TEST 7: Power Transistor Switching Signal Output
NOTE: This test tests for the ignition coil's activation signal directly at the power transistor's electrical connector. TEST 6 does the same thing, but tests for the ignition coil's activation signal at the ignition coil's electrical connector.
Testing the power transistor (ignition control module) on your 1990-1994 Mitsubishi or Dodge 3.0L equipped vehicle can easily be done in three simple tests. The very first thing that has to be verified, will be that the power transistor is producing a Switching signal (that the ignition coil can use to start sparking).
If you have started your diagnostic and troubleshooting from TEST 1, you can skip this test step and go directly to: TEST 8: Making Sure The Power Transistor Is Getting Ground. If you have skipped tests 1 thru' 6 and you only need to test the power transistor, start here.
IMPORTANT: This test assumes that you have a 'no-spark no-start' condition. If your car starts and runs, then this is a clear indication that the power transistor is working fine. If you need to troubleshoot a misfire condition, you need to start with TEST 1: Testing For Spark.
Alright, here's the test:
- 1
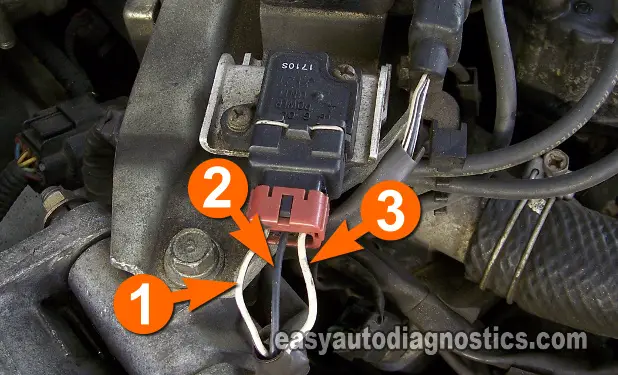
Connect the black lead of the LED light to the wire identified with the number 1 in the photo.
NOTE: The power transistor must remain connected to its electrical connector for this test to work.
You'll need to use a back probe or a wire-piercing probe to access the signal in the wire. You can see an example of this tool here: Wire Piercing Probe. - 2
Connect the red lead of the LED to the battery's positive (+) terminal.
- 3
When everything is set up, have an assistant crank the engine.
- 4
The LED light should flash ON and OFF the whole time that the engine is cranking (although the LED light may not completely turn OFF).
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The LED light flashed ON and OFF. This is the correct test result and confirms that the power transistor is producing an ignition coil activation signal.
You can conclude that the ignition coil is bad and needs to be replace if you have:
- Confirmed that none of the 6 spark plug wires are firing spark (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil's high tension wire is not firing spark (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil's tower is not firing spark (TEST 4).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is receiving 12 Volts (TEST 5).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is receiving an activation signal (triggering signal).
This also means that the power transistor and crankshaft position sensor (within the distributor) are good. Replacing the ignition coil will solve your 'no-spark no-start' condition on your Mitsubishi (or Dodge) vehicle.
CASE 2: The LED light DID NOT flash ON and OFF. Re-check all of your connections and retry the test again.
If the test light still does not flash ON and OFF, then you can conclude that the ignition coil's triggering signal is not present.
This means that the power transistor is not activating the ignition coil. The next step is to start testing the power transistor's Ground and triggering signal circuits, go to: TEST 8: Making Sure The Power Transistor Is Getting Ground.
TEST 8: Making Sure The Power Transistor Is Getting Ground

OK, so far you have verified that the power transistor is not creating and feeding the activation signal that the ignition coil needs to start producing spark (TEST 6 or TEST 7).
The next step is to make sure that power transistor is getting Ground, since without this Ground, it won't create the switching signal.
OK, the test goes like this:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Disconnect the power transistor from its electrical connector.
- 3
Gently probe the terminal that connects to the wire identified with the number 2, in the photo, with the black multimeter test lead.
This wire is usually a black with light blue stripe (BLK/LT BLU) wire. - 4
Connect the red multimeter test lead directly to the battery's positive (+) terminal.
- 5
The multimeter should register between 10 to 12 Volts DC whether the key is in the ON or OFF position.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The multimeter displayed 10 to 12 Volts DC. This is the correct test result and it indicates that the power transistor is being supplied with a good Ground.
The next test is to verify that the power transistor is receiving power. For this test go to: TEST 9: Making Sure The Power Transistor Is Getting An Activation Signal.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT display 10 to 12 Volts DC. Recheck all your connections and retest.
If the multimeter still does not display the indicated voltage, you'll need to find out why. Without this Ground, the power transistor will not work.
Resolving the cause of this missing Ground will solve the 'no-spark no-start' issue with your Mitsubishi or Dodge 3.0L V6 equipped vehicle.
TEST 9: Making Sure The Power Transistor Is Getting An Activation Signal

So far, you have verified that the power transistor is getting power and Ground. Now, you need to verify that the PCM is indeed supplying the power transistor with an activation signal.
This test is done using an LED light. A 12 Volt automotive test light will not work.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Reconnect the power transistor to its electrical connector.
NOTE: This test is done with the power transistor connected to its electrical connector. - 2
Connect the red wire of the LED light to the wire identified with the number 3 in the photo.
This wire is usually a gray with black stripe (GRY/BLK) wire.
You'll need to use a back probe or a wire-piercing probe to access the signal in the wire. You can see an example of this tool here: Wire Piercing Probe. - 3
Connect the black lead of the LED to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the LED light.
- 5
The LED light should flash ON and OFF the whole time that the engine is cranking.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The LED light flashed ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranked. This is the correct test result and confirms that the fuel injection computer is creating and sending a good Triggering signal.
This test result tells you that the power transistor is bad, and that it needs to be replaced, if you have:
- Confirmed that none of the 6 spark plug wires are firing spark (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil's high tension wire is not firing spark (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that that the ignition coil's tower is not firing spark (TEST 4).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is receiving 12 Volts (TEST 5).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil IS NOT receiving an activation signal (TEST 6).
- Confirmed that the power transistor is getting Ground (TEST 8).
- Confirmed that the power transistor is receiving an activation signal from the fuel injection computer (this test section).
CASE 2: The LED light DID NOT flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine was being cranked. This test result tells you that the power transistor is not getting an activation signal from the fuel injection computer.
The most likely cause of this missing activation signal is a bad crankshaft position sensor. To further test this and make sure, go to: TEST 10: Crankshaft Position Sensor Is Getting Power.

