are not sparking.
Your next step is to check the ignition coil pack is getting the 1/4 ignition coil control signal. Go to: TEST 13: Cylinders 1 And 4 Activation Signal (Intake Side).
TEST 8: Checking For Spark Directly On The 2/3 Ignition Coil Towers (Intake Side)

In this test section, we'll check for spark directly on the ignition coil towers for cylinders 2 and 3 (intake side spark plugs).
NOTE: To perform this test, you'll need to crank the engine in your 2.3L Ford Ranger (Ford Mustang, Mazda B2300). Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions!
OK, to start this test, this is what you need to do:
- 1
Disconnect the spark plug wire from the cylinder 2 ignition coil tower.
NOTE: This test is performed on the intake side ignition coil pack. - 2
Place your spark tester in the ignition coil tower (see the illustration above).
- 3
Ground the spark tester directly on the battery negative (-) post using a jump-start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you observer the spark tester.
- 5
The spark tester should spark.
- 6
Repeat steps 1 through 5 on the cylinder 3 ignition coil tower.
OK, let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked. This test result tells you the spark plug wires are bad.
Replace all of the spark plug wires if you have:
- Confirmed that the intake side spark plug wires for cylinders 2 and 3 ARE NOT sparking (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the intake side ignition coil pack towers for cylinders 2 and 3 are sparking (this test section).
Replacing all of the spark plug wires should solve the issue.
CASE 2: The spark tester DID NOT spark. This test result eliminates the spark plug wires as bad, since the ignition coil towers are not sparking.
Your next step is to check the ignition coil pack is getting the 2/3 ignition coil control signal. Go to: TEST 14: Cylinders 2 And 3 Activation Signal (Intake Side).
TEST 9: Testing The CKP Signal With A Multimeter
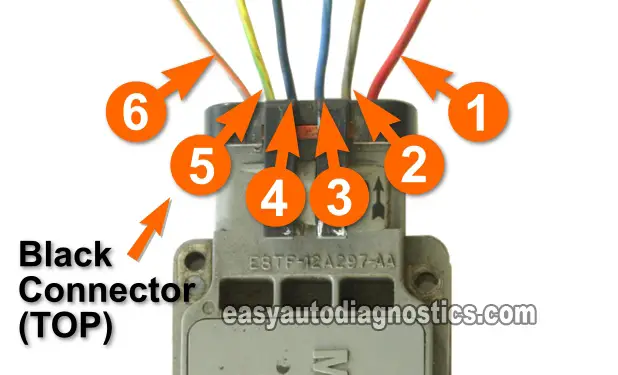
The ignition control module on your 2.3L Ford Ranger (Ford Mustang, Mazda B2300) requires 2 signals from the crankshaft position sensor to activate the ignition coils.
These two signals are:
- The CKP signal (Crankshaft Position signal).
- The CID signal (Cylinder Identification signal).
In this test section you'll test the CKP signal with a multimeter while turning the engine by hand (you cannot use the starter motor).
The CKP signal is fed to the ICM via the top ignition module connector wire labeled number 4 in the photo above.
IMPORTANT: The ignition control module must remain connected to its connectors for this test to work. You'll need to use a back probe on the connector or a wire piercing probe on the wire. You can see an example of this tool here: Wire Piercing Tool
OK, to get the CKP signal test going, this are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the spark plugs on the exhaust manifold side of the engine.
NOTE: This will make it easier to turn the engine by hand. - 2
Connect your multimeter to the wire labeled with the number 4 of the top ignition module connector.
IMPORTANT: The ignition control module must remain connected to its connectors. - 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Slowly turn the engine by hand.
You can do this by using a ratchet wrench and the appropriate socket on the crankshaft pulley.
NOTE: Don't crank the engine with the starter motor as this will not give you the correct test result. - 5
Your multimeter will read an ON/OFF voltage of 10 to 12 Volts.
ON = 10-12 Volts. OFF = 0 Volts.
OK, let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered an ON/OFF voltage of 10-12 Volts and 0 Volts . This tells you that the CKP sensor is creating the CKP signal.
The next step, is to make sure that the crankshaft position sensor is creating the CID signal. Go to: TEST 10: Testing The CID Crankshaft Position Sensor Signal.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT record any voltage changes. This test result tells you the crankshaft position is not generating a CKP signal.
Double-check that you're testing the correct wire on the top ignition control module connector.
If you still don't see the ON/OFF voltage signal on your multimeter, then the crankshaft position sensor is bad and needs to be replaced.
Replacing the CKP sensor (which is located behind the timing belt) will get your 2.3L Ford Ranger (Ford Mustang, Mazda B2300) sparking and starting.

